|
|
| Line 18: |
Line 18: |
|
| |
|
| '''Derive the dispersion relation <math>\omega^{\alpha} (k)\;</math> for this chain''' | | '''Derive the dispersion relation <math>\omega^{\alpha} (k)\;</math> for this chain''' |
|
| |
| === Index <math>\alpha = 1\;</math> for acoustic branch ===
| |
|
| |
| Potential Energy <math>U = 1, 2, 3, ... n \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>U \cong \frac{1}{2} k \sum_{n} (U_n - U_{n-1}) \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow m \ddot{U}_n = - k [2U_n - U_{n-1} - U_{n+1}] = -m \omega U(t) \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| Eigenvectors of Modes A and B (defined arbitrarily)
| |
|
| |
| <math>u_m(t)=e^{i\omega t} u_m \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow -m \omega ^2 \ddot{\vec{u}}_n = - k \mathbf{M} \vec{u} \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| Band Matrix
| |
|
| |
| <math>
| |
| \mathbf{M} = \begin{vmatrix}
| |
| 2 & 1 & 0 & 0\\
| |
| 1 & 2 & 1 & 0\\
| |
| 0 & 1 & 2 & 1\\
| |
| 0 & 0 & 1 & 2
| |
| \end{vmatrix}
| |
| </math>
| |
|
| |
| Running waves through a solid
| |
|
| |
| <math>u_m (t) = e^{ik(na)- \omega t} = e^{i k R_n} \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| where
| |
|
| |
| <math>u_m \rightarrow u_n e^{ik(na)} \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>R_n \;</math> = distance on some coordinate system
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow -m \omega ^2 \vec{u} = - k [2 - e^{ik \alpha} - e^{-ik \alpha}] \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| Derive and get:
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow \omega (k) = 2 \sqrt{ \frac{k}{m} } |sin(ka)|</math>
| |
|
| |
| === '''Index<math>\alpha = 2\;</math> for optical branch''' ===
| |
|
| |
| <math>u_m (t) = e^{ik(na)- \omega t} = e^{i k R_n} \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>u(R_n) \equiv e^{i k R_n} = cos (k a) \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow - m \omega^2 e^{ikna} = -k [2e^{ik(na)} - e^{ik(n+1)a} - e^{ik(n-1)a}] \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow m \omega^2 = k [2 - (e^{ika} + e^{-ika})] \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow \omega^2 = \frac{2k}{m} [1 - cos(ka)] \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow \omega^2 = \frac{\Delta k}{m} \frac{1}{2} [1 - cos(ka)] \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow \omega^2 = \frac{\Delta k}{m} sin^{2}(\frac{ka}{2}) \;</math>
| |
|
| |
| <math>\Rightarrow \omega (k) = 2 \sqrt{ \frac{k}{m} } |sin(\frac{ka}{2})| \;</math>
| |
|
| |
|
| [[Image:Dispersionrelation.jpg]] | | [[Image:Dispersionrelation.jpg]] |
Revision as of 17:09, 2 March 2009
I have no idea what I'm doing - KimberlyWynne 03:11, 2 March 2009 (EST)
Diatomic harmonic chain
Problem 1
I found this site somewhat helpful and explanatory:
http://newton.ex.ac.uk/teaching/resources/rjh/phy2009/PHY2009handout13.pdf
Given:
- a chain of atoms
- with alternating masses
 and
and 
- connected with elastic springs with constant

- moving only in the x-direction
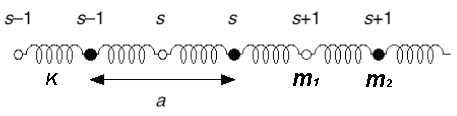
Derive the dispersion relation  for this chain
for this chain
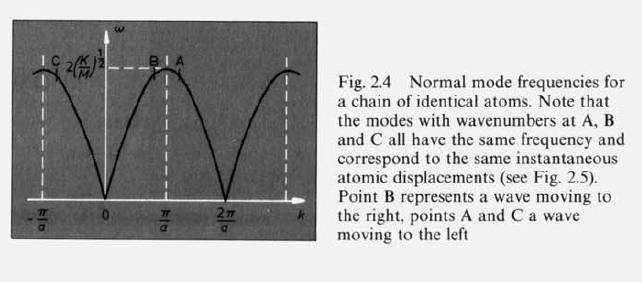
Problem 2
Determine the speed of sound for this chain. What is the lowest frequency of long-wavelength sound corresponding to the optical branch?

where
 = frequency
= frequency = speed of sound
= speed of sound = ???
= ???
Problem 3
Sketch the motion of the atoms corresponding to the edge of the Brillouin zone, both for the optical and the acoustic branch.
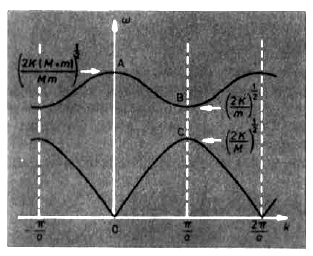
- Acoustic Branch: lower branch
- Optical Branch: upper branch, as
 on this branch the vibrations of the 2 types of atom are in antiphase and the resulting charge oscillation in an ionic craystal give a strong coupling to electromagnetic waves at the frequency of point A.
on this branch the vibrations of the 2 types of atom are in antiphase and the resulting charge oscillation in an ionic craystal give a strong coupling to electromagnetic waves at the frequency of point A.
Problem 4
Determine the Debye temperature for this system, and determine the form of the specific heat  in the limits of high and low temperatures.
in the limits of high and low temperatures.
Debye Temperature 
The Debye temperature, aka the effective sonic velocity, is a measure of the hardness of the crystal
From our class lectures:

From Wikipedia:
![{\displaystyle T_{D}\ {\stackrel {\mathrm {def} }{=}}\ {hc_{s}R \over 2Lk}={hc_{s} \over 2Lk}{\sqrt[{3}]{6N \over \pi }}={hc_{s} \over 2k}{\sqrt[{3}]{{6 \over \pi }{N \over V}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/411d5aa9ab5603b7ea4354a1a15d081145b5d11d)
Specific Heat 
Low Temperature Limit

High Temperature Limit




Net Result (Classical Limit)

Problem 5
Consider low temperatures ( ) and determine the wavelength of the most abundant phonons
) and determine the wavelength of the most abundant phonons 
Given:
- Bose-Einstein Distribution

 = probability that a particle will have energy E
= probability that a particle will have energy E = Boltzmann constant
= Boltzmann constant = Temperature
= Temperature
- Planck's Radiation Formula

- Density by frequency:

- Density by wavelength:

- Wien's law

 is the peak wavelength in meters,
is the peak wavelength in meters, = temperature of the blackbody in Kelvin
= temperature of the blackbody in Kelvin = Wien's displacement constant
= Wien's displacement constant















![{\displaystyle T_{D}\ {\stackrel {\mathrm {def} }{=}}\ {hc_{s}R \over 2Lk}={hc_{s} \over 2Lk}{\sqrt[{3}]{6N \over \pi }}={hc_{s} \over 2k}{\sqrt[{3}]{{6 \over \pi }{N \over V}}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/411d5aa9ab5603b7ea4354a1a15d081145b5d11d)


















