Phy5646
Welcome to the Quantum Mechanics B PHY5646 Spring 2009
This is the second semester of a two-semester graduate level sequence, the first being PHY5645 Quantum A. Its goal is to explain the concepts and mathematical methods of Quantum Mechanics, and to prepare a student to solve quantum mechanics problems arising in different physical applications. The emphasis of the courses is equally on conceptual grasp of the subject as well as on problem solving. This sequence of courses builds the foundation for more advanced courses and graduate research in experimental or theoretical physics.
The key component of the course is the collaborative student contribution to the course Wiki-textbook. Each team of students (see Phy5646 wiki-groups) is responsible for BOTH writing the assigned chapter AND editing chapters of others.
This course's website can be found here.
Outline of the course:
Stationary state perturbation theory in Quantum Mechanics
Very often, quantum mechanical problems cannot be solved exactly. We have seen last semester that an approximate technique can be very useful since it gives us quantitative insight into a larger class of problems which do not admit exact solutions. The technique we used last semester was WKB, which holds in the asymptotic limit Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar\rightarrow 0 } .
Perturbation theory is another very useful technique, which is also approximate, and attempts to find corrections to exact solutions in powers of the terms in the Hamiltonian which render the problem insoluble.All perturbative methods depends on few simple assumptions.The first of these that we have a mathematical expression for a physical quantity for which we are unable to obtain a exact solution.The next assumption is that this physical quantity may be broken down into a part which can be solved exactly and the troublesome part which has no analytic solution.
Typically, the (Hamiltonian) problem has the following structure
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}=\mathcal{H}_0+\mathcal{H}'}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}_0} is exactly soluble and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}'} makes it insoluble.
Rayleigh-Schrödinger Perturbation Theory
We begin with an unperturbed problem, whose solution is known exactly. That is, for the unperturbed Hamiltonian, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}_0} , we have eigenstates, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle } , and eigenenergies, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal \epsilon_n } , that are known solutions to the Schrodinger eq:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}_0 |n\rangle = \epsilon_n |n\rangle \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad (1.1.1) }
To find the solution to the perturbed hamiltonian, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}}
, we first consider an auxiliary problem, parameterized by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal \lambda}
:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H} = \mathcal{H}_0 + \lambda \mathcal{H}^' \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad (1.1.2) }
The only reason for doing this is that we can now, via the parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} , expand the solution in powers of the component of the hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}'} , which is presumed to be relatively small.
If we attempt to find eigenstates Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N(\lambda)\rangle} and eigenvalues Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} of the Hermitian operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} , and assume that they can be expanded in a power series of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal\lambda} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n(\lambda) = E_n^{(0)} + \lambda E_n^{(1)} + ... + \lambda^j E_n^{(j)} + ... }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N(\lambda)\rangle = |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle + \lambda|\Psi_n^{(1)}\rangle + \lambda^2 |\Psi_n^{(2)}\rangle + ... \lambda^j |\Psi_n^{(j)}\rangle + ... \qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\; (1.1.3)}
Where the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle} signify the nth order correction to the unperturbed eigenstate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} , upon perturbation. Then we must have,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H} |N(\lambda)\rangle = E(\lambda) |N(\lambda)\rangle \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\;\;\; (1.1.4)}
Which upon expansion, becomes:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\mathcal{H}_0 + \lambda \mathcal{H}')\left(\sum_{j=0}^{\infty}\lambda^j |\Psi_n^{(j)}\rangle \right) = \left(\sum_{l=0}^{\infty} \lambda^l E_l\right)\left(\sum_{j=0}^{\infty}\lambda^j |\Psi_n^{(j)}\rangle \right) \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\; (1.1.5)}
In order for this method to be useful, the perturbed energies must vary continuously with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} . Knowing this we can see several things about our, as yet undetermined perturbed energies and eigenstates. For one, as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda \rightarrow 0, |N(\lambda)\rangle \rightarrow |n\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n^{(0)} = \epsilon_n} for some unperturbed state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} .
For convenience, assume that the unperturbed states are already normalized: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n | n \rangle = 1} , and choose normalization such that the exact states satisfy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|N(\lambda)\rangle=1} . Then in general Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle} will not be normalized, and we must normalize it after we have found the states (see renormalization).
Thus, we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|N(\lambda)\rangle= 1 = \langle n |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle + \lambda \langle n |\Psi_n^{(1)}\rangle + \lambda^2 \langle n |\Psi_n^{(2)}\rangle + ... \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\;\;\;(1.1.6)}
Coefficients of the powers of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} must match, so,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n | N_n^{(i)} \rangle = 0, i = 1, 2, 3, ... \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;(1.1.7)}
Which shows that, if we start out with the unperturbed state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle }
, upon perturbation, the we add to this initial state a set of perturbation states, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle, |\Psi_n^{(1)}\rangle, ... }
which are all orthogonal to the original state -- so the unperturbed states become mixed together.
If we equate coefficients in the above expanded form of the perturbed Hamiltonian (eq. 1.1.5), we are provided with the corrected eigenvalues for whichever order of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda}
we want. The first few are as follows,
0th Order Energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda = 0 \rightarrow E_n^{(0)} = \epsilon_n } , which we already had from before (1.1.8)
1st Order Energy Corrections Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda = 1 \rightarrow \mathcal{H}_0 |\Psi_n^{(1)}\rangle + \mathcal{H}' |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle = E_n^{(1)} |\Psi_n^{(0)}\rangle + E_n^{(0)} |\Psi_n^{(1)}\rangle } , taking the scalar product of this result of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} , and using our previous results, we get: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n^{(1)} = \langle n|\mathcal{H}'|n\rangle \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\;(1.1.9)}
2nd Order Energy Corrections
Taking the terms in eq 1.1.5 that are second order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} and operating on them with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} provides us with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} up to the second order:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n = \epsilon_n + \lambda\langle m|\mathcal{H}'|n\rangle + \lambda^2 \sum_{m \not= n} \frac{|\langle n|\mathcal{H}'|m\rangle|^2}{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_m}+ O(\lambda^3)}
One interesting thing to not about this is that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |V_{mn} = \langle m |V| n\rangle|^2} is positive definite. Therefore, since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_0 - \epsilon_m < 0} , the second order energy correction will lower the ground state energy.
kth order Energy Corrections In general, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n^{(k)} = \langle n | \mathcal{H}' | N_n^{(k - 1)} \rangle \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;(1.1.10)}
This result provides us with a recursive relationship for the Eigenenergies of the perturbed state, so that we have access to the eigenenergies for an state of arbitrary order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} .
What about the eigenstates? Express the perturbed states in terms of the unperturbed states:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\Psi_n^{(k)}\rangle = \sum_{m \not= n}|m\rangle\langle m|\Psi^{(k)}\rangle}
Go back to equation 1.1.5 and taking the scalar product from the left with and taking orders of we find:
1st order Eigenkets
The first order contribution is then the sum of this equation over all , and adding the zeroth order we get the eigenstates of the perturbed hamiltonian to the 1st order in :
Going beyond order one in gets increasingly messy, but can be done by the same procedure.
Renormalization Earlier we assumed that , which means that our states are not normalized themselves. To reconsile this we introduce the normalized perturbed eigenstates, denoted . These will then be related to the :
Thus gives us a measure of how close the perturbed state is to the original state.
To 2nd order in
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z(\lambda ) = \frac{1}{1 + \lambda^2\sum_{ n \not= m}\frac{|\langle m|V|n\rangle|^2}{(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_m)^2} + ...} = 1 - \lambda^2\sum_{ n \not= m}\frac{|\langle m|V|n\rangle|^2}{(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_m)^2} + ... \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\;\;\;\;(1.1.14)}
Where we use a taylor expansion to arrive at the final result (noting that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{|\langle m|V|n\rangle|^2}{(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_m)^2} < 1} ).
Then, interestingly, we can show that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} is related to the energies by employing equation 1.1.10:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z(\lambda ) = \frac{\partial E_n}{\partial \epsilon_n}\Big|_{\epsilon_m}{\langle m|V|n\rangle} \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;(1.1.15)}
Where the derivative is taken with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_n} , while holding Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle m|V|n\rangle} constant. Using the Brillouin-Wigner perturbation theory (see next section) it can supposedly be shown that this relation holds exactly, without approximation.
Brillouin-Wigner Perturbation Theory
This is another type of perturbation theory. Using a basic formula derived from the Schrodinger equation, you can find an approximation for any power of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda } required using an iterative process.This theory is less widely used as compared to the RS theory.At first order the two theories are equivalent.However,the BW theory extends more easily to higher order and avoid the need for separate treatment of non degenerate and degenerate levels.
Starting with the Schrodinger equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} ({\mathcal H}_o+\lambda {\mathcal H}')|N\rangle &= E_n|N\rangle \\ \lambda {\mathcal H}'|N\rangle &= (E_n-{\mathcal H}_o)|N\rangle \\ \langle n|(\lambda {\mathcal H}'|N\rangle) &= \langle n|(E_n-{\mathcal H}_o)|N\rangle \\ \lambda \langle n|{\mathcal H}'|N\rangle &= (E_n-\epsilon_n)\langle n|N\rangle \\ \end{align} }
If we choose to normalize Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|N \rangle = 1 } , then so far we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (E_n-\epsilon_m) = \lambda\langle n|{\mathcal H}'|N\rangle \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\; (1.2.1)}
which is still an exact expression (no approximation have been made yet). The wavefunction we are interested in, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle } can be rewritten as a summation of the eigenstates of the (unperturbed, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathcal H}_o } ) Hamiltonian:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |N\rangle &= \sum_m|m\rangle\langle m|N\rangle\\ &= |n\rangle\langle n|N\rangle + \sum_{m\neq n}|m\rangle\langle m|N\rangle\\ &= |n\rangle + \sum_{m\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\lambda\langle m|{\mathcal H}'|N\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)}\\ \end{align} \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\;\;\; (1.2.2)}
The last step has been obtained by using eq 1.2.1. So now we have a recursive relationship for both Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n = \epsilon_n+\lambda\langle n|{\mathcal H}'|N\rangle } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle } can be written recursively to any order of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda } desired
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle = |n\rangle+\lambda \sum_{m\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\lambda\langle m|{\mathcal H}'|N\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)} } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n } can be written recursively to any order of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda } desired
For example, the expression for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N\rangle } to a third order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda } would be:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |N\rangle &= |n\rangle + \lambda\sum_{m\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\langle m|{\mathcal H}'}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)}\left(|n\rangle + \lambda\sum_{j\neq n}|j\rangle\frac{\langle j|{\mathcal H}'}{(E_n-\epsilon_j)}\left(|n\rangle + \lambda\sum_{k\neq n}|k\rangle\frac{\langle k|{\mathcal H}'|n\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_k)}\right)\right)\\ &= |n\rangle + \lambda\sum_{m\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\langle m|{\mathcal H}'|n\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)} + \lambda^2\sum_{m,j\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\langle m|{\mathcal H}'|j\rangle\langle j|{\mathcal H}'|n\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)(E_n-\epsilon_j)} + \lambda^3\sum_{m,j,k\neq n}|m\rangle\frac{\langle m|{\mathcal H}'|j\rangle\langle j|{\mathcal H}'|k\rangle\langle k|{\mathcal H}'|n\rangle}{(E_n-\epsilon_m)(E_n-\epsilon_j)(E_n-\epsilon_k)}\\ \end{align} } ,
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{j} |j \rangle \langle j |} is unity.
Note that we have chosen Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|N \rangle = 1} , i.e. the correction is perpendicular to the unperturbed state. That is why at this point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |N \rangle} is not normalized. The normalized exact state, therefore, is written as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z|N \rangle} . Interestingly, the normalization constant Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z} turns out be exactly equal to the derivative of the exact energy with respect to the unperturbed energy. The calculation for the normalization constant can be found through this link.
We can expand 1.2.1 with the help of 1.2.2, this gives:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n = \epsilon_n + \lambda\langle n|H'|n\rangle + \lambda^2\sum ' \frac{|\langle m|H'|n\rangle|^2}{E_n - \epsilon_m} \qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\;\;\;\; (1.2.3)} .
Notice that if we replaced Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle epsilon_n} we would recover the Raleigh-Schrodinger perturbation theory. By itself 1.2.2 provides a transcendental equation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} , since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} appears in the denominator of the right hand side. If we have some idea of the value of a particular Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n} , then we could use this as a numerical method to iteratively get better and better values for .
Degenerate Perturbation Theory
Degenerate perturbation theory is an extension of standard perturbation theory which allows us to handle systems where one or more states of the system have non-distinct energies. Normal perturbation theory fails in these cases because the denominators of the expressions for the first-order corrected wave function and for the second-order corrected energy go to zero.If more than one eigenstate for the Hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathcal H}_o } has the same energy value, the problem is said to be degenerate. If we try to get a solution using perturbation theory, we fail, since Rayleigh-Schroedinger PT includes terms like Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1/\mathcal(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_m) } .
Instead of trying to use these (degenerate) eigenstates with perturbation theory, if we start with the correct linear combinations of eigenstates, regular perturbation theory will no longer fail! So the issue now is how to find these linear combinations.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \longrightarrow } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \{|n_{\alpha}\rangle,|n_{\beta}\rangle,|n_{\gamma}\rangle,\dots\} } where etc
The general procedure for doing this type of problem is to create the matrix with elements Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n_a|{\mathcal H}'|n_b\rangle } formed from the degenerate eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathcal H}_o } . This matrix can then be diagonalized, and the eigenstates of this matrix are the correct linear combinations to be used in non-degenerate perturbation theory.In other words, we choose to manipulate the expression for the Hamiltonian so that goes to zero for all cases r ≠ n. One can then apply the standard equation for the first-order energy correction, noting that the change in energy will apply to the energy states described by the new basis set. (In general, the new basis will consist of some linear superposition of the existing state vectors of the original system.)
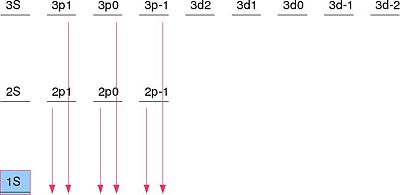
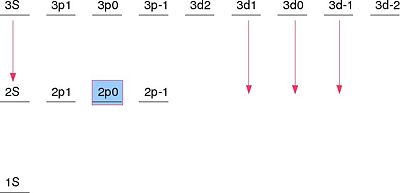
One of the well-known examples of an application of degenerate perturbation theory is the Stark Effect. If we consider a Hydrogen atom with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=2 } in the presence of an external electric field . The Hamiltonian for this system is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathcal H}={\mathcal H}_o-e{\mathcal E}z } . The eigenstates of the system are . The matrix of the degenerate eigenstates and the perturbation is:
The full arguments as to how most of these terms are zero is worked out in G Baym's "Lectures on Quantum Mechanics" in the section on Degenerate Perturbation Theory. The correct linear combination of the degenerate eigenstates ends up being
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \{|2P_{-1}\rangle,|2P_{+1}\rangle,\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(|2S\rangle+|2P_0\rangle\right),\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(|2S\rangle-|2P_0\rangle\right)\} }
Because of the perturbation due to the electric field, the and states will be unaffected. However, the energy of the and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |2P_0\rangle } states will have a shift due to the electric field.
Example: 1D harmonic oscillator
Consider 1D harmonic oscillator perturbed by a constant force.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V = -F\mathbf{x}}
The energy up to second order is given by
Let's see the matrix elements
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle m|V|n\rangle &=-F\langle m|\mathbf{x}|n\rangle\\ &=-F\langle m|\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\left( \mathbf{a}+\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}\right)|n\rangle\\ &=-F\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\left( \langle m|\mathbf{a}|n\rangle+\langle m|\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}|n\rangle\right)\\ &=-F\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\left( \sqrt{n}\langle m|n-1\rangle+\sqrt{n+1}\langle m|n+1\rangle\right)\\ &=-F\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\left( \sqrt{n}\delta_{m,n-1}+\sqrt{n+1}\delta_{m,n+1}\right)\\ \end{align}}
We see that:
- The first order term is:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|V|n\rangle=0}
- The Second order term is:
Finally the energy is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{n}=\epsilon_{n}-\frac{F^{2}}{2m\omega^{2}} }
This results is exactly the same as when we solve the problem without perturbation theory.
Time dependent perturbation theory in Quantum Mechanics
Formalism
Previously, we learned the time independent perturbation theory which can be applied on various systems in which a little change in the Hamiltonian appears as a correction in the form of a series for the energy and wave functions. However, this stationary approach cannot be used to describe the interaction of electromagnetic field with atoms (i.e. photon with Hydrogen atom), since such systems would be inherently time dependent. Therefore we must explore Time Dependent Perturbation Theory.
One of the main tasks of this theory is the calculation of transition probabilities from one state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi_n \rangle}
to another state that occurs under the influence of a time
dependent potential. Generally, the transition of a system from one state to another state only makes sense if the potential acts only within a finite time period from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t = 0}
to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t = T}
. Except for this time period, the total energy is a constant of motion which can be measured.
We start with the Time Dependent Schrodinger Equation,
Then, assuming that the perturbation acts after time Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t_0} , we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial t}|\psi_t \rangle = (H_0 + V_t)|\psi_t\rangle, \qquad t>t_0 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\;\; (2.2)}
The problem therefore consists of finding the solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle}
with boundary condition Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle = |\psi_t^0\rangle}
for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t \leq t_0}
. However, such a problem is not generally soluble.
Therefore, we limit ourselves to the problems in which Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t}
is small. In that case we can treat Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t}
as a perturbation and seek it's effect on the wavefucntion in powers of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t}
.
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t} is small, the time dependence of the solution will largely come from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!H_0} . So we use
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi_t\rangle = e^{-i H_0 t/\hbar}|\psi(t)\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\; (2.3)} ,
which we substitute into the Schrodinger Equation to get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial t}|\psi(t)\rangle=V(t)|\psi(t)\rangle \quad \text{where}\quad V(t) = e^{i H_0 t/\hbar}V_te^{-i H_0 t/\hbar}\qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad (2.4)} .
