PHY6937
Welcome to Phy 6937 Superconductivity and superfluidity
PHY6937 is a one semester advanced graduate level course. Its aim is to introduce concepts and theoretical techniques for the description of superconductors and superfluids. This course is a natural continuation of the "many-body" course PHY5670 and will build on the logical framework introduced therein, i.e. broken symmetry and adiabatic continuity. The course will cover a range of topics, such as the connection between the phenomenological Ginzburg-Landau and the microscpic BCS theory, Migdal-Eliashberg treatment of phonon mediated superconductivity, unconventional superconductivity, superfluidity in He-4 and He-3, and Kosterlitz-Thouless theory of two dimensional superfluids.
The key component of the course is the collaborative student contribution to the course Wiki-textbook. Each team of students is responsible for BOTH writing the assigned chapter AND editing chapters of others.
Team assignments: Spring 2011 student teams
Outline of the course:
Pairing Hamiltonian and BCS instability
To see the origins of superconductivity, it is helpful to look at a toy system, which we already know will give us superconducting behavior. This is useful because the toy system is only a simple change to a non-interacting electron gas. By adding in some small attractive interaction, we will arrive at a superconducting system! This interaction need only occur between two electrons occupying the same position in space (and necessarily having opposite spin!). Additionally, we still find the interesting behaviour regardless of the size of the interaction; the only requirement is that it be non-zero!
We can write the Hamiltonian of the system as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\sum_\vec{r}[\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r})(\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r}) +g\psi_\uparrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\vec{r})]}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ g<0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ |g|<<\epsilon_{F}} .
For this system, the partition function is:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D[\psi_\sigma ^{*} (\tau, \vec{r}), \psi_\sigma (\tau, \vec{r})]e^{-S_{BCS}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}=\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_\vec{r}[\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\tau, \vec{r})(\partial _\tau+\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r}) +g\psi_\uparrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\vec{r})]}
It doesn't matter to multiply partition function by a constant:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z\rightarrow Z=\int D[\psi_\sigma ^{*} (\tau, \vec{r}), \psi_\sigma (\tau, \vec{r})] D[\Delta^{*}(\tau, \vec{r}),\Delta (\tau, \vec{r})] e^{-S_{BCS}-S_{\Delta}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_\Delta=-\int_0^\beta d\tau\sum_{\vec{r}}\frac{1}{g}\Delta^*(\tau,\vec{r})\Delta(\tau,\vec{r})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^\dagger} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \psi} are grassmann numbers. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta^*} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta} are constant. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_\uparrow\psi_\downarrow} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_\downarrow\psi_\uparrow} behave like constant.
Let's make a shift of the constant:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \rightarrow \Delta+g\psi_\uparrow\psi_\downarrow}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta^*\rightarrow \Delta^*+g\psi^\dagger_\downarrow\psi^\dagger_\uparrow}
Then, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_\Delta=-\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_{\vec{r}}{\{\frac{1}{g}\Delta^*\Delta + \Delta^*\psi_\uparrow \psi_\downarrow \Delta\psi^\dagger_\downarrow \psi^\dagger_\uparrow+g\psi^\dagger_\downarrow \psi^\dagger_\uparrow \psi_\uparrow \psi_\downarrow}\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}S=&S_{BCS}+S_{\Delta}\\ =&\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_{\vec{r}}\{ \psi_\sigma^\dagger(\tau, \vec{r})(\partial _\tau+\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\tau, \vec{r}) \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \rightarrow S_0 \\ &+\Delta^*(\tau, \vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\tau, \vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\tau, \vec{r}) \Delta (\tau, \vec{r})\psi^\dagger_\downarrow (\tau, \vec{r})\psi^\dagger_\uparrow (\tau, \vec{r}) \rightarrow S_{int}\\ &-\frac{1}{g}\Delta^* (\tau, \vec{r})\Delta (\tau, \vec{r}) \} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \rightarrow S_{\Delta} \end{align}}
then, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D[\psi_{\sigma}^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}),\psi_{\sigma}(\tau,\mathbf{r})]D[\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}),\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})]e^{-(S_{0}+S_{int.}+S_{\Delta})}} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\langle e^{-S_{int.}}\right\rangle _{0}\cong exp[\frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}+\frac{1}{4!}(\left\langle S_{int.}^{4}\right\rangle _{0}-3\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}^{2})]} by cumulant expansion, which guarantees that until the 2nd order, it is accurate.
