PHZ3400 Crystals: Difference between revisions
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[IMAGE:Diamonds_glitter.png|center|frameless]] | [[IMAGE:Diamonds_glitter.png|center|frameless]] | ||
There is a class of materials that have lattices formed from certain patterns of triangles or tetrahedrons. Because of the crystal structure, these materials exhibit novel behaviors and are called | There is a class of materials that have lattices formed from certain patterns of triangles or tetrahedrons. Because of the crystal structure, these materials exhibit novel behaviors and are called [http://wiki.physics.fsu.edu/wiki/index.php/Geometrically_Frustrated_Materials geometrically frustrated materials]. | ||
===Miller indices=== | ===Miller indices=== | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 19 April 2009
Crystal lettices
"Habit" of crystals
The habit of a crystal is the overall shape in which crystals like to grow. This is also known as the crystal's natural shape. It depends on temperature, density, and volume. The overall macroscopic shape of a crystal suggests the internal structure of the crystal.
Lattice, basis, unit cell
Primitive cell, Wigner-Seitz cell
Examples of crystal lattices
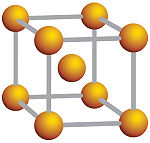
The body-centered cubic (BCC) has a total of 2 atoms per unit cell. It contains eight atoms on the corners that contribute one-eighth of an atom and a whole atom in the center of the unit cell. Examples of BCC structure include lithium, sodium, barium, as well as Cesium chloride (CsCl).
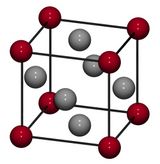
The face-centered cubic (FCC) has a total of 4 atoms per unit cell with lattice points on the faces of the cube of which each unit cube gets exactly one half contribution. In addition to the faces of the cube, each corner contributes one eighth of an atom. Examples of FCC structure include aluminum, copper, nickel, silver, and cerium.
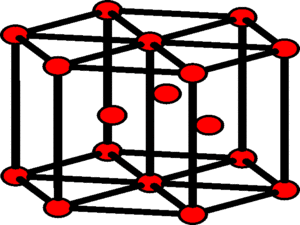
A Hexagonal Close Packing (HCP) structure contains a total of six atoms per unit cell. Examples of HCP structure are found in beryllium and radon.
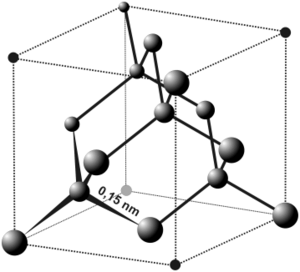
The Diamond Structure is present in silicone, tin, germanium, as well as many semi-conductors.
There is a class of materials that have lattices formed from certain patterns of triangles or tetrahedrons. Because of the crystal structure, these materials exhibit novel behaviors and are called geometrically frustrated materials.
Miller indices
Quasi-crysals
PC software to build your own Penrose tile can be downloaded from this link.
Brain twisters
An interesting link to examples of five-fold symmetry, and the relation to the "Golden Mean" can be found here.
The emergence of the Golden Mean in the route to chaos of the "circle map" can be found in detailed lectures on chaos by Mike Cross (Caltech).