In this equation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(t)} and the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V(t)} are in the interaction representation. Now, we integrate equation #(2.4) to get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int_{t_o}^{t}dt \frac{\partial}{\partial t}|\psi(t)\rangle = \psi(t) - \psi(t_0) = \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt' V(t')|\psi(t')\rangle}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle = |\psi(t_0)\rangle + \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt' V(t')|\psi(t')\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \;\;\ (2.5)}
Equation #(2.5) can be iterated by inserting this equation itself as the integrand in the r.h.s. We can then write equation #(2.5) as
which can be written compactly as
This is the general solution. T is called the time ordering operator, which ensures it the series is expanded in the correct order. For now, we consider only the correction to the first order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V(t)} .
First Order Transitions
If we limit ourselves to the first order we use,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle = |\psi(t_0)\rangle + \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt'V(t')|\psi(t_0)\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\;\ (2.8)}
We want to see the system undergoes a transition to another state, say Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle}
. So we project the wave function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle}
to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle}
. From now on, let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t_0)\rangle = |0\rangle}
for brevity. Projecting into state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle}
and assuming Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|0\rangle =0 }
we get,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}\langle n|\psi(t)\rangle & = \langle n|0\rangle + \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt'\langle n|V(t')|0\rangle\\ & = \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt'\langle n|e^{\frac{1}{\hbar}H_0 t}V_{t'}e^{-\frac{1}{\hbar}H_0 t}|0\rangle\\ & = \frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt'e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)t'}\langle n|V_{t'}|0\rangle \end{align}\qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\,\ (2.9)}
Expression #(2.9) is the probability amplitude of transition. Therefore, we square the final expression to get the probability of having the system in state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle}
at time t.
Squaring, we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{0 \rightarrow n}{P(t)} = |\langle n|\psi(t)\rangle|^2 = \left|\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{t_0}^{t}dt' e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)t'}\langle n|V_{t'}|0\rangle\right|^2 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\, (2.10)}
For example, let us consider a potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t} which is turned on sharply at time Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t_0} , but independent of t thereafter. Furthermore, we let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t_0 = 0} for convenience. Therefore :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V_t = \begin{cases} 0 &\mbox{if} \qquad t<0\\ V &\mbox{if} \qquad t>0 \end{cases} } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \underset{0 \rightarrow n}{P(t)} & = \left|\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{0}^{t}dt' e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)t'}\langle n|V|0\rangle\right|^2\\ & = \left|\frac{1}{i\hbar}\frac{e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)t'}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)}\langle n|V|0\rangle\right|^2\\ & = \frac{sin^2\left(\frac{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0}{2\hbar}t\right)}{\left(\frac{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0}{2}\right)^2}|\langle n|V|0 \rangle|^2 \end{align}\qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\; (2.11) }
The plot of the probability vs. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! \epsilon_n} is given in the following plot:
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta\epsilon\Delta t \geq 2\pi\hbar} . So we conclude that as the time grows, the probability is the largest for the transition to conserve the energy to within an amount given in that relation.
Now, we imagine shining a light of a certain frequency on a Hydrogen atom. We probably ended up getting the atom at a certain bound state. However it might be ionized as
well. The problem with ionization is the fact that the final state is a continuum, so we cannot just simply pick up a state to end with i.e. a plane wave with a specific k.
Furthermore, if the wave function is normalized, the plane waves states will contain a factor of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1/\sqrt{V}}
which goes to zero if V is very large. But, we know that ionization exists, so there must be something missing. Instead of measuring the the probability to a transition to a pointlike wavenumber, k, we want to measure the amplitude of transition to a group of states around a particular k -- i.e, we want to measure from k to k+dk.
Let's suppose that the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} is one of the continuum state, then what we could ask is the probability that the system makes transition to a small group of states about Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} , not to a specific value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle} . For example, for a free particle, what we can find is the transition probability from initial state to a small group of states, viz. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec k\rangle} , or in other words the transition probability to an element of phase space Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! d^3k / (2\pi)^3}
The next step is a mathematical trick. We use
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta(x) = \lim_{\eta \to 0}\frac{1}{\pi x}sin(x/\eta)}
Applying this to our result from above, we see that,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{sin(\frac{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0}{2\hbar}t)}{\frac{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0}{2}} = \frac{\pi}{\hbar}\delta(\frac{\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0}{2\hbar}) \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\;\;\;\; (2.12)}
Which, if used in the equation #(2.11) gives
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{0 \rightarrow n}{P(t)}\quad\underset{t \rightarrow \infty}{\longrightarrow}\quad \frac{t}{\hbar}2\pi \delta(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)|\langle n|V|0\rangle|^2 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;(2.13) }
or as a rate of transition, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{0\rightarrow n}{\Gamma}} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{0 \rightarrow n}{\Gamma} = \frac{d}{dt}\underset{0 \rightarrow n}{P(t)}\quad\underset{t \rightarrow \infty}{\longrightarrow}\quad\frac{2\pi}{\hbar} \delta(\epsilon_n - \epsilon_0)|\langle n|V|0\rangle|^2 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad (2.14) }
which is called The Fermi Golden Rule. Using this formula, we should keep in mind to sum over the entire continuum of final states.
To make things clear, let's try to calculate the transition probability for a system from a state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{k}\rangle} to a final state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{k'}\rangle} due to a potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! V(r)} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \vec{k'}|V|\vec{k}\rangle = \int d^3 r \frac{e^{-i\vec{k'}.\vec{r}}}{\sqrt{L^3}}V(r)\frac{e^{i\vec{k}.\vec{r}}}{\sqrt{L^3}} = \frac{V_{k'k}}{L^3} \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\ (2.15) }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{\vec{k} \rightarrow \vec{k'}}{\Gamma} = \frac{2\pi}{\hbar} \delta(\epsilon_k - \epsilon_{k'})\frac{|V_{k'\rightarrow k}|^2}{L^6}}
What we want is the rate of transition, or actually scattering in this case, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!d\Gamma} into a small solid angle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!d\Omega} . So we must sum over the momentum states in this solid angle:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{k'\in d\Omega}\underset{\vec{k}\rightarrow \vec{k'}}{\Gamma} }
The sum over states for continuum can be calculated an using integral,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{\vec{k'}\in d\Omega'} \quad \longrightarrow \quad d\Omega'\int d\epsilon_{k'}\frac{L^3 m k'}{(2\pi)^3 \hbar^2}\qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\;\ (2.16)}
Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underset{\vec{k}\rightarrow{\vec{k}'\in d\Omega'}}{d\Gamma} = \frac{d\Omega'}{L^3}\frac{mk}{4\pi^2\hbar^3}|V_{k'k}|^2 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\;\;\ (2.17)}
The flux of particles per incident particle of momentum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar k} in a volume Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!L^3} is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar k / m L^3} , so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\Gamma}{d\Omega (\frac{\bar k}{m L^3})} = \frac{m^2}{4\pi^2\hbar^4}|V_{k'k}|^2 = \frac{d\sigma}{d\Omega}} , in the Born Approximation.
This result makes sense since our potential does not depend on time, so what happened here is that we sent a particle with wave vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{k}} through a potential and later detect a particle coming out from that potential with wave vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{k'}} . So, it is a scattering problem solved using a different method.
Harmonic Perturbation Theory
Harmonic perturbation is one of the main interest in perturbation theory. We know that in experiment, we usually perturb the system using a certain signal to extract information about it, for example the difference between the energy levels. We could send a photon with a certain frequency to a Hydrogen atom to excite the electron and let it decay to observe the difference between two energy levels by measuring the frequency of the photon emitted from it. The photon acts as an electromagnetic signal, and it is harmonic (if we consider it as an electromagnetic wave).
In general, we write down the harmonic perturbation as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!V_t = V cos(\omega t) e^{\eta t}\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad\qquad(2.2.1)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!e^{\eta t}} specify the rate at which the perturbation is turned on, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} is a very small positive number which at the end of the calculation is set to be zero.
We start from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!t_0 = - \infty} . Since there's no perturbation at that time. We want to find the probability that there will be a transition from the initial state to some other state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle | n \rangle} . The transition amplitude is,
To the first order of V we write
Now we calculate the probability as usual:
Where all oscillatory terms has been averaged to zero. Transition rate is given by :
now, if the response is immediate, or the potential is turned on suddenly, we take . Therefore:
Which is the Fermi Golden Rule. This result shows that there will be a non-zero transition probability for cases where - Roughly speaking, there will be significant transitions only when is a "resonant frequency" for a particular transition.
Second Order Transitions
Sometimes the first order matrix element is identically zero (parity, Wigner Eckart, etc.) but other matrix elements are nonzero—and the transition can be accomplished by an indirect route.
where is the probability amplitude for the second-order process,
Taking the gradually switched-on harmonic perturbation , and the initial time , as above
The integrals are straightforward, and yield
Exactly as in the section above on the first-order Golden Rule, we can find the transition rate:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d}{dt}\vert{c^{(2)}_{n}(t)}\vert^2 = \frac{2 \pi}{\hbar^4} \vert{\sum_{n}\frac{\langle f|V|n\rangle \langle n|V|i\rangle}{\omega_{n} -\omega_{i} -\omega -i \epsilon}}\vert^2 \delta \left(\omega_{f} -\omega_{i} -2 \omega \right)}
The Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar^4 }
in the denominator goes to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar }
on replacing the frequencies
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega }
with energies E, both in the denominator and the delta function, remember that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E= \hbar \omega }
This is a transition in which the system gains energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2 \hbar \omega }
from the beam, in other words two photons are absorbed, the first taking the system to the intermediate energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega }
, which is short-lived and therefore not well defined in energy—there is no energy conservation requirement into this state, only between initial and final states.
Of course, if an atom in an arbitrary state is exposed to monochromatic light, other second order processes in which two photons are emitted, or one is absorbed and one emitted (in either order) are also possible.
Example of Two Level System : Ammonia Maser
In this model, we assume that the Nitrogen atom, being heavier than Hydrogen, is motionless. The Hydrogen atoms form a rigid equilateral triangle whose axis is always passes through the Nitrogen Atom.
Since there are two different state (the position of the Hydrogen triangle), we write down the wave function as a superposition of both states. Of course it is a function of time.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\Psi_t\rangle = C_1(t)|1\rangle + C_2(t)|2\rangle}
Then we operate on this state the time dependent Schrodinger equation to find:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar \begin{pmatrix} \dot{C}_1(t)\\ \dot{C}_2(t) \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} E_0 & A\\ A & E_0 \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} C_1(t)\\ C_2(t) \end{pmatrix} }
Which in the pressence of electric field, the additional energy enters only on the diagonal part of the Hamiltonian matrix
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar \begin{pmatrix} \dot{C}_1(t)\\ \dot{C}_2(t) \end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix} E_0 + \mu \Epsilon(t) & A\\ A & E_0 - \Epsilon(t) \end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix} C_1(t)\\ C_2(t) \end{pmatrix} }
Typically, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2A \approx 10^-4 eV} which gives the frequency of the movement of the Hydrogen triangle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nu \approx 2.4 \times 10^9 Hz} and the wavelength Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda \approx 1.25 cm} (microwave region)
Solving for the Schrodinger we have above, we find the energy of the two states
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_\pm = E_0 \pm \sqrt{(\mu \Epsilon)^2 + A^2}}
Which graphically, we can draw the graphics of Electric field vs Energy
Because of these two different states, ammonia molecule is separable in the electric field. This can be used to select molecule with certain value of energy.
It should be clear that if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! \Epsilon(t) = 0} our eigenstates are Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underbrace{\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\begin{pmatrix}1\\ \pm 1\end{pmatrix}}_{basis for expansion} } with energies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! E_0 \pm A}
Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{pmatrix}C_1\\C_2\end{pmatrix}=\frac{\gamma_1}{\sqrt{2}}\begin{pmatrix}1\\1\end{pmatrix}+\frac{\gamma_2}{\sqrt{2}}\begin{pmatrix}1\\-1\end{pmatrix}}
So, following above equation, we find
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} i\hbar \dot{\gamma_1} & = & (E_0 +A)\gamma_1 + \mu \Epsilon(t)\gamma_2\\ i\hbar \dot{\gamma_2} & = & (E_0 -A)\gamma_2 + \mu \Epsilon(t)\gamma_1 \end{align} }
Interaction of radiation and matter
Quantization of electromagnetic radiation
Classical view
Let's use transverse gauge (sometimes called Coulomb gauge):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varphi (\mathbf{r},t)=0 }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla \cdot \mathbf{A}=0}
In this gauge the electromagnetic fields are given by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{E}(\mathbf{r},t)=-\frac{1}{c}\frac{\partial \mathbf{A} }{\partial t}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{B}(\mathbf{r},t)=\nabla \times \mathbf{A}}
The energy in this radiation is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon = \frac{1}{8\pi} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r} (\mathbf{E}^{2}+\mathbf{B}^{2})}
The rate and direction of energy transfer are given by poynting vector
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{P} = \frac{c}{4\pi} \mathbf{E} \times \mathbf{B} }
The radiation generated by classical current is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Box \mathbf{A} = -\frac{4\pi}{c} \mathbf{j}}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Box} is the d'Alembert operator. Solutions in the region where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{j}=0} are given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t) = \alpha \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\alpha^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega=c|\mathbf{k}|} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\lambda}\cdot \mathbf{k}=0 } in order to satisfy the transversality. Here the plane waves are normalized with respect to some volume Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V} . This is just for convenience and the physics won't change. We can choose Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\lambda}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}=1} . Notice that in this writing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}} is a real vector.
Let's compute Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varepsilon} . For this
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{E}(\mathbf{r},t) & =-\frac{1}{c}\frac{\partial \mathbf{A} }{\partial t} \\ & =-\frac{1}{c\sqrt{V}}\frac{\partial}{\partial t}\left[\alpha \boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}+\alpha^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ & =-\frac{i\omega}{c\sqrt{V}}\left[-\alpha \boldsymbol{\lambda} e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}+\alpha^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ \mathbf{E}^{2}(\mathbf{r},t) & = -\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}\left[\alpha^{2} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{2} e^{2i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}-\alpha\alpha^{*}\boldsymbol{\lambda}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}-\alpha^{*}\alpha\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda}+\alpha^{*2} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*2} e^{-2i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ \end{align} }
Taking the average, the oscillating terms will disappear. Then we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{E}^{2}(\mathbf{r}) & = \frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}\left[\alpha\alpha^{*}+\alpha^{*}\alpha\right] \\ &=2\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}|\alpha|^2 \\ \end{align} }
It is well known that for plane waves Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{B}=\mathbf{n}\times \mathbf{E} } , where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{n}} is the direction of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k}} . This clearly shows that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{B}^{2}=\mathbf{E}^{2}} . However let's see this explicitly:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{B}(\mathbf{r},t) & =\nabla \times\mathbf{A}\\ & =\nabla \left[\alpha \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\alpha^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right] \\ \end{align} }
Each component is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{B}_{i}(\mathbf{r},t)& =\frac{1}{{\sqrt{V}}}\left[\alpha \varepsilon _{ijk}\partial_{j} \left(\boldsymbol{\lambda}_{k}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right)+\alpha^{*} \varepsilon _{ijk}\partial_{j} \left(\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}_{k}e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right)\right] \\ & =\frac{i}{{\sqrt{V}}}\left[\alpha \varepsilon _{ijk}\mathbf{k}_{j} \boldsymbol{\lambda}_{k}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}-\alpha^{*} \varepsilon _{ijk}\mathbf{k}_{j} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}_{k}e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ \end{align} }
Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{B}(\mathbf{r},t) & =\frac{i}{{\sqrt{V}}}\left[\alpha \mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}-\alpha^{*} \mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ \mathbf{B}^{2}(\mathbf{r},t) & =\frac{-1}{{V}}\left[\alpha \mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}-\alpha^{*} \mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ & =\frac{-1}{{V}}\left[\alpha^{2} (\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda})^{2}e^{2i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}-\alpha \alpha^{*}(\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda})\cdot(\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*})-\alpha^{*} \alpha(\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*})\cdot(\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda})+\alpha^{*2} (\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*})^{2} e^{-2i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right] \\ \end{align} }
Again taking the average the oscillating terms vanish. Then we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{B}^{2}(\mathbf{r}) & =\frac{1}{{V}}\left[\alpha \alpha^{*}+\alpha^{*} \alpha\right](\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda})\cdot(\mathbf{k}\times\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}) \\ & =\frac{1}{{V}}\left[\alpha \alpha^{*}+\alpha^{*} \alpha\right][\mathbf{k}^{2}(\boldsymbol{\lambda}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda^{*}})-(\mathbf{k}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda^{*}})\cdot(\mathbf{k}\cdot\boldsymbol{\lambda^{*}})] \\ & =\frac{2}{{V}}|\alpha|^{2}\mathbf{k}^{2}\\ &=2\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}|\alpha|^2 \\ &= \mathbf{E}^{2}(\mathbf{r},t)\\ \end{align} }
Finally the energy of this radiation is given by
So far we have treated the potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)} as a combination of two waves with the same frequency. Now let's extend the discussion to any form of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)} . To do this we can sum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)} over all values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\lambda}} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}} \right]\\ \end{align}}
To calculate the energy with use the fact that any exponential time-dependent term is in average zero. Therefore in the previous sum all cross terms with different Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k}} vanishes. Then it is clear that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{E}^{2}(\mathbf{r}) & = \sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}\left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right] \\ \mathbf{B}^{2}(\mathbf{r}) & = \sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\frac{\mathbf{k}^2}{V}\left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right] \\ \end{align} }
Then the energy is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \varepsilon &= \frac{1}{8\pi} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r} (\mathbf{E}^{2}+\mathbf{B}^{2}) \\ &=\frac{1}{4\pi} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \mathbf{E}^{2}\\ &=\frac{1}{4\pi} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r} \sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}V}\left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right] \\ &=\frac{1}{4\pi} \sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\frac{\omega^{2}}{c^{2}}\left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right] \\ \end{align}}
Let's define the following quantities:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} Q_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}&=\frac{1}{\sqrt{4\pi}c}(A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*})\\ P_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}&=\frac{-i\omega}{\sqrt{4\pi}c}(A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}-A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*})\\ \end{align}}
Notice that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \omega^{2} Q_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}&=\frac{\omega^{2}}{4\pi c^{2}}(A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*2})\\ P_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}&=\frac{-\omega^{2}}{4\pi c^{2}}(A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}-A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}-A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*2})\\ \end{align}}
Adding
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} P_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}+\omega^{2} Q_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}&=\frac{\omega^{2}}{2\pi c^{2}}(A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*}\cdot A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}})\\ \end{align}}
Then the energy (in this case the Hamiltonian) can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} H=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} P_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2}+\omega^{2} Q_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{2} \end{align}}
This has the same form as the familiar Hamiltonian for a harmonic oscillator.
