Phy5645/Double pinhole experiment: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
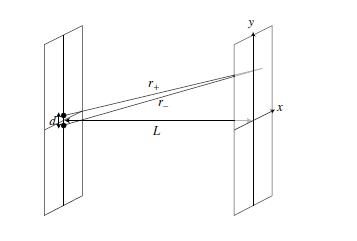
[[Image:Double_pinhole_1.JPG]] | [[Image:Double_pinhole_1.JPG]] | ||
Suppose | Suppose that a beam of electrons, traveling along the <math>z</math> axis, hits a screen at <math>z = 0\!</math> with two pinholes at <math>x = 0, y = \pm d/2\!</math>. For a point <math>(x,y)\!</math> on a second screen at <math>z = L>>d, \lambda\!</math>, the distance from each pinhole is given by <math> r_{\pm}=\sqrt{x^{2}+(y\mp d/2)^{2}+L^{2}}\!</math>. A spherical wave is emitted from each pinhole, and the waves from each add, and hence the wave function at a given point on the second screen is | ||
:<math>\psi(x,y)=\frac{e^{ikr_{+}}}{r_{+}}+\frac{e^{ikr_{-}}}{r_{-}}</math>, | :<math>\psi(x,y)=\frac{e^{ikr_{+}}}{r_{+}}+\frac{e^{ikr_{-}}}{r_{-}}</math>, | ||
Revision as of 16:28, 20 March 2013
Submitted by team 1
Question: Double Pinhole Experiment
Besides the Stern-Gerlach experiment, the double slit experiment also demonstrates the difference between quantum mechanics and classical mechanics. Here, we will discuss a double pinhole experiment rather than a double slit experiment because the former is mathematically simpler and still embodies the basic physics that we wish to demonstrate.
Suppose that a beam of electrons, traveling along the axis, hits a screen at with two pinholes at . For a point on a second screen at , the distance from each pinhole is given by . A spherical wave is emitted from each pinhole, and the waves from each add, and hence the wave function at a given point on the second screen is
- ,
where . Answer the following questions.
(a) Considering just the exponential factors, show that the constructive interference appears approximately at
where .
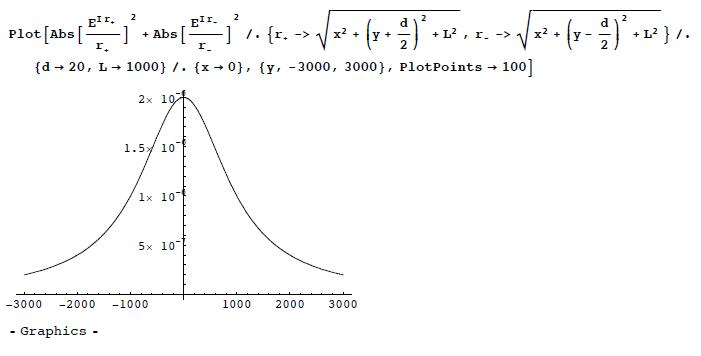
(b) Make a plot of the intensity as a function of , by choosing , and . The intensity is interpreted as the probability distribution for the electron to be detected on the screen, after repeating the same experiment many many times.
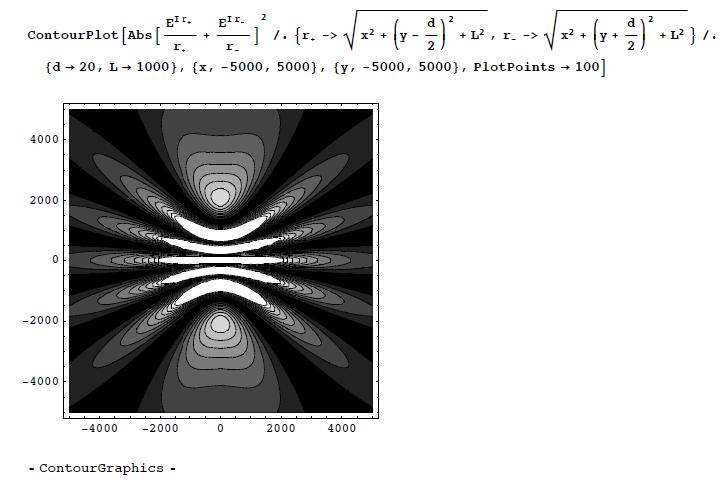
(c) Make a contour plot of the intensity as afunction of x and y, for the same parameters.
(d) If you place a counter at both pinholes to see if the electron has passed one of them, all of a sudden the wave function "collapses". If the electron is observed to pass through the pinhole at , the wave function becomes
- .
If it is observed to pass through that at , the wave function becomes
- .
After repeating this experiment many times with 50:50 probability for each the pinholes, the probability on the screen will be given by
instead. Plot this function on y-axis, and also show the contour plot, to compare its pattern to the case when you do not place a counter. What is the difference from the case without the counter?
Answer:
(a) As directed, we assume that the denominators are approximately the same between two waves. This is justified because the corrections are only of the order of , and we are interested in the case where . We require that the numerators have the same phase, namely . We expand the LHS with respect to ,
Therefore,
and hence
(b) Let us choose the unit where k = 1. Then we pick d = 20, L = 1000. Here is the interference pattern. First along the y-axis (x = 0):
(c) Now on the plane:
(d) For the same parameter as in (b), First along the y-axis (x = 0):
Now on the plane:
The main difference is the absence of the interference pattern.