Use Matsubara's Method
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_{\sigma}(\tau,\mathbf{r})=\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}e^{-i\omega_{n}\tau}\psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}), \omega_{n}=(2n+1)\frac{\pi}{\beta};}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})=\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}e^{-i\Omega_{n}\tau}\Delta_{\mathbf{k}}(i\Omega_{n}), \omega_{n}=2n\frac{\pi}{\beta}.}
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{0}=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}[-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu]\psi_{\sigma}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}).}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int.}=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{2}}\underset{\omega_{n},\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}[\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\psi_{\uparrow}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{\mathbf{q}-k})\psi_{\downarrow}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})+\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})\psi_{\downarrow}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\uparrow}^{\dagger}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{\mathbf{q}-k})].}
The Fourier transform of 1 body Green's function is (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i=1,2} mean Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathbf{r}_{i},\tau_{i}}} ) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G(1-2)=\left\langle \psi(1)\psi^{*}(2)\right\rangle =\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\frac{1}{L^{D}}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{-i\omega_{n}(\tau_{1}-\tau_{2})}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot(\mathbf{r}_{1}-\mathbf{r}_{2})}\frac{1}{-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} ,
so Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_{\sigma}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})=\left\langle \psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\sigma}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\right\rangle _{0}=\frac{\beta}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} .
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=\frac{2L^{2D}}{\beta^{4}}\underset{\omega_{n},\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}[G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})]\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})=L^{D}\frac{2}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})} ,
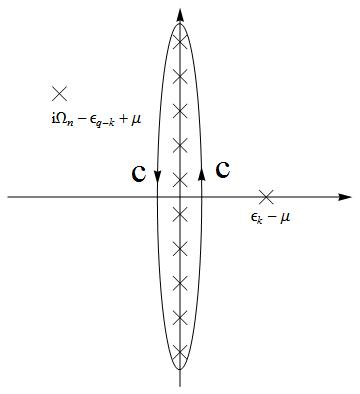
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{3}}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})} is called pairing susceptibility.
Let's calculate it:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{3}}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})=\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\frac{-1}{i\omega_{n}-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{i\omega_{n}-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow=\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\oint_{c}\frac{dz}{2\pi i}\frac{-1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}\frac{1}{e^{\beta z}+1}} .
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}=\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[\frac{1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}+\mu}-\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}]} ,
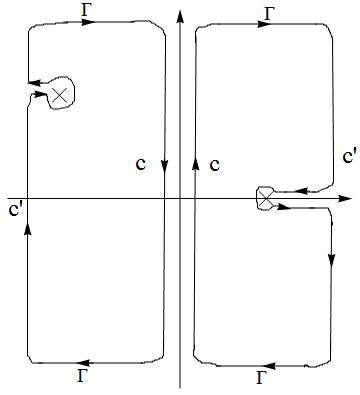
and change the integral path to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow=-\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[\frac{1}{e^{\beta(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}-\mu)}+1}-\frac{1}{e^{\beta(-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\mu)}+1}]=\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[1-f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}})-f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}})].}
In the static (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Omega_{n}=0} ) and uniform (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{q}=0} ) limit,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1-2f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}})=Tanh[\frac{\beta}{2}(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)]} .
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(0,0)=\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{Tanh[\frac{\beta}{2}(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)]}{2(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)}} .
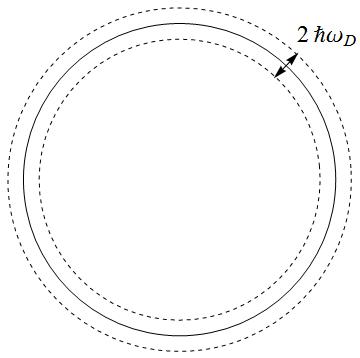
In low energy, integrate the energy in the shell near Fermi energy:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\chi_{p}(0,0)\cong N(0)\int_{\hbar\omega_{D}}^{-\hbar\omega_{D}}d\xi\frac{Tanh[\xi\beta/2]}{2\xi}\cong N(0)\int_{0}^{-\hbar\omega_{D}}d\xi\frac{Tanh[\xi\beta/2]}{\xi}=N(0)ln[\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T}].}
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\chi_{p}(0,0)\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})} .
