4th Week: Decays, Tunneling and Cross Sections: Difference between revisions
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Alpha Decay== | ==Alpha Decay== | ||
<math>\alpha</math>-decay, which is usually seen in heavier elements, is the decay of a parent nucleus to a daughter nucleus through the emission of a helium nucleus. | |||
<math>_{Z}^{A}\textrm{X}\to \; _{Z-2}^{A-4}\textrm{Y} + \;_{2}^{4}\textrm{He}</math> | |||
==Beta Decay== | ==Beta Decay== | ||
Revision as of 14:09, 10 February 2009
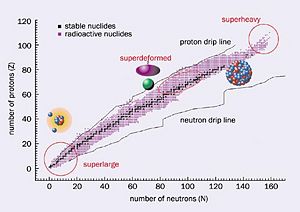
Nuclear Radiation
When looking at the table of nuclides it is obvious that the valley of stability is only a small percentage of all known nuclei. So most nuclei are considered unstable. To become stable these nuclides emit ionizing particles and radiation, resulting in a loss of energy from the original nuclei. This Process is called radioactive decay.
Alpha Decay
-decay, which is usually seen in heavier elements, is the decay of a parent nucleus to a daughter nucleus through the emission of a helium nucleus.
Beta Decay
Gamma Decay