Solution to Set 3: Difference between revisions
m (→Part 1) |
|||
| (11 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
* Classical [[Ising model|Ising antiferromagnet]] on a [[Bipartite lattice|”bipartite” lattice]] given by Hamiltonian <math> H = \frac{J}{2} \sum_{<ij>} S_i S_j -− h\sum_i S_i </math>, | * Classical [[Ising model|Ising antiferromagnet]] on a [[Bipartite lattice|”bipartite” lattice]] given by Hamiltonian <math> H = \frac{J}{2} \sum_{<ij>} S_i S_j -− h\sum_i S_i </math>, | ||
* Magnetization for Lattice A: <math> m_A = < S^{(A)} > </math> | * Magnetization for Lattice A: <math> m_A = < S^{(A)} > \;</math> | ||
* Magnetization for Lattice B: <math> m_B = < S^{(B)} > </math> | * Magnetization for Lattice B: <math> m_B = < S^{(B)} > \;</math> | ||
* Average magnetization: <math>m = \frac{1}{2} (m_A + m_B ),</math> | * Average magnetization: <math>m = \frac{1}{2} (m_A + m_B ),</math> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
* <math>h\;</math> = Magnetic field energy from external sources that breaks the symmetry | * <math>h\;</math> = Magnetic field energy from external sources that breaks the symmetry | ||
The magnetization on each sublattice | ===Mean field approximation=== | ||
Each spin on lattice A feels an average magnetization due to the sins on lattice B (and vice versa). | |||
The magnetization on each sublattice: | |||
*Sublattice A: <math> m_A = < S_i^{A} > \;</math> | |||
*Sublattice B: <math> m_B = < S_j^{B} > \;</math> | |||
===Weiss Mean Field Approximation=== | |||
Use this to decouple the spins to find the energy of each spin <math>i\epsilon A \;</math> | |||
<math>E_{i}^{A} </math> | |||
<math> = \frac{J}{2}S_i \sum_{j \epsilon B}^{z}\left \langle S_{j}^{B} \right \rangle - hS_i</math> | |||
<math> =\left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_B - h \right ) S_i</math> | |||
<math> = B_{eff}^{B}S_i</math> | |||
<math>E_{i}^{B} </math> | |||
<math> = \frac{J}{2}S_j \sum_{j \epsilon A}^{z}\left \langle S_{i}^{A} \right \rangle - hS_j</math> | |||
<math> =\left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_A - h \right ) S_j</math> | |||
<math> = B_{eff}^{A}S_j</math> | |||
===Conditions of the magnetization=== | |||
<math>m_{A} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \left \langle S_{i}^{A} \right \rangle \;</math> | |||
<math> = Z^{-1} \sum_{\left \{S \right \}} S_{i}e^{-\beta \left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_{B}-h \right )S_{i}} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta}{2}zm_{B}+h\beta \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>m_{B} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \left \langle S_{i}^{B} \right \rangle \;</math> | |||
<math> = Z^{-1} \sum_{\left \{S \right \}} S_{i}e^{-\beta \left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_{A}-h \right )S_{i}} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta}{2}zm_{A}+h\beta \right ) \;</math> | |||
===Average Magnetization=== | |||
<math>m\equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} + m_{B} \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>m = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;</math> | |||
===Staggered Magnetization=== | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} \equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} - m_{B} \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) - h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;</math> | |||
==Part 2== | ==Part 2== | ||
'''Assume that <math>h = 0 | '''Assume that <math>h = 0</math>, so that <math>m = 0</math>, and solve the mean-field equations by expanding in <math>m^{\dagger}</math>. | ||
Determine the Neel (ordering) temperature, and calculate the order-parameter exponent.''' | |||
===The Néel Temperature=== | ===The Néel Temperature=== | ||
''Chapter 8.4 of Solid State Physics'' | |||
<math>T_N = \frac{C \lambda}{2}</math> | <math>T_N = \frac{C \lambda}{2}</math> | ||
where | where | ||
* <math>T_N\;</math> is Néel Temperature, the onset temperature for antiferromagnetism | * <math>T_N\;</math> is Néel Temperature, the onset temperature for antiferromagnetism | ||
* <math>C = \frac {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}{k_B}</math> is Curie constant | * <math>C = \frac {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}{k_B}</math> is Curie constant | ||
* <math>\lambda = \frac{4 \sum_{j \neq i} \jmath_{i j}} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2} = - \frac{4 z \jmath} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}</math> | * <math>\lambda = \frac{4 \sum_{j \neq i} \jmath_{i j}} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2} = - \frac{4 z \jmath} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}</math> | ||
===Order Parameter Exponent <math>\beta \;</math>=== | |||
Expand <math>m^{\dagger}</math> to the 3rd order | |||
Since <math>m = 0</math>, <math>m_{A} = -m_{B}</math> | |||