Note that,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{\partial H_{cl}}{\partial Q_{k, \lambda}} = - \dot{P}_{k, \lambda} \\ \frac{\partial H_{cl}}{\partial P_{k, \lambda}} = - \dot{Q}_{k, \lambda} \end{align}}
The makeshift variables, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{k, \lambda}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Q_{k, \lambda}} are canonically conjugate.
We see that the classical radiation field behaves as a collection of harmonic oscillators, indexed by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k}} adn Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\lambda}} , whose frequencies depends on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\mathbf{k}|} .
From classical mechanics to quatum mechanics for radiation
As usual we proceed to do the canonical quantization:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} P_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} & \to \mathbf{P}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\\ Q_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} & \to \mathbf{Q}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\\ \end{align}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} & \to \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\;\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\; , \; [\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}},\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}]=\delta_{\mathbf{kk'}}\delta_{\boldsymbol{\lambda \lambda'}}\\ \end{align}}
Where last are quantum operators. The Hamiltonian can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}_{radiation}&=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}(\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}} \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}+\frac{1}{2}) &=\frac{1}{2}\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}(\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}} \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}} \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}})\\ \end{align}}
The classical potential can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \underbrace{\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \left[A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+A_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{*} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]}_\textrm{Classical Vector potential}\;\;\;\longrightarrow\;\;\; \underbrace{\mathbf{A}_{int}(\mathbf{r},t)=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]}_\textrm{Quantum Operator} }
Notice that the quantum operator is time dependent. Therefore we can identify it as the field operator in interaction representation. (That's the reason to label it with int). Let's find the Schrodinger representation of the field operator:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r})&=e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\mathbf{A}_{int}(\mathbf{r},t)e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\\ &=e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\left[\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]\right]e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\left[e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t} \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\right] \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\left[ e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{rad}t}\right] \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}e^{i\omega t}\right] \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\left[ \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} e^{-i\omega t}\right] \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}}{\sqrt{V}}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]\\ \end{align}}
COMMENTS
- The meaning of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{radiation}} is as following: The classical electromagnetic field is quantized. This quantum field exist even if there is not any source. This means that the vacuum is a physical object who can interact with matter. In classical mechanics this doesn't occur because, fields are created by sources.
- Due to this, the vacuum has to be treated as a quantum dynamical object. Therefore we can define to this object a quantum state.
- The perturbation of this quantum field is called photon (it is called the quanta of the electromagnetic field).
ANALYSIS OF THE VACUUM AT GROUND STATE
Let's call Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |0\rangle} the ground state of the vacuum. The following can be stated:
- The energy of the ground state is infinite. To see this notice that for ground state we have Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}_{radiation}&=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \frac{1}{2} \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}=\infin \end{align}}
- The state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \;\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}|0\rangle} represent an exited state of the vacuum with energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}(1+1/2)} . This means that the extra energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}} is carried by a single photon. Therefore Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}} represent the creation operator of one single photon with energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}} . In the same reasoning, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}} represent the annihilation operator of one single photon.
- Consider the following normalized state of the vacuum:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}|0\rangle}
. At the first glance we may think that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}}
creates a single photon with energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2\hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}}
. However this interpretation is forbidden in our model. Instead, this operator will create two photons each of the carryng the energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}}
.
Proof
Suppose that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}} creates a single photon with energy . We can find an operator who can create a photon with the same energy . This means that
Let's see if this works. Using commutation relationship we have
Replace the highlighted part by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}},\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right]=0 }
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}},\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right]=1} , the initial assumption is wrong, namely:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}|0\rangle \ne \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k'} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}|0\rangle }
This means that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}} } cannot create a single photon with energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2\hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}}} . Instead it will create two photons each of them with energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega_{\mathbf{k}\blacksquare}}
ALGEBRA OF VACUUM STATES
A general vacuum state can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}};...\rangle }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}} is the number of photons in the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}} which exist in the vacuum. Using our knowledge of harmonic oscillator we conclude that this state can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}};...\rangle=\prod_{\mathbf{k_{j}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{j}}}\frac{( \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k} \boldsymbol{\lambda}})^{n_{\mathbf{k_{j}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{j}}}}}{\sqrt{n_{\mathbf{k_{j}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{j}}}!}}|0\rangle }
Also it is clear that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}|n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}};...\rangle=\sqrt{n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}+1}|n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}+1;...\rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}|n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}};...\rangle=\sqrt{n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}}|n_{\mathbf{k_{1}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{1}}};n_{\mathbf{k_{2}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{2}}};...;n_{\mathbf{k_{i}} \boldsymbol{\lambda_{i}}}-1;...\rangle }
Matter + Radiation
Hamiltonian of Single Particle in Presence of Radiation (Gauge Invariance)
The Hamiltonian of a single charged particle in presence of E&M potentials is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}=\frac{[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A(\mathbf{r}t)]^{2}}{2m}+e\phi (\mathbf{r}t) + V(\mathbf{r}t) \end{align}}
The Schrödinger equation is then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} i\hbar \frac{\partial\psi (\mathbf{r}t)}{\partial t}=\left[\frac{[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A(\mathbf{r}t)]^{2}}{2m}+e\phi (\mathbf{r}t) + V(\mathbf{r}t) \right]\psi \end{align}}
Since a gauge transformation
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} A'_{\mu}=A_{\mu}-\partial_{\mu} \chi , \end{align}}
left invariant the E&M fields, we expect that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^{2}} which is an observable it is also gauge independent. Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^{2}} is independent of the phase choice, we can relate this phase with the E&M gauge transformation. In other words, the phase transformation with E&M transformation must leave Schrödinger equation invariant. This phase transformation is given by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \psi'=e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi(\mathbf{r}t)}\psi \end{align}}
Let's see this in detail. We want to see if:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} i\hbar \frac{\partial\psi ' (\mathbf{r}t)}{\partial t}=\left[\frac{[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A'(\mathbf{r}t)]^{2}}{2m}+e\phi '(\mathbf{r}t) + V(\mathbf{r}t) \right]\psi ' = (no\; prime) \end{align}}
Let's put the transformations:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \psi'&=e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi(\mathbf{r}t)}\psi \\ A'&=A+\nabla \chi \\ \phi '&=\phi-\frac{1}{c}\frac{\partial\chi }{\partial t} \end{align}}
Replacing
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} i\hbar \left[\frac{ie}{\hbar c} \frac{\partial \chi}{\partial t} e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\psi + e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi} \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} \right] &= \left[\frac{[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A']^{2}}{2m}+e\phi -\frac{e}{c} \frac{\partial \chi}{\partial t} + V \right]e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\psi\\ i\hbar e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi} \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A']^{2}}{2m}+e\phi + V \right]e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\left[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A'\right]^{2}e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi} +e\phi + V \right]\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\left[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A'\right]e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A']e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi} +e\phi + V \right]\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} \left(e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\left[\mathbf{p}-\frac{e}{c}A'\right]e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\right) ^{2} +e\phi + V \right]\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} \left(e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\left[\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{e}{c}A-\frac{e}{c}\nabla \chi\right]e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\right) ^{2} +e\phi + V \right]\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} \left(e^{-i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}e^{i\frac{e}{\hbar c}\chi}\left[\frac{\hbar}{i} \frac{ie}{\hbar c}\nabla \chi + \frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{e}{c}A-\frac{e}{c}\nabla \chi\right]\right) ^{2} +e\phi + V \right]\psi\\ i\hbar \frac{\partial \psi}{\partial t} &= \left[\frac{1}{2m} \left(\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{e}{c}A \right) ^{2} +e\phi + V \right]\psi = (no\; prime)_{ \blacksquare}\\ \end{align}}
Finally let's write the Hamiltonian in the following way
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}=\underbrace{\frac{\mathbf{p}}{2m}+V}_{\mathbf{H}_{o}} \underbrace{-\frac{e}{2mc}\left(\mathbf{p}A+ A\mathbf{p} \right)+\frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}}A^{2}+e\phi}_{\mathbf{H}_{int}} \end{align}}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{o}} is the Hamiltonian without external fields (say hydrogen atom) and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{int}} is the interaction part with the radiation.
Hamiltonian of Multiple Particles in Presence of Radiation
If we have a system of N particles we have the following hamiltonian
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}=\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{\left[\mathbf{p}_{i}-\frac{e_{i}}{c}\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)\right]^{2}}{2m_{i}} +\sum_{i=1}^N e_{i}\phi(\mathbf{r}_{i},t) + V(\mathbf{r}_{1}...\mathbf{r}_{N}) \end{align}}
Let's asume all particles having same mass and same charge. Then we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}&=\sum_{i=1}^N \left[\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{2m}-\frac{e_{i}}{2mc}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)+\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t) \mathbf{p}_{i} \right) + \frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)^{2}\right] +e\sum_{i=1}^N \phi(\mathbf{r}_{i},t) + V(\mathbf{r}_{1}...\mathbf{r}_{N})\\ \mathbf{H}&=\underbrace{\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{2m} + V(\mathbf{r}_{1}...\mathbf{r}_{N})}_{H_{o}} +\sum_{i=1}^N -\frac{e}{2mc}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)+\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t) \mathbf{p}_{i} \right) +\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)^{2} +e\sum_{i=1}^N \phi(\mathbf{r}_{i},t) \end{align}}
Using delta function operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})} we can write
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)&=\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)\\ \phi(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)&=\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \phi(\mathbf{r},t)\\ \end{align}}
Then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}&=\mathbf{H}_{o} +\sum_{i=1}^N -\frac{e}{2mc}\left(\mathbf{p}_{i} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)+\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t) \mathbf{p}_{i} \right)\\ &\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;+\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)^{2} +e\sum_{i=1}^N \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \phi(\mathbf{r},t)\\ &=\mathbf{H}_{o} -\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\frac{e}{c}\underbrace{\left[ \frac{1}{2}\sum_{i=1}^N \left[\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m} \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})+\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m} \right]\right]}_{\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)\\ &\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;+\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}} \underbrace{\left[ \sum_{i=1}^N \ \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \right]}_{\rho (\mathbf{r})}\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)^{2} +e\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \underbrace{\left[\sum_{i=1}^N \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) \right]}_{\rho (\mathbf{r})} \phi(\mathbf{r},t)\\ &=\mathbf{H}_{o} +\underbrace{\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \left[-\frac{e}{c} \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)+\frac{e^{2}}{2mc^{2}} \rho (\mathbf{r}) \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)^{2} +e\rho (\mathbf{r})\phi(\mathbf{r},t)\right]}_{\mathbf{H}_{int}}\\ &=\mathbf{H}_{o}+\mathbf{H}_{int}\\ \end{align}}
COMMENTS
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \rho (\mathbf{r})=\sum_{i=1}^N \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})} can be interpreted as density of particles operator.
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})}
is called paramagnetic current. It is just a piece of the total current Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J(\mathbf{r})}
. Explicitly we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}(\mathbf{r})&=\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{1}{2}\left[v_{i}(\mathbf{p}_{i},\mathbf{r}_{i})\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) + \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})v_{i}(\mathbf{p}_{i},\mathbf{r}_{i}) \right]\;\;\;\leftarrow\;\;\;v_{i}(\mathbf{p}_{i},\mathbf{r}_{i})=\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m}-\frac{e}{mc}\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)\\ &=\sum_{i=1}^N \frac{1}{2}\left[\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m}\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i}) + \delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m}-\frac{2e}{mc} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})\right]\\ &=\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})-\frac{e}{mc}\sum_{i=1}^N \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})\;\;\;\leftarrow\;\;\;\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r}_{i},t)\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})=\mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)\delta (\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})\\ &=\underbrace{\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})}_{paramagnetic}\underbrace{-\frac{e}{mc} \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t) \rho (\mathbf{r})}_{diamagnetic} \end{align}}
Light Absorption and Induced Emmission
Generally for atomic fields Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})\cdot \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)>>\rho \mathbf{A}^{2}} . Using the transverse gauge we can proximate the interaction Hamiltonian as
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{int}= \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \left[-\frac{e}{c} \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})\cdot \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)\right] }
Let's write Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A}(\mathbf{r},t)} using the Fourier expansion as described above:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{H}_{int}&=- \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \left[\frac{e}{c} \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r}) \cdot \sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar c^{2}}{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}}}\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}\frac{e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} \frac{e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}}{\sqrt{V}}\right]\right]\\ &=-\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}V}}\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})\cdot \left[ \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger} \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{-i(\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}-\omega t)}\right]\\ &=-\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}V}} \left[ \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\underbrace{\left[\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \right]}_{\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{-\omega t}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\underbrace{\left[\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \right]}_{\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{\omega t}\right]\\ &=-\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}V}} \left[ \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{-\omega t}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{\omega t}\right]\\ \end{align}}
Where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{j}_{\mp\mathbf{k}} &=\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\; \frac{1}{2}\sum_{i} \left[\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\delta(\boldsymbol{r}-\boldsymbol{r_{i}})+\delta(\boldsymbol{r}-\boldsymbol{r_{i}})\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\right] e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i} \left[\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\left(\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\delta(\boldsymbol{r}-\boldsymbol{r_{i}})e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\right)+\left(\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\delta(\boldsymbol{r}-\boldsymbol{r_{i}})e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \right) \frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\right] \\ &=\frac{1}{2m} \sum_{i} \left[\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}+e^{\pm i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\right]\\ \end{align}}
Let's use golden rule to calculate transition rates for this time-dependent interaction. The evolution of the state in first approximation is
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |\psi(t)\rangle = |I\rangle+\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int^{t}_{t_{o}}dt'\;e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{o}t'}\mathbf{H}_{int}e^{\eta t'}e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{o}t'}|I\rangle \end{align}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |I\rangle} is the initial state and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{\eta t'}} is the usual slow "switch" factor. The transition amplitude to a state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |F\rangle} is
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle F|\psi(t)\rangle = \langle F|I\rangle+\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int^{t}_{t_{o}}dt'\;\langle F|e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{o}t'}\mathbf{H}_{int}e^{\eta t'}e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{H}_{o}t'}|I\rangle \end{align}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |F\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |I\rangle} are eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{o}} . Then we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle F|\psi(t)\rangle &=\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int^{t}_{t_{o}}dt'\;e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o})+\eta ]t'}\langle F|\mathbf{H}_{int}|I\rangle\\ &=\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int^{t}_{t_{o}}dt'\;e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o})+\eta ]t'}\langle F| -\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega_{\mathbf{k}}V}}\cdot \left[ \mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}e^{-\omega t'}+\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*} e^{\omega t'}\right]|I\rangle\\ &=\frac{-1}{i\hbar}\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V}} \left[ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle \int^{t}_{t_{o}=\infin}dt'\;e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t'} \right]+ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle \int^{t}_{t_{o}=\infin}dt'\;e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t'} \right] \right]\\ &=\frac{-1}{i\hbar}\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V}} \left[ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle \frac{e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )+\eta } \right]+ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle \frac{e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )+\eta } \right] \right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e\sqrt{\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V}} \left[ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle \frac{e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )-i\eta \hbar } \right]+ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle \frac{e^{[\frac{i}{\hbar}(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )+\eta ]t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )-i\eta\hbar } \right] \right]\\ \end{align}}
The transition probability is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} P_{0 \rightarrow n}&=|\langle F|\psi(t)\rangle|^{2}\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e^{2}\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V} \left[ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle|^{2} \frac{e^{2 \eta t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta^{2} \hbar^{2} } \right]+ \left[\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle \frac{e^{2 \eta t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta^{2} \hbar^{2}} \right] \right]\\ \end{align}}
Where all oscillatory terms have been averaged to zero. Taking a time derivative we obtain the transition rate
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Gamma_{0 \rightarrow n}&=\frac{dP_{0 \rightarrow n}}{dt}\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e^{2}\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V} \left[ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle|^{2} \frac{2 \eta e^{2 \eta t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta^{2} \hbar^{2} } \right]+ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle |^{2} \frac{2 \eta e^{2 \eta t}}{(E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta^{2} \hbar^{2}} \right] \right]\\ &\overset{\underset{\mathrm{\eta \rightarrow 0 }}{}}{=}\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} e^{2}\frac{2\pi \hbar }{\omega V} \left[ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle|^{2} \frac{2\pi}{\hbar}\delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \right]+ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle |^{2} \frac{2\pi}{\hbar}\delta (E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega) \right] \right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V} \left[ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \right]+ \left[|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega) \right] \right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \left[ \underbrace{ \left[\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \right] }_{\Gamma^{abs}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} } + \underbrace{ \left[\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}+\hbar \omega) \right] }_{\Gamma^{ind.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} } \right]\\ &=\sum_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \left[\Gamma^{abs}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+ \Gamma^{ind.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\right]\\ \end{align}}
The above equation says that the transition rate between two states is composed by two possibilities: absorption Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma^{abs}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}} or induced emission Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma^{ind.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}} . Let's analyze the matrix elements between states.
Absorption
Let's suppose that initial and final states are:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |I\rangle&=|o\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle \\ |F\rangle&=|n\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {|o\rangle, |n\rangle}} are the initial and final states of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{0}} (say hydrogen atom) with energies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{0}<E_{n}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {|N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle, |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle}} are the initial and final states of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{rad}} (the vacuum).
The matrix element of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma^{abs}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}} isgiven by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|I\rangle &=\langle n|\otimes \langle N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...|\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}\right]|0\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle\\ &=\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle \langle N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle\\ &=\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle \langle M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\rangle\\ &=\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}}\langle M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}-1\rangle\\ &=\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}}\delta_{M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}-1}\\ \end{align}}
The last shows how in the absorption process, the system Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{int}} absorbs a single photon from the radiation. Namely the final state is given by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |F\rangle&=|n\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}-1,...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
Finally we can write the transition rate absorption as following
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Gamma^{abs}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} &=\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}}|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega)\\ &=\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle n|\mathbf{j}_{-\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}|0\rangle |^{2}N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \end{align}}
Induced Emission
Let's suppose that initial and final states are:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |I\rangle&=|n\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle \\ |F\rangle&=|0\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
Where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {|n\rangle, |0\rangle}} are the initial and final states of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{0}} (say hydrogen atom) with energies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{0}<E_{n}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {|N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle, |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle}} are the initial and final states of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{rad}} (the vacuum).