If we ignore the higher order in the cumulant expansion,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}=-\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau\frac{1}{g}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})-\frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau[\frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})]\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r})\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})} .
Because the partition function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D\Delta^{*}D\Delta e^{-S_{eff}(\Delta)}} , if we only consider the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors.
The superconductivity phase transition temperature is the temperature makes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})=0} , which is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}=\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}}\frac{2}{\pi}e^{\gamma}e^{-\frac{1}{N(0)\left|g\right|}}=1.134\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}}e^{-\frac{1}{N(0)\left|g\right|}}} .
Beyond the critical temperature, the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors in the partition function is just Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1} , the same as no cooper pair, which is normal state; below the critical temperature, the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors in the partition function will diverge, which means superconductivity phase transition.
Finite Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{q}} (small) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ (\Omega_n=0)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_p (q,0)-\chi_p (0,0)=\frac{1}{L^D} \sum_k \frac{1}{\beta} \sum_{i\omega_n}\frac{-1}{i\omega_n-\epsilon_k+\mu}(\frac{1}{i\omega_n+\epsilon_{q-k}-\mu}-\frac{1}{i\omega_n+\epsilon_{-k}-\mu}) }
for small ,
and
Thus,
Consider the states near the shell near fermi surface, we have
where,
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \int_{-\infty}^{+\infty} d\xi \frac{1}{(\xi-i\omega_n)(\xi+i\omega_n)^3} &=\frac{2\pi i}{(2i\omega_n)^3}\theta(\omega_n)-\frac{2\pi i}{(2i\omega_n)^3}\theta(-\omega_n)\\ &=\frac{2\pi i}{(2i|\omega|)^3} \end{align} }
So,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \chi_p(q,0)-\chi_p(0,0) &=\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{i\omega_n}N(0)\int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(q\cdot v_F)^2\frac{2\pi i}{(2i|\omega|)^3}\\ &=N(0)v_F^2|\vec{q}|^2\int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(q\cdot v_F)^2 \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{i\omega}\frac{2\pi i}{-i8|\frac{(2n+1)\pi}{\beta}|^3}\\ &=-\frac{1}{4}N(0)v_F^2q^2(<(\hat{q}\cdot \hat{v_F})>_{F.S.})\frac{\beta^2}{\pi^2}(\sum_{N=-\infty}^{+\infty}\frac{1}{|2n+1|^3}) \end{align} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{N=-\infty}^{+\infty}\frac{1}{|2n+1|^3}=\sum_{n=0}^\infty\frac{2}{(2n+1)^3}=\frac{2}{\pi}\frac{7\zeta(3)}{8} }
where, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \zeta(3)} is Riemann zeta function.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <(\hat{q}\cdot \hat{v}_F)^2>_{F.S.}=\frac{1}{D} }
For spherical F.S. in 3D,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(\hat{q}\cdot\hat{v}_F)^2=\frac{2\pi}{4\pi}\int_{-1}^{1}dcos\theta cos^2\theta = \frac{1}{3} }
For circular F.S. in 2D,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(\hat{q}\cdot\hat{v}_F)^2=\frac{1}{2\pi}\int_{0}^{2\pi}d\theta cos^2\theta = \frac{1}{2} }
Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \chi_p(q,0)-\chi_p(0,0) &=-\frac{1}{4}N(0)v_{F}^{2}q^{2}\frac{1}{D}\frac{\beta^{2}}{\pi^{2}}\frac{2}{\pi}\frac{7\zeta(3)}{8} \\ &=-N(0)\frac{7\zeta(3)}{16D\pi^{2}}q^{2}\frac{1}{\pi \hbar^{2}}\left(\frac{\hbar v_{F}}{k_{B}T}\right)^{2} \\ &\equiv-N(0)q^{2}\xi^{2} \end{align} }
So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}&=L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\chi_{p}(q,0)\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n}) \\ &=N(0)ln[\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T}]L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})-L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}N(0)q^{2}\xi^{2}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n}) \end{align} } .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}=\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau\left[\left(\frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})\right)\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r})\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})-N(0)\xi^{2}(\nabla\cdot\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}))(\nabla\cdot\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r}))\right]} .