<math>2m^{\dagger} = \tanh \left ( \frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} \right ) - \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>2m^{\dagger} = 2 \left ( \frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} - \frac{\left( \frac{J\beta}{2} zm^{\dagger} \right )^3}{3} \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>1 = \frac{J\beta}{2}z - \frac{\left( \frac{J\beta}{2}z \right )^3 m^{\dagger 2}}{3} \;</math> | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} = \frac{1}{\frac{J\beta}{2}z}z \sqrt{3\left ( 1-\frac{2T}{Jz} \right )} \;</math> | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} = \frac{2T}{Jz} \sqrt{3\left ( \frac{2Jz}{2Jz} - \frac{2T}{Jz} \right )} \;</math> | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} = \frac{2T}{Jz} \sqrt {\frac{2}{Jz}} \sqrt{3\left ( \frac{Jz}{2} -T \right )} \;</math> | |||
<math>m^{\dagger} = T \left ( \frac{2}{Jz} \right )^{\frac{3}{2}} \sqrt {3 \left ( T_{N} - T \right )} \;</math> | |||
<math>\beta = \frac{1}{2}</math> | |||
==Part 3== | ==Part 3== | ||
'''Now consider a small external field <math>h > 0\;</math>, so that both order parameters can assume a nonzero value (Note: <math>m\;</math> will be small). By keeping only the leading terms in <math>h\;</math> and <math>m\;</math>, calculate the uniform spin susceptibility <math>\chi = \partial m/ \partial h</math>, as a function of temperature. Plot <math>\chi\;</math> as a function of temperature, and show that it has a cusp around <math>T_N\;</math>.''' | '''Now consider a small external field <math>h > 0\;</math>, so that both order parameters can assume a nonzero value (Note: <math>m\;</math> will be small). By keeping only the leading terms in <math>h\;</math> and <math>m\;</math>, calculate the uniform spin susceptibility <math>\chi = \partial m/ \partial h</math>, as a function of temperature. Plot <math>\chi\;</math> as a function of temperature, and show that it has a cusp around <math>T_N\;</math>.''' | ||
===Average magnetization as a function of small external field ''m(h)''=== | |||
<math>m \equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} + m_{B} \right ) \;</math> | |||
<math>m = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;</math> | |||
<math>2 m = \left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]h + J \beta z m \left [ - 1 + \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]</math> | |||
<math>m(h) = \frac{\left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]h} { 2 + J \beta z m \left [ 1 - \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} \;</math> | |||
===Uniform Spin Susceptibility=== | |||
<math>\chi(h) = \frac{\partial m}{\partial h} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \frac{\left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} { 2 + J \beta z \left [ 1 - \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} \;</math> | |||
===Susceptibility vs. Temperature Graph=== | |||
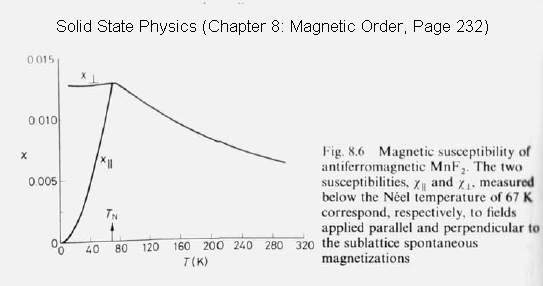
There is a cusp around <math>T_{N}</math> | |||
[[Image:xtgraph.jpg]] | [[Image:xtgraph.jpg]] | ||
| Line 75: | Line 163: | ||
==Part 4== | ==Part 4== | ||
'''Imagine adding a ”staggered” external field <math>h^{\dagger}</math>, which would be positive on sublattice A, but would be negative on sublattice B. Concentrate on the system with no uniform field <math>(h = 0)\;</math>, and determine the behavior of the staggered susceptibility <math>\chi^{\dagger}= \partial m^{\dagger} / \partial h^{\dagger} </math>. Show that <math>\chi^{\dagger}</math> blows up at the Neel temperature.''' | '''Imagine adding a ”staggered” external field <math>h^{\dagger}</math>, which would be positive on sublattice A, but would be negative on sublattice B. Concentrate on the system with no uniform field <math>(h = 0)\;</math>, and determine the behavior of the staggered susceptibility <math>\chi^{\dagger}= \partial m^{\dagger} / \partial h^{\dagger} </math>. Show that <math>\chi^{\dagger}</math> blows up at the Neel temperature.''' | ||
===Staggered Spin Susceptibility=== | |||
<math>\chi^{\dagger}(h) = \frac{\partial m^{\dagger}}{\partial h^{\dagger}} \;</math> | |||
'''Case <math>T < T_{N}</math>:''' | |||
<math>\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{\partial m^{\dagger}}{\partial h^{\dagger}} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \frac{1 - \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J z \left ( \tfrac{2}{Jz} \right )^{\tfrac{3}{2}} \sqrt{3\left | T_{N}-T \right |} \right )} { 2T + J z \left [ 1 - \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J z \left ( \tfrac{2}{Jz} \right )^{\tfrac{3}{2}} \sqrt{3\left | T_{N}-T \right | }\right ) \right ]} \;</math> | |||
<math>=\frac{1}{2T+Jz} \;</math> | |||
'''Case <math>T > T_{N}</math>:''' | |||
<math>\lim_{h\to 0} \frac{\partial m^{\dagger}}{\partial h^{\dagger}} \;</math> | |||
<math>=\frac{1}{T+Jz} \;</math> | |||
===At Neel Temperature=== | |||
<math>\lim_{T \to T_{N}}\chi^{\dagger}(h) =\frac{d\chi}{dT}|_{T\to T_{N}^{-}} - \frac{d\chi}{dT}|_{T\to T_{N}^{+}} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \frac{1}{2T+Jz} - \frac{1}{T+Jz} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \frac{-T}{2T^{2} + 3TJz +J^{2}z^{2}} \;</math> | |||
