4th Week: Decays, Tunneling and Cross Sections
Nuclear Radiation
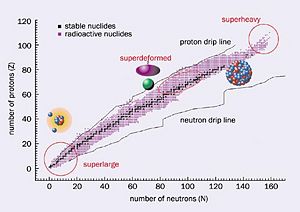
When looking at the table of nuclides it is obvious that the valley of stability is only a small percentage of all known nuclei. So most nuclei are considered unstable. To become stable these nuclides emit ionizing particles and radiation, resulting in a loss of energy from the original nuclei. This Process is called radioactive decay.
Alpha Decay
Alpha decay, which is usually seen in heavier elements, is the transformation of a parent nucleus to a daughter nucleus through the emission of a helium nucleus.
Beta Decay
There are three types of Beta decays, -decay, -decay, and electron capture.
The first one, decay, occurs when a nucleus with an over abundance of neutrons transforms to a more stable nucleus by emitting an electron. This process can be denoted as:
From electric-charge conservation, the proton number in such decays is increased by one unit.
Likewise, a -decay occurs when a proton-rich nucleus emits a positron, therefore reducing the nuclear charge by one.
Gamma Decay