The matrix element of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma^{ind.em}_{0 \rightarrow n;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}} isgiven by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle F|\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|I\rangle &=\langle 0|\otimes \langle N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...|\left[\mathbf{a}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\right]|n\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle\\ &=\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle \langle N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...|\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...\rangle\\ &=\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle \langle M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|\mathbf{a}^{\dagger}_{\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\rangle\\ &=\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1}\langle M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}|N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1\rangle\\ &=\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1}\delta_{M_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}},N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1}\\ \end{align}}
The last shows how in the emmision process, the system Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{H}_{int}} release a single photon from the radiation. Namely the final state is given by:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |F\rangle&=|0\rangle \otimes |N_{1\boldsymbol{\lambda}},...,N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1,...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
Finally we can write the transition rate absorption as following
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Gamma^{ind.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} &=\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle \sqrt{N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1}|^{2} \delta (E_{0}-E_{n}+\hbar \omega)\\ &=\frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle |^{2} (N_{K\boldsymbol{\lambda}}+1) \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \end{align}}
Important Phenomena: Spontaneous Emission
Let's suppose that initial is a single Hydrogen atom in the 2P state in the vacuum (and nothing else!!!). The state can be written as
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |I\rangle&=|2P\rangle \otimes |0,...,0,...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
According to induced emission, there could be a process in which the final state is:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} |F\rangle&=|1S\rangle \otimes |0,...,1,...\rangle \\ \end{align}}
Where a single photon has been emitted without any external perturbation. This is emission process is called Spontaneous emission.For a experimental observation of a Lamb-like shift in a solid state setup see Science 322, 1357 (2008). DOI: 10.1126/science.1164482.
Einstein's Model of Absorption and Induced Emmision
Let's use Statistical Mechanics to study a cavity with radiation. For this we need to use Plank distribution:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle N_{\boldsymbol{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\rangle=\frac{1}{e^{\frac{\hbar c k}{K_{B}T}}-1} \end{align}}
This is just the occupation number of the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}} . Let's suppose the following situation:
- Our cavity is made up with atoms with two quantum levels with energies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{n}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{0}} such that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{n}>E_{0}} .
- The walls are emitting and absorbing radiation (Thermal Radiation) such that system is at equilibrium. Since there is just two levels, the photons emitted by atoms must have energy equal to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{n}-E_{0}} .
The Boltzmann distribution tells us that the probabilities to find atoms at energies Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{n}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{0}} are respectively
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} P_{n}=\frac{1}{Q}e^{-\frac{E_{n}}{K_{B}T}}\\ P_{0}=\frac{1}{Q}e^{-\frac{E_{0}}{K_{B}T}}\\ \end{align}}
Let's call <N> the number of photons at equilibrium. At equilibrium we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} 0&=\frac{dN}{dt}\\ 0&=\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{abs}+\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{ind.em} \end{align}}
It is natural to express the absorption and emission rate as:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{abs}&=-BNP_{0}\\ \left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{ind.em}&=BNP_{n} \end{align}}
Where B is some constant. Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_{n}<P_{0}} we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left|\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)\right|_{abs}>\left|\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)\right|_{ind.em}}
This means that eventually all photons will be absorbed and then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle N \rangle =0} . This of course is not a physical situation. Einstein realized that There is another kind of process of emission that balances the rates in such way that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle N \rangle \ne 0} . This emission is precisely the spontaneous emission and can be written as
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{spon.em}&=AP_{n} \end{align}}
Then we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} 0&=\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{abs}+\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{ind.em}+\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{spon.em}\\ 0&=-BNP_{0}+BNP_{n}+AP_{n}\\ \end{align}}
And solving for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A } we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} A&=B \langle N \rangle \left(e^{\frac{E_{n}-E_{0}}{K_{B}T}}-1\right)\\ &=B \langle N \rangle \frac{1}{ \langle N \rangle }\\ &=B \end{align}}
As conclusion we obtain for the emission rate the follwing:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{emission}&=\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{ind.em}+\left(\frac{dN}{dt}\right)_{spon.em}\\ &=BNP_{n}+AP_{n}\\ &=BP_{n}(N+1)\\ \end{align}}
Notice that the factor Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (N+1)} matches with our previous result.
Details of Spontaneous Emission
Power of the emitted light
Using our previous result for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma^{spon.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}} , we can calculate the power Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle dP} of the light with polarization Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{\lambda}} per unit of solid angle that the spontaneus emission produce:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} dP&=\sum_{k}\hbar \omega \;\Gamma^{spon.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\\ &=d\Omega V \int \frac{dk\;k^{2}}{(2\pi)^{3}}\;\hbar \omega \;\Gamma^{spon.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\\ &=d\Omega V \int \frac{d\omega\;\omega^{2}}{(2\pi c)^{3}}\;\hbar \omega \;\Gamma^{spon.em}_{n \rightarrow 0;\mathbf{k}\boldsymbol{\lambda}}\\ \end{align} }
Then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{dP}{d\Omega} &=V \int\frac{d\omega\;\omega^{2}}{(2\pi c)^{3}}\;\hbar \omega \left[ \frac{4\pi^{2} e^{2} }{\omega V}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle|^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega) \right]\\ &=\frac{e^{2}\hbar}{2\pi c^{3}}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle|^{2}\int d\omega\;\omega^{2} \delta (E_{n}-E_{o}-\hbar \omega)\\ &=\frac{e^{2}\hbar}{2\pi c^{3}}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle|^{2}\frac{(E_{n}-E_{o})^{2}}{\hbar^{3}}\;\;\;\leftarrow\;\;\;\omega_{n,0}=E_{n}-E_{0}\\ &=\frac{e^{2}\omega^{2}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle|^{2}\\ \end{align} }
Conservation of Momentum
Consider a matter in the eigenstate of the momentum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar q_{n}} . Suppose that it make a transition to eigenstate with momentum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar q_{0}} via spontaneus emission. The momentum must conserve. Therefore we have a process where:
Initial MomentaFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \;\;\;\rightarrow\;\;\;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}matter& \rightarrow \hbar q_{n}\\vacuum& \rightarrow 0\end{align}}
Final MomentaFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \;\;\;\rightarrow\;\;\;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}matter& \rightarrow \hbar q_{0}\\vacuum& \rightarrow \hbar q_{n}-\hbar q_{0}\end{align}}
Let's calculate the matrix element Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle}
for two cases.
Case 1: Single free charged particle
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\frac{1}{2} \left[\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}e^{- i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}+e^{- i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}\frac{\boldsymbol{p_{i}}}{m}\right]|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{1}{2}\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}| \left[\frac{\hbar \mathbf{q_{0}}}{m}e^{- i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}+e^{- i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}\frac{\hbar \mathbf{q_{n}}}{m}\right]|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\hbar (\mathbf{q_{0}}+\mathbf{q_{n}})}{2m}\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}| e^{- i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\hbar (\mathbf{q_{0}}+\mathbf{q_{n}})}{2m} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}_{i} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{r}_{i}\rangle \langle \mathbf{r}_{i}| e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\hbar (\mathbf{q_{0}}+\mathbf{q_{n}})}{2m} \int d^{3}\mathbf{r}_{i} e^{-i\mathbf{q_{0}}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}} e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}} e^{i\mathbf{q_{n}}\cdot\mathbf{r}_{i}}\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\hbar (\mathbf{q_{0}}+\mathbf{q_{n}})}{2m} \delta(\mathbf{q_{n}}-\mathbf{q_{0}}-\mathbf{k}) \\ \end{align} }
This result is very interesting!!!. It says that the emitted light must be
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \hbar \mathbf{k} =\hbar \mathbf{q_{n}} -\hbar \mathbf{q_{0}} \end{align} }
However this is impossible from the point of view of conservation of energy:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \hbar c k =\frac{\hbar q^{2}_{n}}{2m}-\frac{\hbar q^{2}_{0}}{2m} \end{align} }
This means that a single charged particle can not make transitions. So a single charged particle doesn't see the vacuum fluctuations.
Case 2: General Case (System of particles)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\int d^{3}\mathbf{r} j(\mathbf{r}) e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|j(\mathbf{r})|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ \end{align} }
We can use the total momentum of the system Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{P}=\sum_{i}\mathbf{p}_{i}} as generator of translations for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{r}} . So that we can write
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} j(\mathbf{r})=e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{P}\cdot\mathbf{r}}j(\mathbf{r}=0)e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{P}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \end{align} }
Then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|j(\mathbf{r})|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{P}\cdot\mathbf{r}}j(0)e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathbf{P}\cdot\mathbf{r}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r} \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|e^{-i\mathbf{q_{0}}\cdot\mathbf{r}}j(0)e^{i\mathbf{q_{n}}\cdot\mathbf{r}}|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|j(0)|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\int d^{3}\;\mathbf{r} e^{i\mathbf{q_{n}}\cdot\mathbf{r}} e^{-i\mathbf{q_{0}}\cdot\mathbf{r}} e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}\\ &=\boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}\cdot \langle \mathbf{q_{0}}|j(0)|\mathbf{q_{n}}\rangle\delta(\mathbf{q_{n}}-\mathbf{q_{0}}-\mathbf{k})\\ \end{align} }
The last shows that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \hbar \mathbf{k} =\hbar \mathbf{q_{n}} -\hbar \mathbf{q_{0}} \end{align} }
Electric Dipole Transitions
Let's consider a nucleus (say hydrogen atom) well localized in space. Typically the wave length of the emitted light is much bigger than electron's orbit around nucleus (say Bohr radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a_{B}} ). This means that:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \;\;\;\;\lambda >>> a_{B}\;\;\;\;\leftrightarrow\;\;\;\;\;\mathbf{k}<<<1}
The matrix element is then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle &=\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}|n\rangle\\ &=\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \langle 0|\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})|n\rangle\\ &=\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;e^{-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} \langle 0|\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})|n\rangle\\ &=\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\left[1-i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}+...\right] \langle 0|\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\langle 0|\mathbf{j}(\mathbf{r})|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\int d^{3}\mathbf{r}\;\langle 0|\frac{1}{2}\left[\sum_{i} \frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m} \delta(\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})+\delta(\mathbf{r}-\mathbf{r}_{i})\frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m}\right]|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle 0|\sum_{i} \frac{\mathbf{p}_{i}}{m}|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\langle 0|\frac{\mathbf{P}}{m}|n\rangle\;\;\;\;\;\;\; \leftarrow\;\;\;\;\;\frac{\mathbf{P}}{m}=\frac{[\mathbf{R},\mathbf{H}_{0}]}{i\hbar}\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{1}{i\hbar}\langle 0|[\mathbf{R}\cdot \mathbf{H}_{0}-\mathbf{H}_{0}\cdot\mathbf{R}]|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{1}{i\hbar}\langle 0|[\mathbf{R}E_{n}-E_{0}\mathbf{R}]|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{E_{n}-E_{0}}{i\hbar}\langle 0|\mathbf{R}|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\hbar\omega_{n,0}}{i\hbar}\langle 0|\mathbf{R}|n\rangle\\ &\cong\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\cdot\frac{\omega_{n,0}}{i}\underbrace{\langle 0|\mathbf{R}|n\rangle}_{\mathbf{d}_{0,n}}\\ &\cong\frac{\omega_{n,0}}{i}\mathbf{d}_{0,n}\cdot\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\\ \end{align}}
Notice that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{d}_{0,n}} is the off diagonal elements of the dipole moment operator. The power per unit of solid angle for a given polarization Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{dP}{d\Omega} &=\frac{e^{2}\omega^{2}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}|\langle 0|\mathbf{j}_{\mathbf{k}}\cdot \boldsymbol{\lambda}^{*}|n\rangle|^{2}\\ &\cong\frac{e^{2}\omega^{2}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}\left|\frac{\omega_{n,0}}{i}\mathbf{d}_{0,n}\cdot\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\right|^{2}\\ &\cong\frac{e^{2}\omega^{4}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}\left|\mathbf{d}_{0,n}\cdot\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\right|^{2}\\ \end{align}}
Selection Rules
Let's assume that initial and final states are eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{L}^{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{L}_{z}} . Using commutation relationships we can obtain the following selection rules the vector Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{d}_{0,n}} :
1. Selection Rules for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m}
1.1Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{z}]=0} . From this we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} 0&=\langle l' m' |[\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{z}]| l m \rangle\\ &=\langle l' m' |\mathbf{L}_{z} \mathbf{R}_{z} - \mathbf{L}_{z}\mathbf{R}_{z}| l m \rangle\\ &=\hbar(m'-m)\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{z}| l m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
This means that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{z}| l m \rangle=0} if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m'-m\neq 0} .
1.2
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{x}]=i\hbar\mathbf{R}_{y}}
. From this we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle l' m' |[\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{x}] |l m \rangle&=i\hbar \langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{y}] l m \rangle\\ (m'-m)\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{x}| l m \rangle&=i\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{y}] l m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{y}]=-i\hbar\mathbf{R}_{x}}
. From this we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle l' m' |[\mathbf{L}_{z},\mathbf{R}_{y}] |l m \rangle&=-i\hbar \langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{x}] l m \rangle\\ (m'-m)\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{y}| l m \rangle&=-i\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{x}] l m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
Combining
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} (m'-m)^{2}\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x}|l m \rangle=\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x}|l m \rangle\\ (m'-m)^{2}\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{y}|l m \rangle=\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{y}|l m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
From here we see that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} (m'-m)^{2}\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x,y}|l m \rangle&=\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x,y}|l m \rangle\\ ((m'-m)^{2}-1)\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x,y}|l m \rangle &=0\\ \end{align}}
This means that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}_{x,y}|l m \rangle=0} if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [(m'-m)^{2}-1]\neq0 \;\;\;\;\rightarrow\;\;\;\;m'\neq m\pm 1}
2. Selection Rule for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l}
Consider the following commutator proposed by Dirac
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\mathbf{L}^{2},[\mathbf{L}^{2},\mathbf{R}]]=2\hbar ^{2}(\mathbf{R}\mathbf{L}^{2}+\mathbf{L}^{2}\mathbf{R})}
After some algebra we can see that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (l'+l)(l'+l+2)((l'-l)^{2}-1)\langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}|l m \rangle=0}
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l} is non negative Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (l'+l+2)\neq0\;\;\;\;\forall\;\;\;\;l',l } . There are two possibilities:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}|l m \rangle=0} if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (l'+l)\neq 0} . However for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l'=l=0} , which corresponds to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle 0 0|\mathbf{R}|0 0 \rangle=0} . This possibility is trivial and it doesn't say anything new.
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle l' m'|\mathbf{R}|l m \rangle=0} if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ((l'-l)^{2}-1)\neq 0\;\;\;\;\rightarrow\;\;\;\;l'\neq l\pm 1}
Summary
If the initial and final states are eigenstates for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{L}^{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{L}_{z}} then the possible transitions that can occur in the dipole approximation are
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} l'&= l\pm 1\\ m'&= m\\ m'&= m\pm 1\\ \end{align}}
Example: Transitions Among Levels n=1,2,3 of Hydrogen Atom
Let's consider the levels n=1,2,3 of Hydrogen Atom. The possible transitions to the state 1S according to the sharp selection rules are the following
The possibles transitions to the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2p_0 }
are the following
Power & Polarization of Emitted Light
Case Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m'=m} : In this case the selection rules tells as that:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{d}_{0,n}= \langle 0|\mathbf{R}|n\rangle= \begin{pmatrix} \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{x}|n\rangle \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{y}|n\rangle \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{z}|n\rangle \\ \end{pmatrix} =\begin{pmatrix} 0 \\ 0 \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{z}|n\rangle \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
Then we can say
- The light is always plane polarized in the plane defined by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{k}} .
- The power is given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{dP}{d\Omega} &\cong\frac{e^{2}\omega^{4}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}\left|\mathbf{d}_{0,n}\cdot\mathbf{\lambda}^{*}\right|^{2}\\ &\cong\frac{e^{2}\omega^{4}_{n,0}}{2\pi c^{3}}\left|\langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{z}|n\rangle\right|^{2}\;sin^{2}\theta\\ \end{align}}
Case Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m'=m\pm 1} : In this case the selection rules tells as that:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{d}_{0,n}= \langle 0|\mathbf{R}|n\rangle= \begin{pmatrix} \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{x}|n\rangle \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{y}|n\rangle \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{z}|n\rangle \\ \end{pmatrix} =\begin{pmatrix} \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{x}|n\rangle \\ \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{y}|n\rangle \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
From the previews result we have
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mp \langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{y}| l m \rangle&=-i\langle l' m' |\mathbf{R}_{x}] l m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
Then
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{d}_{0,n}= \langle 0|\mathbf{R}_{x}|n\rangle \begin{pmatrix} 1 \\ \pm i \\ 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
Then we can say
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{d}_{0,n}} rest at the XY plane. The polarization of the emitted light is circular.
