Solution to Set 6: Difference between revisions
(→Given) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
==Problem 2== | ==Problem 2== | ||
[[Image:Detective.gif]] | [[Image:Detective.gif|right]] | ||
The resistivity of a certain material at room temperature is 0.02 Wm and the Hall coefficient is <math>5{\rm x}10^{-4}</math> <math>m^3 /C</math>. An electric field of 1 V/m is applied across it. Deduce all the information you can think of about this material. | The resistivity of a certain material at room temperature is 0.02 Wm and the Hall coefficient is <math>5{\rm x}10^{-4}</math> <math>m^3 /C</math>. An electric field of 1 V/m is applied across it. Deduce all the information you can think of about this material. | ||
Revision as of 01:17, 9 April 2009
Problem 1.
Given
Aluminum(Al) is trivalent with
- atomic mass Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_{a} = 27} amu
- density Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n = 2.7 g/cm^3}
- room temperature Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = 293 - 296.5 K}
- mean free time between electron collisions Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t_{avg} = 4{\rm x}10^{-14}} s.
(a) Resistivity
Calculate the resistivity Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho} of aluminum(Al) at room temperature.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho = \frac{1}{\sigma} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{ 37.8 \times 10^{6} S m^{-1}} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = 2.82 \times 10^{-8} \;} Ω·m
(b) Current
If a 2-V voltage is applied to the ends of an aluminum wire 10 m long and with a cross- sectional area of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1 mm^2} , what is the current flowing through it?
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R = \frac{\iota \cdot \rho}{A} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\left (10m \right ) \cdot \left (2.646 \times 10^{-8} \Omega \cdot m \right )}{\left (10^{-6}m \right )} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = 0.2646 \Omega \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I = \frac{V}{R} = \frac{2V}{0.2646 \Omega} = 7.559 A \;}
Problem 2
The resistivity of a certain material at room temperature is 0.02 Wm and the Hall coefficient is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 5{\rm x}10^{-4}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^3 /C} . An electric field of 1 V/m is applied across it. Deduce all the information you can think of about this material.
Given
- Temperature Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = 20^{\circ} C \;}
- Resistivity Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho = 0.02 \Omega \cdot m \;}
- Hall coefficient Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{H} = 5{\rm x}10^{-4} \tfrac{m^{3}}{C} \;}
- Electric field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E = 1 \tfrac{V}{m} \;}
Deduction
- Conductivity
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma = \frac{1}{\rho} = \frac{1}{0.02 \Omega \cdot m} = 50 \tfrac{S}{m} \;}
- Current Density
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J} = \frac{E}{\rho} = \frac{1 \tfrac{V}{m}}{0.02 \Omega \cdot m} = 50 \tfrac {A}{m^{2}} \;}
- Magnetic Field
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{H} = \frac{E}{\mathbf{J} \cdot B} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B = \frac{E}{\mathbf{J} \cdot R_{H}} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\left (1 \tfrac{V}{m} \right )}{\left ( 50 \tfrac{A}{m^{2}} \right ) \left ( 5 \times 10^{-4} m^3 \right )} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = 40 T \;}
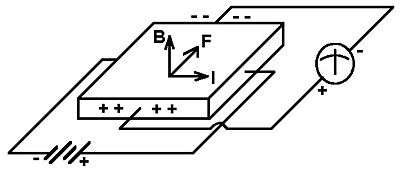
Problem 3.
a) Sketch a setup used to measure the Hall effect. Label each part.
b) A semiconductor crystal is 5 mm long, 4 mm wide, and 2 mm thick. A 40mA current flows across the length of the sample after a 2-V battery is connected to the ends. When a 0.1T magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the large surface of the specimen, a Hall voltage of 15mV develops across the width of the sample. Determine the i) conductivity, ii) carrier density, iii) mobility, iv) Fermi velocity, for this semiconductor.
Problem 4
a) Derive the expressions for the Fermi energy, Fermi velocity, and electronic density of states for a two-dimensional free electron gas.
b) A 2D electron gas formed in a GaAs/AlGaAs quantum well has a density of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2{\rm x}10^{11} cm^{-2}} . Assuming that the electrons there have the free electron mass, calculate the Fermi energy and Fermi velocity.