Note that the last term in the expression tells us that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff} } would increase if gradient of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta } is not zero.
Note that the above expression has a one-one correspondant to the Giznburg-Landau functional:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\int d^{D}r\left[ \alpha (T-T_{c}) |\Psi(r)|^{2}+\frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}}|\nabla \Psi|^{2} \right] } ,
here the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta } in the previous expression corresponds to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Psi } in the G-L expression.
Little Parks experiment
Refer to the fig, a thin shell of superconductor with radius R is shown and a small uniform magnetic field is passing through the hollow center of the cylinder. The experiment intends to show the variation of the critical temperature with change of the magnetic field passing through the hollow superconductor cylinder.
Before showing it, we first have to rewrite the Giznburg-Landau functional to make it taken the presence of magnetic field into account. Hamiltonian for a free electron moving in a magnetic field can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2m}(p-\frac{eA}{c})^{2}\psi + V\psi = E\psi }
The physical observable magnetic field B would remain the same if we choose a different vector potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A\rightarrow A+ \nabla \chi } . To maintain the same eigen-energy E being observed, the wave function have to undergo a phase change: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi \rightarrow e^{i\phi}\psi } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi=\frac{e}{c\hbar}\chi }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta^{*}(r) }
Microscopic derivation of the Giznburg-Landau functional
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=Z_{0}< e^{-S_{int}} >}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z_{0}=\int D\psi ^{*} D\psi D\Delta ^{*} D\Delta e^{-(S_{\Delta} +S_{0})}}
we can expand this average for smallFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} nearFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}} , for this perpose we can assume asecond order phase transition so that it increases continiously from zero to finite number after Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}}
we need to calculate the average of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-s_{int}}} which can be calculated by Tylor expansion:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-S_{int}}=<-S_{int}+\frac{1}{2}S_{int}^{2}-\frac{1}{3}S_{int}^{3}+\frac{1}{4!}S_{int}^{4}+...>}
=Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1-<S_{int}>+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}> -\frac{1}{3!}< S_{int}^{2}> +\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}> +...}
.......................the odd power terms are zero because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <\psi _{\uparrow}(r,\tau )\psi _{\downarrow}(r,\tau ) > =0 }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =e^{\frac{1}{2}< S_{int}^{2}>}e^{\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>-\lambda }}
if we expand these two terms in to the second order the following expression can be got:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (1+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}>+\frac{1}{2}(<\frac{1}{2} S_{int}^{2}>)^{2} +...)(1+\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>+...)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =1+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}>+\frac{1}{8}(< S_{int}^{2}>)^{2} +...)+\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>-\lambda +...}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} can be choosed in such a way .......
so, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda =\frac{1}{8}< S_{int}^{2}> ^{2} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =e^{\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}>+\frac{1}{4!}(< S_{int}^{4}>-3<S_{int}^{2}>^{2})+...}}
according to the expression we got before:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int}=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta ^{2}}\sum_{\omega _{n},\Omega _{n}}\sum _{k,q}[\Delta ^{*}_{q}(i\Omega _{n})\psi_{\downarrow}(i\Omega _{n}-i\omega _{n}),\vec{q}-\vec{k})\psi_{\uparrow}(i\omega _{n},k)+\Delta _{q}(i\Omega_{n})\psi_{\uparrow}^{\dagger }(i\omega _{n},k)\psi_{\downarrow}^{\dagger }(i\Omega _{n}-i\omega _{n}),\vec{q}-\vec{k})]}
let's write Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int}} in terems od Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a} for simplification. where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a=\int \Delta ^{*}(1)\psi_{\downarrow}(1) \psi_{\uparrow}(1)+\Delta (1)\psi_{\downarrow}^{*}(1) \psi_{\uparrow}^{*}(1)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_{1}} is a couple grassman number, so we do not need to be worry about the sign when these terms comute with other terms.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle < S_{int}^{4}> =\int_{1234} < (a_{1}^{*}+a_{1})(a_{2}^{*}+a_{2})(a_{3}^{*}+a_{3})(a_{4}^{*}+a_{4})>}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =(< a_{1}^{*}a_{2}^{*}a_{3}a_{4}>+ < a_{1}^{*}a_{2}a_{3}^{*}a_{4}>+< a_{1}^{*}a_{2}a_{3}a_{4}^{*}>+< a_{1}a_{2}^{*}a_{3}^{*}a_{4}> +< a_{1}a_{2}^{*}a_{3}a_{4}^{*}>)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =6< a_{1}^{*}a_{2}^{*}a_{3}a_{4}>=6\int _{1234}\Delta ^{*}(1)\Delta ^{*}(2)\Delta(3)\Delta(4)< \psi_{\downarrow}(1)\psi_{\uparrow}(1)\psi_{\downarrow}(2)\psi_{\uparrow}(2)\psi_{\downarrow}^{*}(3)\psi_{\uparrow}^{*}(3)\psi_{\downarrow}^{*}(4)\psi_{\uparrow}^{*}(4)> }
Recall
see the solution which are independent
Effects of an applied magnetic field; Type I and Type II superconductivity
Derivation of the Ginzburg-Landau equations
Our starting point will be the Ginzburg-Landau (GL) free energy in the presence of an external magnetic field,
where is the total vector potential and is an external current density, assumed to be controlled experimentally. This current satisfies
where is the external magnetic field. The expression is the sum of the energy due to the superconducting order parameter, with the magnetic field introduced via the gauge invariance argument given above, the energy of the magnetic field alone, and the work done by the superconductor to maintain the external current at a constant value.
Let us first derive the "saddle point" equations satisfied by the magnetic field in the normal state. In this case, we set to zero everywhere and set
We will find this derivative by first finding the variation in the free energy for this case, which is
where is a small variation in the vector potential; we assume that it vanishes on the "surface" of our system. We now transform the first term using the identity,
obtaining
The first term is a "surface" term; since we assumed that vanishes everywhere on the "surface", we are left with just
We conclude that the variational derivative that we are interested in is
At the "saddle point", this derivative is zero, so we obtain the equation,
We may introduce the total magnetic field , thus obtaining
Comparing this to the definition of given above, we conclude that in the normal state. In reality, this will only be approximately true due to para- or diamagnetic effects in the metal, but these effects will be small in comparison to those due to superconductivity, which we will now derive.
First, we will apply the "saddle point" condition for the superconducting order parameter, , which is
Again, we start by finding the variation in the free energy in terms of a small variation in the order parameter:
The last term is equal to
The second term in this expression is a "surface" term. If we assume that is zero on the "surface", then this term vanishes, leaving us with
We can now immediately write down the variational derivative, which, upon being set to zero, gives us the first GL equation,
We also need to minimize the free energy with respect to the magnetic field. We have already done this for the normal case, and there is only one more term that we need to consider in the superconducting case; we will therefore only treat this term. We can quickly write down the variation in the superconducting part of the free energy , which is
Combining this result with the previous result for the normal metal, we obtain the second GL equation,
or, introducing and ,
Note that, given the definition of and the Maxwell equation (assuming static fields),
where is the total current density, we conclude that the left-hand side of this equation is the current density induced inside the superconductor.
Let us now suppose that we do not assume that vanishes on the surface. It may then be shown that the following boundary condition holds on the surface (see P. G. de Gennes, Superconductivity in Metals and Alloys):
This relation holds for a superconductor-metal interface; for a superconductor-insulator interface, . We may show that this condition implies that the normal component of the current density on the surface vanishes. If we multiply the above condition by on both sides, we obtain
Taking the complex conjugate of both sides gives us
Adding these two equations together gives us
The left-hand side is proportional to the normal component of the current density inside the superconductor.