- Lets put a detector to see the light coming toward positive Z axis. Since right circular polarized light has angular momentum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar}
while negative circular polarized light has angular momentumFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\hbar}
we can state the following:
- If we see a circular polarized light then by conservation of angular momentum we know that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \hbar m=\hbar m' + \hbar^{photon}\;\;\;\;\;\rightarrow \;\;\;\;\; m'-m=-1 \end{align}}
- If we see a negative circular polarized light then by conservation of angular momentum we know that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \hbar m=\hbar m' - \hbar^{photon}\;\;\;\;\;\rightarrow \;\;\;\;\; m'-m=1 \end{align}}
Scattering of Light
( Notes and LaTex code, courtesy of Dr. Oskar Vafek)
We can analyze how a charged system interact with photons and scatter it. The problem of light scattering can be considered as a transition from initial state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\chi_0\rangle=|0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle} to a final state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1\rangle } . For this transition we can calculate the transition amplitude. Let us deal with some basics first. First of all we can write the Schrodinger equation for an electron in a potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V(r)} interacting with quantized EM radiation as:Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial t}|\psi\rangle =\mathcal{H}|\psi\rangle }
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}=\frac{1}{2m}\left(p-\frac{e}{c}A(r)\right)^2+V(r)+\sum_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hbar\omega_{k}\left(\hat{a}_{k\hat{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\hat{a}_{k\hat{\hat{\lambda}}}+\frac{1}{2}\right) }
We are considering the transverse gauge, in which the vector potential operator can be defined as: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\hat{A}(r)}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}\sum_{k,\lambda}\left[\sqrt{\frac{2\pi\hbar}{\omega_{k}}}c\;\left(\hat{a}_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hat{\lambda}e^{ik\cdot r}+\hat{a}^{\dagger}_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hat{\lambda^*}e^{-ik\cdot r}\right)\right]}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\hat{a}_{k\hat{\lambda}},\hat{a}_{k'\hat{\lambda'}}^{\dagger}]=\delta_{kk'}\delta_{\hat{\lambda}\hat{\lambda'}};\;\;\;\; [\hat{a}_{k\hat{\lambda}},\hat{a}_{k'\hat{\lambda'}}]=0 }
Let us define,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}=\mathcal{H}_0+\mathcal{H}'}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}_0=\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0+\mathcal{H}^{(rad)}_0=\left(\frac{p^2}{2m}+V(r)\right)+\sum_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hbar\omega_{k}\left(\hat{a}_{k\hat{\lambda}}^{\dagger}\hat{a}_{k\hat{\hat{\lambda}}}+\frac{1}{2}\right)}
andFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}'=-\frac{e}{mc}\mathbf{A(r)}\cdot p+\frac{e^2}{2mc^2}\mathbf{A(r)}\cdot \mathbf{A(r)}}
We can use the Dirac picture to represent the wavefunction as: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi(t)\rangle=e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}_0t}|\chi(t)\rangle }Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar\frac{\partial}{\partial t}|\chi\rangle =\mathcal{H}'_I(t)|\chi\rangle =e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}_0t}\mathcal{H}'e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}_0t}|\chi\rangle =e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t}\left(e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(rad)}_0t}\mathcal{H}' e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(rad)}_0t}\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t}|\chi\rangle}
More precisely,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}'_I(t)= e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t}\left(e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(rad)}_0t}\mathcal{H}' e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(rad)}_0t}\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t} =e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t}\left( -\frac{e}{mc}A(r,t)\cdot p+\frac{e^2}{2mc^2}A(r,t)\cdot A(r,t)\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t}}
where the the vector potential operator which is now time dependent can be defined as,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A(r,t)}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}}\sum_{k,\lambda}\left[\sqrt{\frac{2\pi\hbar}{\omega_{k}}}c\;\left(\hat{a}_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hat{\lambda}e^{ik\cdot r-i\omega_{k} t}+\hat{a}^{\dagger}_{k,\hat{\lambda}}\hat{\lambda^*}e^{-ik\cdot r+i\omega_{k}t}\right)\right]}
Using second order time dependent perturbation theory up to to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2^{nd}} order, we can write the wavefunction is Dirac picture as,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\chi(t)\rangle\approx|\chi_0\rangle+\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'\mathcal{H}'_I(t')|\chi_0\rangle+ \frac{1}{(i\hbar)^2}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'\int_{-\infty}^{t'}dt''\mathcal{H}'_I(t')\mathcal{H}'_I(t'')|\chi_0\rangle }
where the perturbation is slowly switched on at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle t=-\infty} .
As mentioned before,we need to calculate the transition probability from
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\chi_0\rangle=|0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle} to the final state
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1\rangle }
Therefore we need to calculate that following transition probability,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C(t)=\langle n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1|\chi(t)\rangle }
Using second order time dependent perturbation theory the probability for such a transition is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C(t)=\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'\langle n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1|\mathcal{H}'_I(t')|0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle +\frac{1}{(i\hbar)^2}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'\int_{-\infty}^{t'}dt''\langle n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1|\mathcal{H}'_I(t')\mathcal{H}'_I(t'')|0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle }
The required transition can be made by term proportional to )(the diamagnetic term)in first order, while term proportional to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{A(r)}} (paramagnetic term) gives non-zero overlap in second order perturbation theory. Therefore we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}C(t)&=\frac{1}{i\hbar}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'\langle n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1| e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t'}\left( \frac{e^2}{2mc^2}\mathbf{A(r},t')\cdot \mathbf{A(r},t')\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t'} |0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle \\ &+ \frac{1}{(i\hbar)^2}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt' \int_{-\infty}^{t'}dt''\langle n;N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1|e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t'}\left( -\frac{e}{mc}A(r,t')\cdot p\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t'}\times\\ &\times e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t''}\left( -\frac{e}{mc}A(r,t'')\cdot p\right)e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\mathcal{H}^{(at)}_0t''} |0;N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle\\ \end{align}}We can ignore the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf r-} dependence in gauge field by using dipole approximation, that is we can say Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{exp}(-iK.r)=1-iK.r }
Let's define Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{C(t)=C_1(t)+C_2(t)}}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}C_1(t) &=\frac{\delta_{n,0}}{i\hbar}\frac{e^2}{2mc^2} \frac{1}{V}\frac{2\pi\hbar c^2}{\sqrt{\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}}\hat{\lambda}\cdot {\hat{\lambda}^{'*}} \langle N_{k,\lambda}-1,N_{k',\lambda'}=1|(a_{k\lambda}a^{\dagger}_{k'\lambda'}+a^{\dagger}_{k'\lambda'}a_{k\lambda}) |N_{k,\lambda},N_{k',\lambda'}=0\rangle \times\\ &\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt'e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0)t'}e^{-i(\omega_{k}-\omega_{k'})t'}e^{2\eta t'}\\ &=\frac{\delta_{n,0}}{i\hbar}\frac{e^2}{m} \frac{1}{V}\frac{2\pi\hbar }{\sqrt{\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}}\hat{\lambda}\cdot {\hat{\lambda}^{'*}}\sqrt{N_{k\lambda}} \times\frac{e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0)t}e^{-i(\omega_{k}-\omega_{k'})t}e^{2\eta t}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0)-i(\omega_{k}-\omega_{k'})+2\eta} \end{align}}
The second order term is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} C_2(t)&= \frac{1}{(i\hbar)^2}\frac{e^2}{m^2c^2}\frac{1}{V}\frac{2\pi\hbar c^2}{\sqrt{\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}}\sqrt{N_{k\lambda}} \sum_{\alpha}\int_{-\infty}^{t}dt' \int_{-\infty}^{t'}dt'' e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_{\alpha})t'}e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}(\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0)t''}\times\\ &\left( \langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}e^{-i\omega_{k}t'}e^{\eta t'}e^{i\omega_{k'}t''}e^{\eta t''}+ \langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}e^{i\omega_{k'}t'}e^{\eta t'}e^{-i\omega_{k}t''}e^{\eta t''}\right)\\ &= \frac{1}{(i\hbar)^2}\frac{e^2}{m^2}\frac{1}{V}\frac{2\pi\hbar}{\sqrt{\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}}\sqrt{N_{k\lambda}} \times\frac{e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-\hbar\omega_{k}\right)t}e^{2\eta t}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-\hbar\omega_{k}-2i\hbar\eta\right)} \times\\ &\sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}\left(\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta\right)}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\frac{i}{\hbar}\left(\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta\right)}\right)\\ \end{align}}
Therefore,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}C(t)&=C_1(t)+C_2(t)\\ &=-\frac{e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-\hbar\omega_{k}\right)t}e^{2\eta t}}{\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-\hbar\omega_{k}-2i\hbar\eta\right)}\frac{\sqrt{N_{k\lambda}}}{V} \frac{2\pi \hbar e^2}{m\sqrt{\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}}\times\\ &\left(\delta_{n,0}\hat{\lambda}\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}-\frac{1}{m} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\right)\\ \end{align}}
The time dependent probability is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}\mathcal{P}(t)&=|C(t)|^2\\ &=\frac{e^{4\eta t}}{\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-\hbar\omega_{k}\right)^2+4\hbar^2\eta^2}\frac{N_{k\lambda}}{V^2} \frac{4\pi^2 \hbar^2 e^4}{m^2\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}\times\\ &\left|\delta_{n,0}\hat{\lambda}\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}-\frac{1}{m} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\right|^2\\ \end{align}}
and the transition rate is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}\Gamma&=\frac{\partial \mathcal{P}(t)}{\partial t}\\ &=\frac{2\pi}{\hbar} \frac{N_{k\lambda}}{V^2} \frac{4\pi^2 \hbar^2 e^4}{m^2\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}\times \delta\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}+\hbar\omega_{k'}\right) \times\\ &\left|\delta_{n,0}\hat{\lambda}\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}-\frac{1}{m} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\right|^2\\ \end{align}}
We observe that, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{i}{\hbar}[\mathcal{H}_0^{(at)},r]=\frac{1}{m}p\;\;\Rightarrow\;\; \langle n| p |\alpha\rangle=\frac{i}{\hbar}m\langle n|[\mathcal{H}_0^{(at)},r] |\alpha\rangle=\frac{i}{\hbar}m(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_{\alpha})\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle }
Taking (as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta\rightarrow 0} ) we get,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}&\frac{1}{m} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ &=\frac{i}{\hbar} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_{\alpha})\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_n+\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{(\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0)\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ &=\frac{i}{\hbar} \sum_{\alpha}\left(-\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}+ \langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}\right)\\ &+i\omega_{k} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_n+\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ &=\delta_{n0}\hat{\lambda}\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}+i\omega_{k} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_n+\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ \end{align}}
where in the second line we have used the energy conserving Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta-} function, giving Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_n+\hbar\omega_{k'}=\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k}} . Using the above commutation relation again we finally find
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}&\frac{1}{m} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| p |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| p |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ &=\delta_{n0}\hat{\lambda}\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}+m\omega_{k}\omega_{k'} \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right)\\ \end{align}}
Therefore
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Gamma =\frac{2\pi}{\hbar} \frac{N_{k\lambda}}{V^2} \frac{4\pi^2 \hbar^2 e^4}{m^2\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}\times \delta\left(\epsilon_n-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}+\hbar\omega_{k'}\right)m^2\omega^2_{k}\omega^2_{k'}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ( \sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n|r|\alpha \rangle \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| r|0\rangle {\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}} {\epsilon_\alpha-\epsilon_0 + \hbar \omega_{k'}-i\hbar \eta} + \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r|0\rangle \hat{\lambda}}{\epsilon_\alpha-\epsilon_0 - \hbar \omega_{k}-i\hbar \eta}\right)}
To get the total transition rate we need to sum over all wavevectors in a solid angle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d\Omega'} . Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}dw\!\!&=\!\!\sum_{k'\in d\Omega'}\Gamma \\&= \frac{2\pi}{\hbar} \frac{d\Omega' \omega^2_{k'}}{8\pi^3c^3\hbar}\frac{N_{k\lambda}}{V} \frac{4\pi^2 \hbar^2 e^4}{m^2\omega_{k}\omega_{k'}}m^2\omega^2_{k}\omega^2_{k'}\left|\sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot {\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot {\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right) \right|^2\\ &=d\Omega'\frac{e^4\omega_{k}\omega^3_{k'}}{c^3}\frac{N_{k\lambda}}{V} \left|\sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot {\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k'}-i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot {\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{\alpha}-\epsilon_0-\hbar\omega_{k}-i\hbar\eta}\right) \right|^2\\\end{align}}where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_n+\hbar\omega_{k'}=\epsilon_0+\hbar\omega_{k}} . Finally the differential cross-section is found by dividing by the photon flux Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{c N_{k\lambda}/V}} to yield
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\sigma}{d\Omega'} =\frac{e^4\omega_{k}\omega^3_{k'}}{c^4} \left|\sum_{\alpha}\left( \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}^{'*}}{\epsilon_{0}-\epsilon_{\alpha}-\hbar\omega_{k'}+i\hbar\eta}+ \frac{\langle n| r |\alpha\rangle \cdot \hat{\lambda}^{'*}\langle \alpha| r |0\rangle\cdot{\hat{\lambda}}}{\epsilon_{0}-\epsilon_{\alpha}+\hbar\omega_{k}+i\hbar\eta}\right) \right|^2}
Therefore the scattering cross-section is inversely proportional to the fourth power of wavelength ( for elastic scattering). This explains why sky is blue since blue light having lower wavelength, gets scattered more.Non-perturbative methods
One of the important method in the approximate determination of the wave function and eigenvalue is the Variational Principle. Variational method is a very general one that it can be used whenever the equations can be put into variational form.Variational principle is the springboard to many numerical computation.
Principle of the Variational Method
Consider a completely arbitrary system with time independent Hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} and we assume that it's entire spectrum is discrete and non-degenerate.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}|{\varphi}_{n}\rangle} =Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}_{n}|{\varphi}_{n}\rangle} ; n = 0,1,2
Let's apply the variational principle to find the ground state of the system.Let Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle } be an arbitrary ket of the system. We can define the expectation value of the Hamiltonian as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle=\frac{\langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle}{\langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle}\qquad \text{(4.1)} }
The variational principle states that,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle\geq \mathcal{E}_0 \qquad \text{(4.2)}}
Since the exact eigenfunctions of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\varphi}\rangle } form a complete set, we can express our arbitrary ket Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle } as a linear combination of the exact wavefunction.Therefore,we haveFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle=\sum_{n} C_n |{\varphi}_n\rangle \qquad \text{(4.3)}}
Multiplying both sides by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}} we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle= \sum_{n} |C_n|^{2}\langle{\varphi}_n|{\varphi}_n\rangle =\sum_{n}|C_n|^{2} \mathcal{E}_n }
However, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}_n \geq \mathcal{E}_0 } . So, we can write the above equation asFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle \leq \mathcal{E}_0 \sum_{n} |C_n|^{2}}
Or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}_0 \leq \frac{ \langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle } {\langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle} \qquad \text{(4.4)}} .
with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle}=\sum_{n} |C_n|^{2}} , thus proving Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.2)}}
Thus Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.2)}} gives an upper bound to the exact ground state energy. For the equality to be applicable in the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.2)}} all coefficients except Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{C}_0} should be zero and then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle } will be the eigenvector of the Hamiltonian and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}_0} the ground state eigenvalue.
Generalization of Variational Principle: The Ritz Theorem.
We claim that the expectation value of the Hamiltonian is stationary in the neighborhood of its discrete eigenvalues. Let us again consider the expectation value of the Hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.1)}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle=\frac{\langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle}{\langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle}}
Here Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle} is considered as a functional of . Let us define the variation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle} such that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi\rangle} goes to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi\rangle +| \delta \psi\rangle } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle | \delta \psi\rangle } is considered to be infinetly small. Let us rewrite Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.1)}} as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle\langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle=\langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle\qquad \text{(4.5)}} .
Differentiating the above relation,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle\delta\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle+\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle[\langle{\psi}|\delta{\psi}\rangle+\langle\delta{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle]=\langle{\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\delta\psi}\rangle+\langle{\delta\psi}|\mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle\qquad \text{(4.6)}}
However, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle} is just a c-number, so we can rewrite Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.6)}} as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi} | {\psi}\rangle\delta\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle =\langle{\psi} | [\mathcal{H}-\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle] | {\delta\psi}\rangle+\langle{\delta\psi} | [\mathcal{H}-\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle]|{\psi}\rangle\qquad \text{(4.7)}} .
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta|\mathcal{H}\rangle=0 } , then the mean value of the Hamiltonian is stationary.Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi} | [\mathcal{H}-\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle] | {\delta\psi}\rangle+\langle{\delta\psi} | [\mathcal{H}-\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle]|{\psi}\rangle=0 } .
Define,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\varphi}\rangle =|[\mathcal{H}-\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle] | {\psi}\rangle \qquad \text{(4.8)}} .
Hence,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.7)}} become
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\varphi}|\delta{\psi}\rangle+ \langle\delta{\varphi}|{\psi}\rangle=0 \qquad \text{(4.9)}} .
We can define the variation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle} asFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\delta{\psi}\rangle=\delta\lambda|\delta{\psi}\rangle} ,
with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} being a small (real) number. Therefore Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad\text{(4.9)}} can be written asFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|{\psi}\rangle \delta\lambda=0 \qquad\text{(4.10)}}
Since the norm is zero, the wave function itself should be zero. Keeping this in mind, if we analyze Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad{(4.8)}} it's clear that we can rewrite it as an eigenvalue problem.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}|{\psi}\rangle=\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle{\psi}\rangle \qquad \text{(4.11)}} .
Finally we can say that expectation value of the Hamiltonian is stationary iff the arbitrary wavefunction Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\psi}\rangle} is actually the eigenvector of the Hamiltonian with the stationary values of the expectation values of the Hamiltonian, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle } being precisely the eigen values of the Hamiltonian.The general method is to find a approximate trial wavefunction that contain one or more parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{\alpha, \beta, \gamma} } . If the expectation value Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle } can be differentiated with respect to these paramters, the extrema of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle } can be found using the following equation.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle}{\partial\alpha}=\frac{\partial\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle}{\partial\beta}=\frac{\partial\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle}{\partial\gamma}=0 }
The absolute minimum of the expectation value of the Hamiltonian obtained by this method correspond to the upper bound on the ground state energy. The other relative, extrema corresponds to excited states.There are many virtues of using the Variational method.Even a poor approximation to the actual wave function can yield an excellent approximation to the actual energy.
Upper Bound on First Excited State
We claim that if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle{\psi}|{\varphi}_0\rangle=0} , then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle \geq \mathcal{E}_1} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}_1} is the energy of the first excited state and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |{\varphi}_0\rangle} is the exact ground state of the Hamiltonian.
From Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad\text{(4.3)}} it is clear that if the above condition is satisfied then, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{C}_0=0 } . Therefore,we can write the expectation value of the hamiltonian as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle =\sum_{n=1} |\mathcal{C}_n|^2\mathcal{E}_n \geq \mathcal{E}_1 \sum_{n=1} \mathcal|{C}_n|^2}
Thus if we can find a suitable trial wavefunction that is orthogonal to the ground state exact wavefunction then by calculating the expectation value of the Hamiltonian, we get an upperbound on the first excited state. The trouble is that we might not know the exact ground state( which is one reason why we implement the variational principle). However if we have a Hamiltonian which is an even function, then the exact ground state will be an even function and hence any odd trial function will be a right candidate.
A Special Case where The Trial Functions form a Subspace
Assume that we choose for the trial kets the set of kets belonging to a vector subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}} . In this case, the variational method reduces to the resolution of the eigenvalue equation of the Hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} inside Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} , and no longer in all of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}} .
