Solution to Set 5
I have no idea what I'm doing - KimberlyWynne 03:11, 2 March 2009 (EST)
Diatomic harmonic chain
Problem 1
I found this site somewhat helpful and explanatory:
http://newton.ex.ac.uk/teaching/resources/rjh/phy2009/PHY2009handout13.pdf
Given
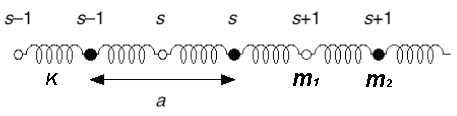
- a chain of atoms
- with alternating masses Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_1\;} and
- connected with elastic springs with constant
- moving only in the x-direction
Derive the dispersion relation for this chain
Equations of motion
Set determinant to 0
Step 1:
Step 2:
Step 3:
Problem 2
Determine the speed of sound for this chain. What is the lowest frequency of long-wavelength sound corresponding to the optical branch?
where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_{\alpha } \;} = frequency
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_{\alpha } \;} = speed of sound
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k \;} = ???
Problem 3
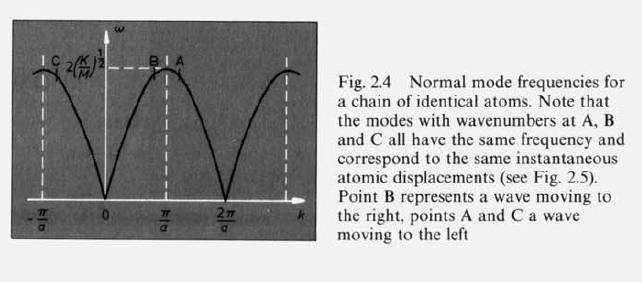
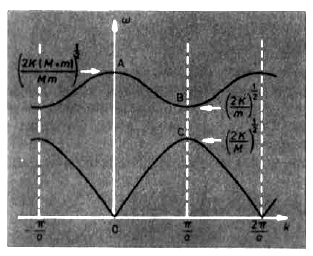
Sketch the motion of the atoms corresponding to the edge of the Brillouin zone, both for the optical and the acoustic branch.
- Acoustic Branch: lower branch
- Optical Branch: upper branch, as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k \rightarrow 0 } on this branch the vibrations of the 2 types of atom are in antiphase and the resulting charge oscillation in an ionic craystal give a strong coupling to electromagnetic waves at the frequency of point A.
Problem 4
Determine the Debye temperature for this system, and determine the form of the specific heat Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_V (T)} in the limits of high and low temperatures.
Debye Temperature Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_D \;}
The Debye temperature, aka the effective sonic velocity, is a measure of the hardness of the crystal
From our class lectures:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k_B T_D = \hbar \omega_D = \hbar c k_D \;}
From Wikipedia:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_D\ \stackrel{\mathrm{def}}{=}\ {hc_sR\over2Lk} = {hc_s\over2Lk}\sqrt[3]{6N\over\pi} = {hc_s\over2k}\sqrt[3]{{6\over\pi}{N\over V}}}
Specific Heat Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_V \;}
Low Temperature Limit
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{C_V}{Nk} \sim {12\pi^4\over5} \left({T\over T_D}\right)^3}
High Temperature Limit
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{high} >> \frac{\hbar\omega}{k_B} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\hbar\omega}{k_B T} << 1 \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{\frac{\hbar\omega}{k_B T}} \approx 1 + \frac{\hbar\omega}{k_B T} + (\frac{\hbar\omega}{k_B T})^2 \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{C_V}{Nk} \sim 3\, }
Net Result (Classical Limit)
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_V \approx k_B \;}
Problem 5
Consider low temperatures (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T \ll T_D\;} ) and determine the wavelength of the most abundant phonons Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{max}}
Given
- Bose-Einstein Distribution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(E)=\frac{1}{e^{E / k_B T}-1} \;}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f(E) \;} = probability that a particle will have energy E
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k_B \;} = Boltzmann constant
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T \;} = Temperature
- Planck's Radiation Formula Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E = \frac{h \omega}{e^{h \omega / k_B T} - 1} \;}
- Density by frequency: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho (\omega) = \frac{dn_s}{d\omega} = \frac{8 \pi}{c^3} \omega^{2} \;}
- Density by wavelength: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho (\lambda) = \frac{dn_s}{d\lambda} = \frac{8 \pi}{\lambda^{4}} \;}
- Wien's law Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_{\mathrm{max}} = \frac{b}{T} \;}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda_max \;} is the peak wavelength in meters,
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T \;} = temperature of the blackbody in Kelvin
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b \;} = Wien's displacement constant



![{\displaystyle m_{1}{\ddot {u}}_{n}=-k_{1}[2u_{n}-v_{n}-v_{n-1}]\;}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d507ab1dd4181501aaf51e3648993a76a10df7e6)
![{\displaystyle m_{2}{\ddot {v}}_{n}=-k_{2}[2v_{n}-u_{n}-u_{n+1}]\;}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/48f27906e8c7cd286406d55c3150046e5a8a13e1)





![{\displaystyle \omega ^{2}=k({\frac {m_{1}+m_{2}}{m_{1}m_{2}}})\pm k{\sqrt {({\frac {m_{1}+m_{2}}{m_{1}m_{2}}})^{2}-{\frac {4}{m_{1}m_{2}}}sin^{2}({\frac {ka}{2}})]}}\;}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/fa617ed0cb12d35b5a449588027ac8436ce2fc0c)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{vmatrix}2k-m_{1}\omega ^{2}&-C[1-\mathrm {exp} (-ika)]\\-C[1+\mathrm {exp} (-ika)]&2k-m_{2}\omega ^{2}\end{vmatrix}}=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a3758b8b15129746b19769178f4f11eb63057f36)