<math> = \mathbf{constant} \;</math> | |||
Latest revision as of 16:00, 7 April 2009
Ferromagnetism
| ||||||||
Given Information
- Classical Ising antiferromagnet on a ”bipartite” lattice given by Hamiltonian Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H = \frac{J}{2} \sum_{<ij>} S_i S_j -− h\sum_i S_i } ,
- Magnetization for Lattice A: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_A = < S^{(A)} > \;}
- Magnetization for Lattice B: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_B = < S^{(B)} > \;}
- Average magnetization: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = \frac{1}{2} (m_A + m_B ),}
- "Staggered” magnetization: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = \frac{1}{2} (m_A - m_B ),}
(Note: It's the difference between the two sublattices)
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = 1\;} for perfect ferromagnetic order
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = 1} for perfect antiferromagnetic order
Part 1
Use Weiss mean-field decoupling to replace one of the spins in the Hamiltonian by its thermal average. The Weiss field experienced by a given spin is then proportional to the sublattice magnetization on the other sublattice. Write down self-consistent equations for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_A\;} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_B\;} , and express them through the order parameters Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m\;} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger}} .
Given the Hamiltonian for a classical Ising antiferromagnet on a ”bipartite” lattice:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H = \frac{J}{2} \sum_{<ij>} S_i S_j -− h\sum_i S_i }
where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H\;} = Hamiltonian, the total energy of the system
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle J\;} = Interaction Energy where J < 0 because it’s anti-ferromagnetic
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S\;} = Spin with value of 1 or -1
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h\;} = Magnetic field energy from external sources that breaks the symmetry
Mean field approximation
Each spin on lattice A feels an average magnetization due to the sins on lattice B (and vice versa).
The magnetization on each sublattice:
- Sublattice A: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_A = < S_i^{A} > \;}
- Sublattice B: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_B = < S_j^{B} > \;}
Weiss Mean Field Approximation
Use this to decouple the spins to find the energy of each spin Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\epsilon A \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{i}^{A} } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{J}{2}S_i \sum_{j \epsilon B}^{z}\left \langle S_{j}^{B} \right \rangle - hS_i} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_B - h \right ) S_i} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = B_{eff}^{B}S_i}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{i}^{B} } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{J}{2}S_j \sum_{j \epsilon A}^{z}\left \langle S_{i}^{A} \right \rangle - hS_j} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_A - h \right ) S_j} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = B_{eff}^{A}S_j}
Conditions of the magnetization
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_{A} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \left \langle S_{i}^{A} \right \rangle \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = Z^{-1} \sum_{\left \{S \right \}} S_{i}e^{-\beta \left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_{B}-h \right )S_{i}} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta}{2}zm_{B}+h\beta \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_{B} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \left \langle S_{i}^{B} \right \rangle \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = Z^{-1} \sum_{\left \{S \right \}} S_{i}e^{-\beta \left ( \frac{J}{2}zm_{A}-h \right )S_{i}} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta}{2}zm_{A}+h\beta \right ) \;}
Average Magnetization
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m\equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} + m_{B} \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;}
Staggered Magnetization
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} \equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} - m_{B} \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) - h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;}
Part 2
Assume that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h = 0} , so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = 0} , and solve the mean-field equations by expanding in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger}} .