To see this, we simply apply the argument of Sec. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \text{4.2}} , limiting it to the kets Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi\rangle} of the subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} . The maxima and minima of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle} , characterized by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle=0} , are obtained when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi\rangle} is an eigen vector of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} . The corresponding eigenvalues constitute the variational method approximation for the true eigenvalues of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}} .
We stress the fact that the restriction of the eigenvalue equation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} to a subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} of the state space Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}} can considerably simplify its solution. However, if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} is badly chosen, it can also yield results which are rather far from true eigenvalues and eigenvectors of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}} in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{E}} . The subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{F}} must therefore be chosen so as to simplify the problem enough to make it soluble, without too greatly altering the physical reality. In certain cases, it is possible to reduce the study of a complex system to that of a two-level system, or at least, to that of a system of a limited number of levels. Another important example of this procedure is the method of the linear combination of atomic orbitals, widely used in molecular physics. This method consists essentially of the determination of the wave functions of electrons in a molecule in the form of linear combinations of the eigenfunctions associated with the various atoms which constitute the molecule, treated as if they were isolated. It therefore limits the search for the molecular states to a subspace chosen using physical criteria. Similarly, in complement, we shall choose as a trial wave function for an electron in a solid a linear combination of atomic orbitals relative to the various ions which constitute this solid.
Applications of Variational Method
Harmonic Potential
Armed with the variational method let us apply it first to a simple Hamiltonian. Consider the following Hamiltonian with harmonic potential whose eigenvalues and eigenfunctions are known exactly. We will determine how close we can get with a suitable trial function.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{H}=-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+\frac{1}{2}mw^2x^2 \qquad\qquad\text{(4.12)}}
The above hamiltonian is even therefore, to find the ground state upper bound we need to use an even trial function. Let us consider the following state vector with one parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{\alpha}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(x)=A e^{-\alpha x^2} :\alpha>0 \qquad\qquad\text{(4.13)}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A \,\!} is the normalization constant.
Let us normalize the trial wavefunction to be unity
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1=\langle\psi|\psi\rangle= |A|^2\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-2\alpha x^2} dx =|A|^2\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2\alpha}} \Rightarrow A=\left[ \frac{2\alpha}{\pi}\right] ^{1/4}\qquad\text{(4.14)}}
While, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle= |A|^2 \int_{-\infty}^{\infty} dx e^{-\alpha x^2}\left[ -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+\frac{1}{2}mw^2x^2 \right] e^{-\alpha x^2}=\frac{\hbar^2\alpha}{2m}+\frac{mw^2}{8\alpha}\qquad\text{(4.15)}}Minimizing the expectation value with respect to the parameter we get,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle}{d\alpha}= \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}-\frac{mw^2}{8\alpha^2}=0 \Rightarrow \alpha=\frac{mw}{2\hbar}}
Putting this value back in the expectation value we getFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \mathcal{H}\rangle_{min}=\frac{1}{2}\hbar w}
Due to our judicious selection of trial wavefunction, we were able to find the exact ground state energy. If we want to find the first excited state, a suitable candidate for trial wavefunction would be an odd function.
Ground State of Helium
Let us use variational principle to determine the ground state energy of Helium. Helium has two electrons and two protons. For simplicity, we ignore the presence of neutrons.
We can write the Hamiltonian can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}(\boldsymbol\nabla_1^2+\boldsymbol \nabla_2^2)- \frac{Ze^2}{|r_1|} - \frac{Ze^2}{|r_2|}+\frac{e^2}{|\boldsymbol {r}_1-\boldsymbol {r}_2|} }
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf {r_1,r_2} } are the coordinates of the two electrons.If we ignore the mutual interaction term, then the wavefunction will be the product of the two individual electron wavefunction which in this case is that of a hydrogen like atom. Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal \psi(\boldsymbol {r_1,r_2})=\psi_{100}( \boldsymbol r_1)\psi_{100}(\boldsymbol r_2)\qquad \text{(4.16)}}where we ignored spin and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_{100}=(\frac{Z^3}{\pi{a_0}^3})^{1/2}exp(-{\frac{Z r}{a_0}})}
Therefore we can write
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal \psi_{100}\boldsymbol{(r_1,r_2)}=\frac{Z^3}{\pi{a_0}^3}exp\left(-{\frac{Z (r_1+r_2)}{a_0}}\right)\qquad \text{(4.17)}}
We can write the ground state energy for this situation with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf Z=2} as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E= 2 \left( -\frac{m(2e^2)^2}{2\hbar^2}\right)=-8 Rd \simeq -108.8 eV }However, the ground state energy has been experimentally determined accurately to -78.6 eV. Therefore our model is not a good one. Now let us apply variational method using a trial wavefunction. The trial wavefucntion we are going to is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.16)}} itself but with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{Z} } as variable. This argument is perfectly valid since each electron screens the nuclear charge seen by the other electron and hence the atomic number is less than 2.
We can manipulate the Hamiltonian with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \boldsymbol{ {Z}} } going to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\sigma} } and rewriting the potential term as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\sigma e^2}{|r|}+\frac{(Z-\sigma) e^2}{|r|}} . So the Hamiltonian becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H= -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}(\boldsymbol\nabla_1^2+\boldsymbol \nabla_2^2)- \frac{\sigma e^2}{|r_1|}+\frac{(Z-\sigma) e^2}{|r_1|}-\frac{\sigma e^2}{|r_2|}+\frac{(Z-\sigma) e^2}{|r_2|}+\frac{e^2}{|\boldsymbol {r}_1-\boldsymbol {r}_2|} }
Now we can use the variational principle. The expectation value of the Hamiltonian is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle H\rangle= \int{d^3r_1}\int{d^3r_2} \psi*_{100}( \boldsymbol r_1)\psi*_{100}(\boldsymbol r_2)\times}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left[-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\boldsymbol\nabla_1^2- \frac{\sigma e^2}{|r_1|}+\frac{(Z-\sigma) e^2}{|r_1|} -\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\boldsymbol\nabla_2^2-\frac{\sigma e^2}{|r_2|}+\frac{(Z-\sigma) e^2}{|r_2|}+\frac{e^2}{|\boldsymbol {r}_1-\boldsymbol {r}_2|}\right] \psi_{100}( \boldsymbol r_1)\psi_{100}(\boldsymbol r_2)\qquad \text{(4.18)}}
The first two terms give Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_1=\frac{-\sigma me^4}{2\hbar^2}} . The fourth and fifth term will give the same. The third term and sixth term nwill giveFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_2=-{(Z-\sigma) e^2} \langle\frac{1}{r_1}\rangle = -{(Z-\sigma) e^2}\frac{\sigma}{a_0} }
The seventh term will give an expectation value of
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_3= \frac{5 \sigma m e^4}{8\hbar^2} }
Adding all this we get,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E=-\frac{m e^4}{2 \hbar^2}\left( 2 \sigma^2 + 4 \sigma(Z-\sigma)-\frac{5 \sigma}{4}\right) }
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\sigma} } is the variational parameter, we can minimize the Energy with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\sigma} } . This will give us
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\sigma}=Z- \frac{5}{16}}
Putting Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf Z=2 } we get Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{\sigma}=1.6875 } which is an improvemnet.
Substituting this in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \qquad \text{(4.16)} } we get Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf E= -77.38 eV }which is very close to the experimental value. Thus using variational principle we were able to calculate the ground state energy of the helium atom very close to the experimental value.
Rational wave functions
The calculations of the previous sections enabled us to familiarize ourselves with the variational method, but they do not really allow us to judge its effectiveness as a method of approximation, since the families chosen always included the exact wave function. Therefore, we shall now choose trial functions of a totally different type, for example
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_{a}(x)=\frac{1}{x^2+a}\qquad; \quad a>0 }
A simple calculation then yields:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \psi_{a}|\psi_{a}\rangle=\int_{-\infty}^{+\infty}\frac{dx}{\left(x^2+a\right)^2}=\frac{\pi}{2a\sqrt{a}}}
and finally:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle (a)=\frac{\hbar^2}{4m}\frac{1}{a}+\frac{1}{2}m \omega^2 a}
The minimum value of this function is obtained for:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a=a_{0}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\frac{\hbar}{m \omega}}
and is equal to:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle (a_{0})=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\, \hbar \omega }
The minimum value is therefore equal to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{2}} times the exact ground state energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega/2} . To measure the error committed, we can calculate the ratio of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle (a_{0})-\hbar \omega/2} to the energy quantum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \omega} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\langle\mathcal{H}\rangle (a_{0})-\frac{1}{2} \hbar \omega}{\hbar \omega}=\frac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2} \simeq 20 \%}
Discussions
The example of the previous section shows that it is easy to obtain the ground state energy of a system, without significant error, starting with arbitrary chosen trial kets. This is one of the principal advantages of the variational method. Since the exact eigenvalue is a minimum of the mean value Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle } , it is not surprising that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\mathcal{H}\rangle } does not vary very much near this minimum.
On the other hand, as the same reasoning shows, the "approximate" state can be rather different from the true eigenstate. Thus, in the example of the previous section, the wave function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1/\left(x^2+a_{0}\right)} decreases too rapidly for small values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} and much too slowly when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} becomes large. The table below gives quantitative support for this qualitative assertion. It gives, for various values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x^2} , the values of the exact normalized eigenfunction:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \varphi_{0}(x)=(2 \alpha_{0}/\pi)^{1/4} e^{-\alpha_{0} x^2}}
and of the approximate normalized eigenfunction:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}} (a_{0})^{3/4} \psi_{a_{0}}(x) = \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}} \frac{(a_{0})^{3/4}}{x^2+a_{0}} = \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}} \left(2 \sqrt{2} \alpha_{0} \right)^{1/4} \frac{1}{1+2\sqrt{2} \alpha_{0} x^2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\sqrt{\alpha_{0}}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left(\frac{2}{\pi}\right)^{1/4}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{2}{\pi}} \frac{\left(2 \sqrt{2} \right)^{1/4}}{1+2\sqrt{2} \alpha_{0} x^2}} 0 0.893 1.034 1/2 0.696 0.605 1 0.329 0.270 3/2 0.094 0.140 2 0.016 0.083 5/2 0.002 0.055 3 0.0001 0.039 It is therefore necessary to be very careful when physical properties other than the energy of the system are calculated using the approximate state obtained from the variational method. The validity of the result obtained varies enormously depending on the physical quantity under consideration. In the particular problem which we are studying here, we find, for example, that the approximate mean value of the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X^2} is not very different from the exact value:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\langle \psi_{a_{0}}|X^2|\psi_{a_{0}}\rangle}{\langle \psi_{a_{0}}|\psi_{a_{0}}\rangle}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\frac{\hbar}{m \omega}}
which is to be compared with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar/{2 m \omega}} . On the other hand, the mean value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle X^4} is infinite for the approximate normalized eigenfunction, while it is, of course, finite for the real wave function. More generally, the table shows that the approximation will be very poor for all properties which depend strongly on the behavior of the wave function for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x \gtrsim 2/\sqrt{\alpha_{0}}} .
The drawback we have just mentioned is all the more serious as it is very difficult, if not impossible, to evaluate the error in a variational calculation if we do not know the exact solution of the problem (and, of course, if we use the variational method, it is because we do not know this exact solution).
The variational method is therefore a very flexible approximation method, which can be adapted to very diverse situations and which gives great scope to physical intuition in the choice of trial kets. It gives good values for the energy rather easily, but the approximate state vectors may present certain completely unpredictable erroneous features, and we can not check these errors. This method is particularly valuable when physical arguments give us an idea of the qualitative or semi-qualitative form of the solutions.
Spin
General Theory of Angular Momentum
Up to now we have been working with the rotational degree of freedom using the orbital angular momentum. Namely we use the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf L} (the generator of rotations in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{R}^{3}} ) to construct wave functions which carry the rotational information of the system.
To clarify, all what we have done consist in quantise everything that we know from classical mechanics. Specifically this is:
- Invariance of time translation ---> Conservation of the Hamiltonian
- Invariance of Spatial translation ---> Conservation of the Momentum
- Invariance of Spacial Rotations ---> Conservation of Orbital Angular Momentum
However nature shows that there are other kinds of degrees of freedom that don't have classical analog. The first one was observed for the first time in 1992 by Stern and Gerlach (see Cohen-Tannoudji Chap 4). They saw that electrons have one additional degree of freedom of the angular momentum. This degree of freedom was called "Spin 1/2" since they exhibit just two single results: Up and Down.
The goal of this section is to extend the notion of orbital angular momentum to a general case. For this we use the letter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}} for this abstract angular momentum. As we will see, orbital angular momentum is just a simple case of the general angular momentum.
Since the equations has the same form (same commutation relationships) as in the case of orbital angular momentum we can easily extend everything:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J^{2}}&=|j,m \rangle = \hbar^{2} j(j+1)|j,m \rangle\\ \mathbf{J}_{z}&=|j,m \rangle = \hbar m|j,m \rangle;\;\;\;\;\;-j\le m\le j \\ \mathbf{J_{\pm}}&=|j,m \rangle = \hbar \sqrt{j(j+1)-m(m\pm 1)}|j,m \rangle\\ \end{align}}
One important feature is that the allowed values for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m} are integers or half-integers (See Shankar). Therefore the possible values for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j} are
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} j=0,\;1/2,\;1,\;3/2,\;2,\;5/2... \end{align}}
We can construct the following table:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{array}{c|r|r|r|r|r|r|r} j \rightarrow& 0 & 1/2 & 1 & 3/2 & 2 & 5/2 & ...\\ \hline m& 0 & 1/2 & 1 & 3/2 & 2 & 5/2 & ...\\ \downarrow& &-1/2 & 0 & 1/2 & 1 & 3/2 & \\ & & &-1 &-1/2 & 0 & 1/2 & \\ & & & &-3/2 &-1 &-1/2 & \\ & & & & &-2 &-3/2 & \\ & & & & & &-5/2 & \\ \hline &(2\cdot 0+1)&(2\cdot \frac{1}{2}+1)&(2\cdot1+1)&(2\cdot \frac{3}{2}+1)&(2\cdot2+1)&(2\cdot \frac{5}{2}+1)&(2\cdot j+1) \\ &=1 &=2 &=3 &=4 &=5 &=6 &\\ \hline \end{array}}
Each of this columns represent subspaces of the basis Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j,m \rangle } that diagonalize Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}} . For orbital angular momentum the allowed values for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m} are integers. This is due to the periodicity of the azimuthal angle.For electrons, they have an additional degree of freedom which takes values "up" or "down". Physically this phenomena appears when the electron is exposed to magnetic fields. Since the coupling with the magnetic field is via magnetic moment it is natural to consider this degree of freedom as internal angular momentum. Since there are just 2 states therefore it angular momentum is represented by the subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1/2} .
It is important to see explicitly the representation of this group. Namely we want see the matrix elements of the operators Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{x}} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{y}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}} . The procedure is as follow:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}} are diagonal since the basis are their eigenvectors.