The GL Equations in Dimensionless Form
We will find it convenient to introduce dimensionless variables when working with the GL equations. We start by introducing a dimensionless order parameter, , where












![{\displaystyle F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}\left[\alpha (T-T_{c})|\Psi ({\vec {r}})|^{2}+{\tfrac {1}{2}}b|\Psi ({\vec {r}})|^{4}+{\frac {\hbar ^{2}}{2m}}\left|\left(\nabla -i{\frac {2e}{\hbar c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}})\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}})\right|^{2}+{\frac {1}{8\pi }}(\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}))^{2}-{\frac {1}{c}}{\vec {J}}_{\text{ext}}({\vec {r}})\cdot {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}})\right],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1cac2adc0b4734f2e8b457a64661b84736033eee)







![{\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}'\left[{\frac {1}{4\pi }}(\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))\cdot (\nabla \times \delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))-{\frac {1}{c}}{\vec {J}}_{\text{ext}}({\vec {r}}')\cdot \delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/59e6bc43aa6095d8c72a1b307918b856263b0958)

![{\displaystyle (\nabla \times {\vec {A}})\cdot (\nabla \times {\vec {B}})=\nabla \cdot [{\vec {A}}\times (\nabla \times {\vec {B}})]+{\vec {A}}\cdot [\nabla \times (\nabla \times {\vec {B}})],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/28b705ccca6e572ac769022668c581c6e106974f)
![{\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}'\left[{\frac {1}{4\pi }}\nabla \cdot [\delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\times (\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))]+{\frac {1}{4\pi }}\delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\cdot [\nabla \times (\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))]-{\frac {1}{c}}{\vec {J}}_{\text{ext}}({\vec {r}}')\cdot \delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/65781b2aa9f03a7ec663da3dbd510d80cc68fdfe)
![{\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}\left[{\frac {1}{4\pi }}[\nabla \times (\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))]-{\frac {1}{c}}{\vec {J}}_{\text{ext}}({\vec {r}}')\right]\cdot \delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}').}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32f5a9d8f2d242acf97c54fae07eba2b74eac198)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {\delta F}{\delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}})}}={\frac {1}{4\pi }}[\nabla \times (\nabla \times {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}'))]-{\frac {1}{c}}{\vec {J}}_{\text{ext}}({\vec {r}}').}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aa0b02cc210949630b62c730ace203d48a1d2ba1)






![{\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}'\left[\alpha (T-T_{c})\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\,\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')+b|\Psi ({\vec {r}}')|^{2}\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\,\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')-{\frac {e}{mc}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\cdot \left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\,\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')-{\frac {1}{2m}}{\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')\cdot \left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2e97d3c2adba853ec3d5fb808ecdcfd1246de576)
![{\displaystyle -{\frac {1}{2m}}\left\{{\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \cdot \left[\left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\,\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')\right]-\left[{\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \cdot \left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\right]\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')\right\}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f170f9f83d228f16fd6fd85d8a3bdc8468efa679)
![{\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}'\left\{\alpha (T-T_{c})\Psi ({\vec {r}}')+b|\Psi ({\vec {r}}')|^{2}\Psi ({\vec {r}}')-{\frac {e}{mc}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\cdot \left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')+{\frac {1}{2m}}\left[{\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \cdot \left({\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla -{\frac {2e}{c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\right]\right\}\delta \Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}').}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/1e883a52f49db26c167bd9a557cb2ed07e069f55)


![{\displaystyle \delta F_{SC}=i{\frac {e\hbar }{mc}}\int d^{d}{\vec {r}}'\left[\Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')\left(\nabla -i{\frac {2e}{\hbar c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ({\vec {r}}')-\Psi ({\vec {r}}')\left(\nabla +i{\frac {2e}{\hbar c}}{\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}')\right)\Psi ^{*}({\vec {r}}')\right]\cdot \delta {\vec {A}}({\vec {r}}').}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/492f190737a40ec8709bc52689d02861c52c748e)










![{\displaystyle {\hat {n}}\cdot \left[\left(\Psi ^{*}{\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \Psi -\Psi {\frac {\hbar }{i}}\nabla \Psi ^{*}\right)-{\frac {4e}{c}}|\Psi |^{2}{\vec {A}}\right]=0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/81e95ecd7c999651340ab4a4a0f8f3237035573d)