Determine the Neel (ordering) temperature, and calculate the order-parameter exponent.
The Néel Temperature
Chapter 8.4 of Solid State Physics
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_N = \frac{C \lambda}{2}}
where
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_N\;} is Néel Temperature, the onset temperature for antiferromagnetism
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C = \frac {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}{k_B}} is Curie constant
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda = \frac{4 \sum_{j \neq i} \jmath_{i j}} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2} = - \frac{4 z \jmath} {N \mu_0 g^2 \mu_b^2}}
Order Parameter Exponent Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta \;}
Expand Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger}} to the 3rd order
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = 0} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m_{A} = -m_{B}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2m^{\dagger} = \tanh \left ( \frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} \right ) - \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2m^{\dagger} = 2 \left ( \frac{J\beta }{2}zm^{\dagger} - \frac{\left( \frac{J\beta}{2} zm^{\dagger} \right )^3}{3} \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1 = \frac{J\beta}{2}z - \frac{\left( \frac{J\beta}{2}z \right )^3 m^{\dagger 2}}{3} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = \frac{1}{\frac{J\beta}{2}z}z \sqrt{3\left ( 1-\frac{2T}{Jz} \right )} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = \frac{2T}{Jz} \sqrt{3\left ( \frac{2Jz}{2Jz} - \frac{2T}{Jz} \right )} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = \frac{2T}{Jz} \sqrt {\frac{2}{Jz}} \sqrt{3\left ( \frac{Jz}{2} -T \right )} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m^{\dagger} = T \left ( \frac{2}{Jz} \right )^{\frac{3}{2}} \sqrt {3 \left ( T_{N} - T \right )} \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta = \frac{1}{2}}
Part 3
Now consider a small external field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h > 0\;} , so that both order parameters can assume a nonzero value (Note: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m\;} will be small). By keeping only the leading terms in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h\;} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m\;} , calculate the uniform spin susceptibility Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi = \partial m/ \partial h} , as a function of temperature. Plot Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi\;} as a function of temperature, and show that it has a cusp around Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_N\;} .
Average magnetization as a function of small external field m(h)
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m \equiv \frac{1}{2}\left ( m_{A} + m_{B} \right ) \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m = \frac{1}{2}\left [ \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m-m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) + \tanh \left ( -\frac{J\beta }{2}z\left ( m+m^{\dagger} \right ) + h\beta \right ) \right ] \;}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2 m = \left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]h + J \beta z m \left [ - 1 + \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle m(h) = \frac{\left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]h} { 2 + J \beta z m \left [ 1 - \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} \;}
Uniform Spin Susceptibility
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi(h) = \frac{\partial m}{\partial h} \;} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\left [ \beta - \beta \tanh^2\left ( \tfrac{1}{2}J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} { 2 + J \beta z \left [ 1 - \tanh^2 \left ( \tfrac{1}{2} J \beta z m^{\dagger} \right ) \right ]} \;}
Susceptibility vs. Temperature Graph
There is a cusp around Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{N}}
Part 4
Imagine adding a ”staggered” external field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle h^{\dagger}} , which would be positive on sublattice A, but would be negative on sublattice B. Concentrate on the system with no uniform field , and determine the behavior of the staggered susceptibility . Show that blows up at the Neel temperature.
Staggered Spin Susceptibility
Case :
Case :
At Neel Temperature






![{\displaystyle ={\frac {1-\tanh ^{2}\left({\tfrac {1}{2}}Jz\left({\tfrac {2}{Jz}}\right)^{\tfrac {3}{2}}{\sqrt {3\left|T_{N}-T\right|}}\right)}{2T+Jz\left[1-\tanh ^{2}\left({\tfrac {1}{2}}Jz\left({\tfrac {2}{Jz}}\right)^{\tfrac {3}{2}}{\sqrt {3\left|T_{N}-T\right|}}\right)\right]}}\;}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3d8261404e9b910b43e2b2d8c80f2b4e3fb0ee5f)