- TO find Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{x}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{y}} we use the fact that
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{x}&=\frac{1}{2}[\mathbf{J}_{+}+\mathbf{J}_{-}]\\ \mathbf{J}_{y}&=\frac{1}{2i}[\mathbf{J}_{+}-\mathbf{J}_{-}]\\ \end{align}}
And the matrix elements of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{\pm}} are given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \langle j',m'|\mathbf{J}_{\pm}|j,m\rangle &= \langle j',m'|\hbar \sqrt{j(j+1)-m(m\pm1)}|j,m\pm 1\rangle \\ &= \hbar \sqrt{j(j+1)-m(m\pm1)}\delta_{j' j} \delta_{m' m\pm 1} \\ \end{align}}
Let's find the representations for the subspaces Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=0,\frac{1}{2},1}
Subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=0} : (matrix 1x1)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}=0}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}=0}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle 00|\mathbf{J}_{\pm}|00\rangle =0 \;\;\;\rightarrow\;\;\;\mathbf{J}_{x}=\mathbf{J}_{y}=0}
Subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1/2} : (matrix 2x2)- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}= \begin{array}{r|c|c} & |1/2,1/2\rangle & |1/2,-1/2\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1/2,1/2| & \frac{3}{4}\hbar^{2} & 0 \\ \hline \langle 1/2,-1/2| & 0 & \frac{3}{4}\hbar^{2} \\ \hline \end{array} =\frac{3}{4}\hbar^{2} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}= \begin{array}{r|c|c} & |1/2,1/2\rangle & |1/2,-1/2\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1/2,1/2| & \frac{1}{2}\hbar & 0 \\ \hline \langle 1/2,-1/2| & 0 & \frac{-1}{2}\hbar \\ \hline \end{array} =\frac{1}{2}\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} }
- For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{+} } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{-}} are given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{+}&=\hbar \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{2}+1)-m(m+1)}\;\;\;\delta_{\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2}} \delta_{m',m+1}\\ &=\begin{array}{r|c|c} & |1/2,1/2\rangle & |1/2,-1/2\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1/2,1/2| & 0 & \hbar \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{2}+1)-(\frac{-1}{2})((\frac{-1}{2})+1)} \\ \hline \langle 1/2,-1/2| & 0 & 0 \\ \hline \end{array} =\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{-}&=\hbar \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{2}+1)-m(m-1)}\;\;\;\delta_{\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2}} \delta_{m',m-1}\\ &=\begin{array}{r|c|c} & |1/2,1/2\rangle & |1/2,-1/2\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1/2,1/2| & 0 & 0\\ \hline \langle 1/2,-1/2| & \hbar \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{2}+1)-(\frac{1}{2})((\frac{1}{2})-1)} & 0 \\ \hline \end{array} =\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
- The matrices for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{x} } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{y}} are given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{x}&=\frac{1}{2}[\mathbf{J}_{+}+\mathbf{J}_{-}] =\frac{1}{2}\left [ \hbar\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} + \hbar\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \right ]\\ &=\frac{\hbar}{2}\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathbf{J}_{y}&=\frac{1}{2i}[\mathbf{J}_{+}-\mathbf{J}_{-}] =\frac{1}{2i}\left [ \hbar\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} - \hbar\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \right ]\\ &=\frac{\hbar}{2i}\begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ -1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} =\frac{\hbar}{2}\begin{pmatrix} 0 & -i \\ i & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
Subspace Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1} : (matrix 3x3)- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}^{2}= \begin{array}{r|c|c|c} & |1,1\rangle & |1,0\rangle & |1,-1\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1,1| & 2\hbar^{2} & 0 &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,0| & 0 & 2\hbar^{2} &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,-1| & 0 & 0 &2\hbar^{2} \\ \hline \end{array} =2\hbar^{2} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1\\ \end{pmatrix} }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{z}= \begin{array}{r|c|c|c} & |1,1\rangle & |1,0\rangle & |1,-1\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1,1| & \hbar & 0 &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,0| & 0 & 0 &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,-1| & 0 & 0 &-\hbar \\ \hline \end{array} =\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1\\ \end{pmatrix} }
- For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{+} } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{-}} are given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{+}&=\hbar \sqrt{1(1+1)-m(m+1)}\;\;\;\delta_{1,1} \delta_{m',m+1}\\ &=\begin{array}{r|c|c|c} & |1,1\rangle & |1,0\rangle & |1,-1\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1,1| & 0 & \hbar \sqrt{1(1+1)-0(0+1)} &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,0| & 0 & 0 &\hbar \sqrt{1(1+1)-(-1)((-1)+1)} \\ \hline \langle 1,-1| & 0 & 0 &0 \\ \hline \end{array} =\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & \sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align} }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{-}&=\hbar \sqrt{\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{2}+1)-m(m-1)}\;\;\;\delta_{\frac{1}{2},\frac{1}{2}} \delta_{m',m-1}\\ &=\begin{array}{r|c|c|c} & |1,1\rangle & |1,0\rangle & |1,-1\rangle \\ \hline \langle 1,1| & 0 & 0 &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,0| &\hbar \sqrt{1(1+1)-1(1-1)} & 0 &0 \\ \hline \langle 1,-1| & 0 &\hbar \sqrt{1(1+1)-1(1-1)} &0 \\ \hline \end{array} =\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{2} &0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
- The matrices for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{x} } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{J}_{y}} are given by
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \mathbf{J}_{x}&=\frac{1}{2}[\mathbf{J}_{+}+\mathbf{J}_{-}] =\frac{1}{2}\left [ \hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & \sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} + \hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{2} &0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \right ]\\ &=\frac{\hbar}{\sqrt{2}} \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 0 \\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \mathbf{J}_{y}&=\frac{1}{2i}[\mathbf{J}_{+}-\mathbf{J}_{-}] =\frac{1}{2i}\left [ \hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & \sqrt{2} & 0\\ 0 & 0 & \sqrt{2}\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix} - \hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 0 & 0\\ \sqrt{2} & 0 & 0\\ 0 & \sqrt{2} &0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \right ]\\ &=\frac{\hbar}{\sqrt{2i}} \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0\\ -1 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & -1 & 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} =\frac{\hbar}{\sqrt{2}} \begin{pmatrix} 0 & -i & 0\\ i & 0 & -i\\ 0 & i & 0 \\ \end{pmatrix} \end{align}}
Summary
The following table is the summary of above calculations.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{array}{r|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c} & j=0 & j=1/2 &j=1 \\ \hline \mathbf{J}^{2} &0 &\frac{3}{4}\hbar^{2} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{pmatrix} &2\hbar^{2} \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 1 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1\\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \hline \mathbf{J}_{z} &0 &\frac{1}{2}\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \end{pmatrix} &\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 1 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 0\\ 0 & 0 & -1\\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \hline \mathbf{J}_{x} &0 &\frac{1}{2}\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{pmatrix} &\frac{\hbar}{\sqrt{2}} \begin{pmatrix} 0 & 1 & 0\\ 1 & 0 & 1\\ 0 & 1 & 0\\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \hline \mathbf{J}_{y} &0 &\frac{1}{2}\hbar \begin{pmatrix} 0 & -i \\ i & 0 \end{pmatrix} &\frac{\hbar}{\sqrt{2}} \begin{pmatrix} 0 & -i & 0\\ i & 0 & -i\\ 0 & i & 0\\ \end{pmatrix}\\ \hline \end{array} }
Spin 1/2 Angular Momentum
The angular momentum of a stationary spin 1/2 particle is found to be quantized to the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \pm\frac{\hbar}{2}} regardless of the direction of the axis chosen to measure the angular momentum. There is a vector operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \textbf{\overrightarrow{S}}=(S_{x}, S_{y}, S_{z})} when projected along an arbitrary axis satisfies the following equations:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}|\hat{m}\uparrow\rangle = \dfrac{\hbar}{2}|\hat{m}\uparrow\rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}|\hat{m}\downarrow\rangle = \dfrac{-\hbar}{2}|\hat{m}\downarrow\rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{m}\uparrow\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{m}\downarrow\rangle} form a complete basis, which means that any state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{n}\uparrow\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{n}\downarrow\rangle} can be expanded as a linear combination of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{m}\uparrow\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{m}\downarrow\rangle} .
The spin operator obeys the standard angular momentum commutation relations
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [S_{\mu}, S_{\nu}]=i\hbar\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}S_{\lambda}\Rightarrow [S_{x}, S_{z}]=-i\hbar S_{y}}
The most commonly used basis is the one which diagonalizes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot \hat{z} =S_{z}} .
By acting on the states Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{z}\uparrow\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\hat{z}\downarrow\rangle} with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{S}_{z}} , we find Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{z}|\hat{z}\uparrow\rangle = \dfrac{\hbar}{2}|\hat{z}\uparrow\rangle} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{z}|\hat{z}\downarrow\rangle = \dfrac{-\hbar}{2}|\hat{z}\downarrow\rangle}
Now by acting to the left with another state, we can form a 2x2 matrix.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} S_{z} & =\left( \begin{array}{ll} \langle\hat{z}\uparrow|S_{z}|\hat{z}\uparrow\rangle & \langle\hat{z}\uparrow|S_{z}|\hat{z}\downarrow\rangle \\ \langle\hat{z}\downarrow|S_{z}|\hat{z}\uparrow\rangle & \langle\hat{z}\downarrow|S_{z}|\hat{z}\downarrow\rangle \end{array} \right)\\ & =\left(\begin{array}{ll} \hbar/2 & 0 \\ 0 & -\hbar/2 \end{array}\right)\\ & =\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\left( \begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & -1 \end{array}\right)\\ &=\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\sigma_{z} \end{align}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal\sigma_{z}} is the z Pauli spin matrix. Repeating the steps (or applying the commutation relations), we can solve for the x and y components.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{x}=\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\left(\begin{array}{ll} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{array} \right)=\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\sigma_{x}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{y}=\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\left( \begin{array}{ll} 0 & -i \\ i & 0 \end{array} \right)=\dfrac{\hbar}{2}\sigma_{y}}
It should be noted that a spin lying along an axis may be rotated to any other axis using the proper rotation operator.Properties of the Pauli Spin Matrices
Each Pauli matrix squared produces the unity matrix
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma_{x}^2=\sigma_{y}^2=\sigma_{z}^2=\left( \begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right)}
The commutation relation is as follows
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{[\sigma_{\mu}, \sigma_{\nu}]}=2i\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}\sigma_{\lambda}}
and the anticommutator relation
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \{\sigma_{\mu}, \sigma_{\nu} \}= [ \sigma_{\mu}, \sigma_{\nu} ]_+ = \sigma_{\mu}\sigma_{\nu}+\sigma_{\nu}\sigma_{\mu}=2\delta_{\mu\nu} \left( \begin{array}{ll} 0 & 1 \\ 1 & 0 \end{array} \right)}
For example, if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{\sigma_{\mu}\sigma_{\nu}=-\sigma_{\nu}\sigma_{\mu}}}
Then,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma_{\mu}\sigma_{\nu}=\dfrac{1}{2}[\sigma_{\mu}, \sigma_{\nu}]+\dfrac{1}{2}{\sigma_{\mu}, \sigma_{\nu}}=i\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}\sigma_{\lambda}+\delta_{\mu\nu}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{\mu}S_{\nu}=\dfrac{\hbar^2}{4}\delta_{\mu\nu}+\dfrac{i\hbar}{2}\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}S_{\lambda}}
The above equation is true for 1/2 spins only!!
In general,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}(a \cdot \sigma)(b\cdot\sigma) & =(a_{x}\sigma_{x}+a_{y}\sigma_{y}+a_{z}\sigma_{z})(b_{x}\sigma_{x}+b_{y}\sigma_{y}+b_{z}\sigma_{z})\\ & =a_{\mu}\sigma_{mu}b_{\nu}\sigma_{nu}\\ & =a_{\mu}b_{\nu}\sigma_{mu}\sigma_{nu}\\ & =a_{\mu}b_{\nu} \left( \left( \begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right) \delta_{\mu\nu}+i\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}\sigma_{\lambda} \right)\\ & = \left( \begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right) a\cdot b+i(a\times b)\cdot\sigma \end{align}}
Finally, any 2x2 matrix can be written in the form
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle M=\alpha \left( \begin{array}{ll} 1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1 \end{array} \right) +\beta \cdot \sigma= \left( \begin{array}{ll} M_{11} & M_{12} \\ M_{21} & M_{22} \end{array} \right) }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\alpha=\frac{1}{2}(M_{11}+M_{22})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\beta_{x}=\frac{1}{2}(M_{12}+M_{21})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\beta_{y}=\frac{i}{2}(M_{12}-M_{21})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\beta_{z}=\frac{1}{2}(M_{11}-M_{22})}
for infinitesimal Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathcal{\alpha}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}=\hat{m}+\overrightarrow{\alpha}x \hat{m} + O(\alpha^2)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{n}=\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}+\overrightarrow{S}\cdot(\overrightarrow{\alpha} \times \overrightarrow{m})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{\mu}\hat{n_{\mu}}=S_{\mu}\hat{m_{\mu}}+S_{\mu}\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}\alpha_{\nu}\hat{m_{\lambda}}}
Note that using the previous developed formulas, we find that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} S_{\mu}\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda}=\dfrac{1}{i\hbar}[S_{\nu}, S_{\lambda}]\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{n} & =\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}+\dfrac{1}{i\hbar}[\overrightarrow{\alpha}\cdot\overrightarrow{S}, \hat{m}\cdot\overrightarrow{S}]\\ & =\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}+\dfrac{1}{i\hbar}[\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}, \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}]\end{align}}
To this order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{\alpha}} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{n}=e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} (\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{m}) e^{\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}}}
for finite Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha } (correct for all orders)
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{S}\cdot\hat{n} \left( e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} |\hat{m} \uparrow\rangle \right)= \dfrac{\hbar}{2}\left( e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} |\hat{m} \uparrow\rangle \right)}
Another way of expressing the rotation of the spin basis by an angle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha} about some axis Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{\alpha}} (and the one derived in class) is the following. Consider the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}}} from the previous equation. This can also be written,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} = e^{-\frac{i}{2}\overrightarrow{\sigma}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} = \sum_{i = 0}^{\infty} \frac{-(i\alpha\sigma\cdot\hat{\alpha}/2)^n}{n!}}
Because of the commutation relations of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sigma} , it can easily be shown that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\sigma\cdot\hat{\alpha})^2n = 1} (n is an integer), thus the above equation can be split:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-\frac{i}{\hbar}\overrightarrow{S}\cdot\overrightarrow{\alpha}} = \sum_{i = even}^{\infty} \frac{-(i\alpha/2)^n}{n!} + \sigma\cdot\hat{\alpha}\sum_{i = odd}^{\infty} \frac{-(i\alpha/2)^n}{n!} = cos(\alpha/2) + i\sigma\cdot\hat{\alpha}sin(\alpha/2)}
This form may be more convenient when performing rotations.
Addition of angular momenta
Formalism
Classically, the sum of two angular momentum is the sum of the C-number vectors. Quantum mechanically we have to be careful about the eigenstates.
For two angular momenta, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{J_{1}}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{J_{2}}} , such that, for their respective eigenstates, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1, m_1\rangle} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_2, m_2\rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_1|j_1, m_1\rangle = \hbar^2 j_1(j_1+1)|j_1, m_1\rangle}
and similarly for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_1|j_2, m_2\rangle} .
We define their total angular momentum as, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{J}=\overrightarrow{J_{1}}+\overrightarrow{J_{2}}=\overrightarrow{J_{1}}\otimes\mathbb{I}_2 + \mathbb{I}_1\otimes\overrightarrow{J_{2}}\Rightarrow|j_{1} m_{1}\rangle \otimes |j_{2} m_{2}\rangle=|j_{1} j_{2} m_{1} m_{2}\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad (6.1.1)}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{I}_1 } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{I}_2 } are the identity matrices of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{J_{1}}} 's and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{J_{2}}} 's Hilbert spaces, and where Hilbert space size is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!(2j_1+1)(2j_2+1)} .We have the following commutation relations:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [J_{\mu}, J_{\nu}] = i\hbar\epsilon_{\mu\nu\lambda} J_{\lambda} \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\ (6.1.2)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [J_{1,2}^2, J^2]= [J_{1,2}^2, J_{z}]=0 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\; (6.1.3)}
And consequently, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \![J^2, J_z] = 0 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad (6.1.4)}
However, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [J^2, J_{1z, 2z}] \neq 0 } . Therefore, to construct a basis, one can not take a direct product between the set of eigenkets of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J^2} and those of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J_{1z,2z}} . For example,
assume two spin 1/2 particles with basis Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {|\uparrow\uparrow\rangle, |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle, |\downarrow\uparrow\rangle, |\downarrow\downarrow\rangle} } . These states are eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{1}^2, J_{2}^2, J_{1z}, J_{2z}} , but are they eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J^2} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_z^2} ?
Let us see what happens with the state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle} :Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J^2 |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle =(J_{x}^2+J_{y}^2+J_{z}^2)|\uparrow\downarrow\rangle = ((J_{x}+iJ_{y})(J_{x}-iJ_{y})+i[J_{x}, J_{y}] + J_{z}^2)|\uparrow\downarrow\rangle}
define Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{\pm}=(J_{x}\pm iJ_{y})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J^2 |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle =(J_{+}J_{-}-\hbar J_{z} + J_{z}^2)| \uparrow\downarrow\rangle = ((J_{1+}+J_{2+})(J_{1-}+J_{2-})+(J_{1z}+J_{2z})^2-\hbar (J_{1z}+J_{2z}))|\uparrow\downarrow\rangle }
Now Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (J_{1z}+J_{2z}) |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle = (\dfrac{\hbar}{2}-\dfrac{\hbar}{2}) |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle = 0 }
Also, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (J_{1+}+J_{2+})(J_{1-}+J_{2-})|\uparrow\downarrow\rangle = (J_{1+}+J_{2+})|\downarrow\downarrow\rangle = |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle + |\downarrow\uparrow\rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \therefore J^2 |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle = |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle + |\downarrow\uparrow\rangle }
Which means that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\uparrow\downarrow\rangle } is not an eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J^2} . Similarly, it can be shown that the other three states are also not eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J^2} . As a result, there are two
choices for sets of base kets which can be used:1. The simultaneous eigenkets of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_1^2} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_2^2} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J_{1z}} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J_{2z}} , denoted by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle} . These four operators commute with each other, and they operate on the base kets
according to:Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{1,2}^2|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle = \hbar_2 j_{1,2}(j_{1,2} + 1)|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\; (6.1.5)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{1z,2z}|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle = \hbar m_{1,2}|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad (6.1.6)}
2. The simultaneous eigenkets of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!J^2} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_1^2} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_2^2} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_z} , denoted by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j m j_1 j_2\rangle} . These four operators operate on the base kets according to:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J^2|j m j_1 j_2\rangle = \hbar^2 j(j + 1)|j m j_1 j_2\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\;\;\; (6.1.7)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{z}|j m j_{1} j_{2}\rangle=\hbar m |j m j_{1} j_{2}\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\;\;\;\;\ (6.1.8)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{1,2}^2|j m j_{1} j_{2}\rangle=\hbar^2 j_{1,2}(j_{1,2}+1) |j m j_{1} j_{2}\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\;\ (6.1.9)}
Clebsch-Gordan Coefficients
Now that we have constructed two different bases of eigenkets, it is imperative to devise a way such that eigenkets of one basis may be written as
linear combinations of the eigenkets of the other basis. To achieve this, we write:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j m j_1 j_2\rangle = \sum_{m_1,m_2}|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle\langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j m j_1 j_2\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\ (6.2.1) }
In above, we have used the completeness of the basis Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle} , given by:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{m_1,m_2}|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle\langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2| = 1 \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \quad\;\;\; (6.2.2)}
The coefficients Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j m j_1 j_2\rangle} are called Clebsch-Gordan coefficients, which have the following properties, giving rise to two
"selection rules":1. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m \neq m_1 + m_2} , then the coefficients vanish.
Proof: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \because J_z = J_{1z} + J_{2z}} , we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (J_z - J_{1z} - J_{2z})|j m j_1 j_2\rangle = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|(J_z - J_{1z} - J_{2z})|j m j_1 j_2\rangle = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \therefore (m - m_1 - m_2)\langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j m j_1 j_2 \rangle = 0 } . Q.E.D.
2. The coefficients vanish, unless Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 - j_2| \le j \le j_1 + j_2 }
This follows from a simple counting argument. Let us assume, without any loss of generality, that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j_1 > j_2 } . The dimensions of the two bases should
be the same. If we count the dimensions using the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2\rangle } states, we observe that for any value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j } , the values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! m } run from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! -j} to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j } .
Therefore, for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j_1 } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j_2 } , the number of eigenkets is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! (2j_1 + 1)(2j_2 + 1) } . Now, counting the dimensions using the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j m j_1 j_2 \rangle } eigenkets, we
observe that, again, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! m } runs from Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! -j } to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! j } . Therefore, the number of dimensions is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N = \sum_a^b (2j + 1) } . It is easy to see that for
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! a = j_1 - j_2 } and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \! b = j_1 + j_2, N = (2j_1 + 1)(2j_2 +1)} .
Further, it turns out that, for fixed Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!j_1} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!j_2} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!j} , coefficients with different values for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!m_1} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \!m_2} are related to each other through recursion
relations. To derive these relations, we first note that: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{\pm}|j m j_1 j_2\rangle = \sqrt{(j \mp m)(j \pm m + 1)}\hbar |j m \pm 1 j_1 j_2\rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad\;\ (6.2.3) }
Now we write, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{\pm}|j m j_1 j_2 \rangle = (J_{1 \pm} + J_{2 \pm}) \sum_{m_1,m_2}|j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 \rangle \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j m j_1 j_2 \rangle \qquad \qquad \qquad \qquad (6.2.4)}
Using equation #(6.2.4), we get (with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_1 \to m'_1 } , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_2 \to m'_2 } ):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \sqrt{(j \mp m)(j \pm m + 1)}|j m \pm 1 j_1 j_2 \rangle = \sum_{m'_1,m'_2}( \sqrt{(j_1 \mp m'_1)(j_1 \pm m'_1 + 1)}|j_1 j_2 m'_1 \pm 1 m'_2 \rangle \ + \\ \sqrt{(j_2 \mp m'_2)(j_2 \pm m'_2 + 1)}|j_1 j_2 m'_1 m'_2 \pm 1 \rangle )\langle j_1 j_2 m'_1 m'_2|j m j_1 j_2 \rangle \end{align}}
The Clebsch-Gordan coefficients form a unitary matrix, and by convention, they are all taken real. Any real unitary matrix is orthogonal, as we studybelow.
Orthogonality of Clebsch-Gordan Coefficients
We have the following symmetry:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 |j m j_1 j_2 \rangle = (-1)^{j_1 +j_2 -j} \langle j_1, j_2, -m_1, -m_2 |j, -m, j_1, j_2 \rangle}
If we put the coefficients into a matrix, it is real and unitary, meaning Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle j m j_1 j_2 |j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 \rangle = \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 |j m j_1 j_2 \rangle ^*}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle | j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 \rangle = \sum_{j,m} |j m j_1 j_2 \rangle \langle j m j_1 j_2 |j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2 \rangle } . E.g.,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\uparrow_1 \downarrow_2 \rangle = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|10 \rangle + |00 \rangle )}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\downarrow_1 \uparrow_2 \rangle = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(|10 \rangle - |00 \rangle )}
We have the following orthogonality relations:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{jm}\langle j_1 m'_1 j_2 m'_2|jmj_1 j_2\rangle \langle jmj_1 j_2 | j_1 m_1 j_2 m_2\rangle = \delta_{m_1 m'_1} \delta_{m_2 m'_2} }Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{m_1 m_2}\langle j m j_1 j_2|j_1 m_1 j_2 m_2\rangle \langle j_1 m_1 j_2 m_2 | j' m' j_1 j_2\rangle = \delta_{j j'} \delta_{m m'} }
Hydrogen atom with spin orbit coupling given by the following hamiltonian
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H'=\dfrac{c^2}{2m^2 c^2 r^3}\overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S}}
Recall, the atomic spectrum for bound states
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n = \dfrac{-e^2}{2a_o}\dfrac{1}{n^2}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ; n=1, 2, 3, ...}
The ground state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |1s\rangle} , is doubly degenerate:
First excited state is 8-fold degenerate: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \dfrac{\uparrow\downarrow}{1s}\dfrac{\uparrow\downarrow}{}\dfrac{\uparrow\downarrow}{2p}\dfrac{\uparrow\downarrow}{}}
nth state is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2n^2} fold degenerate
We can break apart the angular momentum and spin into its x, y, z-components
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S} = L_x S_x + L_y S_y + L_z S_z }
Define lowering and raising operators
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow L_\pm = L_x \pm iL_y}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow S_\pm = S_x \pm iS_y}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S} = L_z S_z + \dfrac{1}{2} L_{+} S_{-} + \dfrac{1}{2} L_{-} S_{+} }
For the ground state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (|1s, \uparrow\rangle, |1s, \downarrow\rangle )} , nothing happens. Kramer's theorem protects the double degeneracy.
For the first excited state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (|2s, \uparrow\rangle, |2s, \downarrow\rangle )} , once again nothing happens.
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (|2p, \uparrow\rangle, |2p, \downarrow\rangle )} , there is a four fold degeneracy.
We can express the solutions in matrix form
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( \begin{array}{llllll} \dfrac{\hbar^2}{2} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \dfrac{\hbar^2}{2} \end{array} \right)}
But there is a better and more exact solution, which we can solve for by adding the momenta first.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S} = \dfrac{1}{2} (\overrightarrow{L} + \overrightarrow{S})^2 -\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{L^2} -\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{S^2} = \dfrac{1}{2}(J^2 -L^2 - S^2)}
add the angular momenta:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |1s\rangle : l=0, s=\dfrac{1}{2}: 0\otimes \dfrac{1}{2}= \dfrac{1}{2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |2s\rangle : l=0, s=\dfrac{1}{2}: 0\otimes \dfrac{1}{2}= \dfrac{1}{2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |2p_m, 0 \rangle : l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2}: 1\otimes \dfrac{1}{2}= \dfrac{3}{2} \oplus \dfrac{1}{2}}
So that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S} |j=\dfrac{3}{2}, m, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle =\dfrac{1}{2} (\hbar^2\dfrac{3}{2}\dfrac{5}{2}-2 \hbar^2 - \dfrac{3}{4} \hbar^2) |j=\dfrac{3}{2}, m, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \dfrac{\hbar^2}{2} | j=\dfrac{3}{2}, m, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \overrightarrow{L}\cdot\overrightarrow{S} |j=\dfrac{1}{2}, m, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle =\dfrac{-\hbar^2}{2} | j=\dfrac{1}{2}, m, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j=\dfrac{3}{2}, m= \dfrac{3}{2}, l=1, s=\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = |l=1, m_l =1 \rangle |s=\dfrac{1}{2}, m_s = \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j= \dfrac{3}{2}, m= \dfrac{3}{2} \rangle = |m_l =1 \rangle |m_s = \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Define J_
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_ |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = (L_+ S_)|1 \rangle |\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hbar \sqrt{\dfrac{3}{2} \dfrac{5}{2}- \dfrac{3}{2}\dfrac{1}{2}} |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \hbar \sqrt{2}|0 \rangle |\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle + \hbar \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{2} \dfrac{3}{2} + \dfrac{1}{4}}|1, -\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{3} |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \sqrt{2}|0 \rangle |\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle + |1, -\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle}Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}|0 \rangle |\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle + \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}|1 \rangle | - \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{-1}{2} \rangle = \sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}|0 \rangle |\dfrac{-1}{2} \rangle + \sqrt{\dfrac{1}{3}}|-1 \rangle | \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\dfrac{3}{2}, \dfrac{-3}{2} \rangle = |-1 \rangle | - \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle}
Can express as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j=\dfrac{1}{2}, m =\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \alpha |0 \rangle |\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle + \beta |1 \rangle |- \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j=\dfrac{1}{2}, m = -\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle = \alpha ' |0 \rangle |-\dfrac{1}{2} \rangle + \beta ' |-1 \rangle | \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle }
When we project these states on the previously found states Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( \langle \dfrac{3}{2} \dfrac{1}{2} | \dfrac{1}{2} \dfrac{1}{2} \rangle =0\right) } we find that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha = -\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \sqrt{\dfrac{2}{3}}}
Addition of three angular momenta
To add three angular momenta Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_1, \bold J_2, \bold J_3} first we add Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_{12}=\bold J_1 + \bold J_2} , construct the simultaneous eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_{1} ^{2}, \bold J_2 ^{2}, \bold J_{12} ^{2}, \bold J_{12z}, \bold J_3 ^{2}, \bold J_{3z}} . We write such states as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 \rangle} . Such states can be given in terms of Clebsch-Gordan coefficients and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_3 m_1 m_2 m_3 \rangle} (eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_1^{2}, \bold J_2^{2}, \bold J_3^{2}, \bold J_{1z}, \bold J_{2z}, \bold J_{3z}} ):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 \rangle = \sum_{m_1,m_2} |j_1 j_2 j_3 m_1 m_2 m_3 \rangle \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12}\rangle}
Next we add Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_{12}} to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_3} , forming simultaneous eigenstates Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_{12} j_3 j m \rangle} of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_1^{2}, \bold J_2^{2}, \bold J_{12}^{2}, \bold J_3^{2}, \bold J^{2}, \bold J_{z}} . These are given in terms of the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle | j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 \rangle} by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_{12} j_3 j m \rangle = \sum_{m_{12},m_{3}} | j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 \rangle \langle j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 | j_{12} j_3 j m \rangle }
Therefore, we can construct eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_1^{2}, \bold J_2^{2}, \bold J_{12}^{2}, \bold J_3^{2}, \bold J^{2}, \bold J_{z}} in terms of eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_1^{2}, \bold J_2^{2}, \bold J_3^{2}, \bold J_{1z}, \bold J_{2z}, \bold J_{3z}} as follows:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j_1 j_2 j_{12} j_3 j m \rangle = \sum_{m_{1},m_{2},m_{3}} |j_1 j_2 j_3 m_1 m_2 m_3 \rangle \sum_{m_{12}} \langle j_1 j_2 m_1 m_2|j_1 j_2 j_{12} m_{12}\rangle \langle j_{12} m_{12} j_3 m_3 | j_{12} j_3 j m \rangle }
Thus the analogous addition coefficients for three angular momenta are products of Clebsch-Gordan coefficients.
Note that for addition of two angular momenta, the dimension of Hilbert space is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (2J_1 + 1)(2J_2 + 1)} . For three angular momenta, it is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (2J_1 + 1)(2J_2 + 1)(2J_3 + 1)} .
Elementary applications of group theory in Quantum Mechanics
Irreducible tensor representations and Wigner-Eckart theorem
Representation of rotations
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J} is the total angular momentum of a system, the operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}=e^{-i \bold J \vec \alpha}} acting to the right on a state of the system, rotates it in a positive sense about the axis Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec \alpha} by an angle Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec \alpha|} . Suppose that we act with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}} on an eigenstate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jm \rangle} of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J^2} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_z} . Under the rotation, generally no longer an eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J_z} with eigenvalue m. However rotated state remains an eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J^2} with the same eigenvalue because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J^2} commute. Indeed
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold J^2 R_{\vec \alpha}|jm \rangle = \bold R_{\vec \alpha} J^2 |jm \rangle = j(j+1)R_{\vec \alpha}|jm \rangle}
Therefore the rotated state can be expressed as a linear combination of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jm'' \rangle} as follows:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}|jm \rangle= \sum _{m''=-j} ^{j}|jm'' \rangle d_{m''m} ^{(j)}(\vec \alpha)}
Multiplying this equation on the left by a state Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle jm'|} , and using the orthonormality of the angular momentum eigenstates we find
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{m'm} ^{(j)}(\vec \alpha) = \langle jm'|e^{-i \bold J \vec \alpha}|jm \rangle }
Thus we can associate with each rotation a Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2J+1} by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2J+1} dimension matrix Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold d_{\vec \alpha} ^{(j)}} whose matrix elements are Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{m'm} ^{(j)}(\vec \alpha)} . These matrix elements don't depend on dynamics of the system; they are determined entirely by the properties of the angular momentum.
The matrices have a very important property. Two rotations performed in a row, say Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec \alpha} followed by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec \beta} , are equivalent to a single rotation, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec \gamma} . Thus
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \gamma}=R_{\vec \beta}R_{\vec \alpha}}
Taking matrix elements of both sides and putting in a complete set of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |j'm'\rangle} states between Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \beta}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}} we find
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle jm|R_{\vec \gamma}| jm'\rangle=\sum_{m''}\langle jm|R_{\vec \beta}| jm''\rangle \langle jm''|R_{\vec \alpha}| jm'\rangle} ,
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d_{mm'} ^{(j)}(\vec \gamma)=\sum_{m''}d_{mm''} ^{(j)}(\vec \beta)d_{m''m'} ^{(j)}(\vec \alpha)}
or equivalently
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d ^{(j)}(\vec \gamma)=d ^{(j)}(\vec \beta)d ^{(j)}(\vec \alpha)}
A set of matrices associated with rotations having this property is call a representation of the rotation group.
The rotation operators Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R_{\vec \alpha}} act on the set of states Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jm \rangle} for fixed j, in an irreducible fashion. To see what this means, let's consider the effect of rotations on the set of eight states for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=2} . Under any rotation a Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1} state becomes a linear combination of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1} states, with no Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=2} components, conversely a Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=2} state becomes a linear combination of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=2} states with no Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j=1} components. Thus this set of eight states which transform each among themselves under rotation with no mixing. One says that the rotations act on these eight states reducibly. On the other hand, for a set of states all with the same j, there is no smaller subset of states that transforms privately among itself under all rotations; the rotations are said to act irreducibly. Put another way, if we start with any state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jm \rangle} , then we can rotate it Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2j+1} linearly independent states, and therefore there can't be any subspace of j states that transforms among itself under rotations. One can prove this in detail starting from the fact that one can generate all the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jm \rangle} states starting form Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |jj \rangle} by applying Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J_{-}} enough times.
Tensor operators
Wigner-Eckart theorem
Elements of relativistic quantum mechanics
In nonrelativistic quantum mechanics, states of particles are described by Schrodinger equation of states:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar\frac{\partial\psi(\bold r, t)}{\partial t}=\left(-\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\nabla^2+V(\bold r, t)\right)\psi(\bold r, t)}
Schrodinger equation is a first order in time. However, it is a second order in space. Therefore, it is not invariant under the Lorentz transformation. Equation of states in relativistic quantum mechanics must be invariant under the Lorentz transformation. In order to satisfy this condition, equation of state must contain the derivatives with respect to time and space of the same order. Equations of states in relativistic quantum mechanics are Klein-Gordon equation (for spinless particles) and Dirac equation (for spin Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac {1}{2}} particles). The former contains second ordered derivatives while the latter contains first ordered derivatives with respect to both time and space. The way to derive these equations is similar to that of Schrodinger equation: starting from the equation connecting energy and momentum, substituting Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E} by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\hbar \frac {\partial}{\partial t}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \bold p} by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -i\hbar \nabla} .
Follow this link to learn about Klein-Gordon equation.
Follow this link to learn about Dirac equation.
- If we see a circular polarized light then by conservation of angular momentum we know that













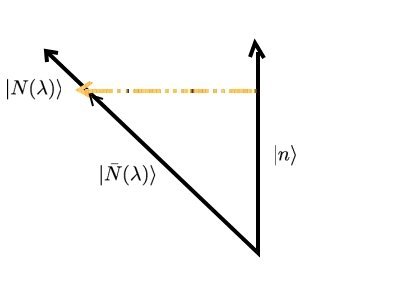
















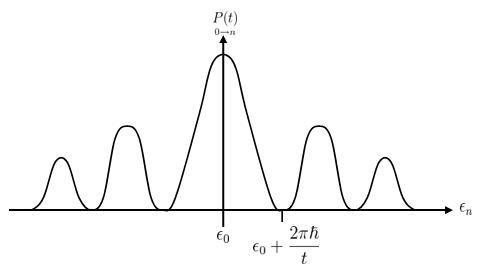


![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}|\langle n|\psi _{t}\rangle |^{2}&={\frac {1}{4}}|\langle n|V|0\rangle |^{2}e^{2\eta t}\sum _{ss'}{\frac {e^{{-i}{\hbar }(s-s')\hbar \omega t}}{(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}-s\hbar \omega -i\eta \hbar )(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}-s\hbar \omega +i\eta \hbar )}}\\{\underset {0\rightarrow n}{P(t)}}&={\frac {1}{4}}|\langle n|V|0\rangle |^{2}e^{2\eta t}\left[{\frac {1}{(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}-\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta ^{2}\hbar ^{2}}}+{\frac {1}{(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}+\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta ^{2}\hbar ^{2}}}\right]\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/79e85d7e54c08d8f011fa896285a38a6b30ada59)
![{\displaystyle {\underset {0\rightarrow n}{\Gamma (t)}}={\frac {d{P(t)_{0\rightarrow n}}}{dt}}={\frac {1}{4}}|\langle n|V|0\rangle |^{2}e^{2\eta t}\left[{\frac {2\eta }{(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}-\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta ^{2}\hbar ^{2}}}+{\frac {2\eta }{(\epsilon _{0}-\epsilon _{n}+\hbar \omega )^{2}+\eta ^{2}\hbar ^{2}}}\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e9ce556e14a56d6d5a60d3d8529f762605a8dd9a)

![{\displaystyle {\underset {0\rightarrow n}{\Gamma (t)}}={\frac {1}{4}}|\langle n|V|0\rangle |^{2}{\frac {2\pi }{\hbar }}\left[\delta (\epsilon _{n}-\epsilon _{0}+\hbar \omega )+\delta (\epsilon _{n}-\epsilon _{0}-\hbar \omega )\right]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/26e8f6e2a031a1e50d6a548531d8cc88b82b5585)









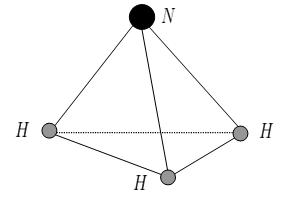
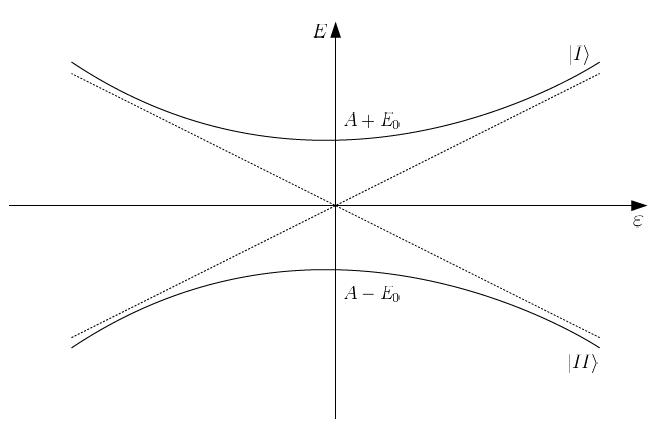




![{\displaystyle \left[\underbrace {\mathbf {a} _{\mathbf {k} {\boldsymbol {\lambda }}}\mathbf {a} _{\mathbf {k} {\boldsymbol {\lambda }}}} ,\mathbf {a} _{\mathbf {k'} {\boldsymbol {\lambda }}}^{\dagger }\right]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/5fc19140a88ea8da792bfbe190f2b6f120b3696b)