PHY6937
Welcome to Phy 6937 Superconductivity and superfluidity
PHY6937 is a one semester advanced graduate level course. Its aim is to introduce concepts and theoretical techniques for the description of superconductors and superfluids. This course is a natural continuation of the "many-body" course PHY5670 and will build on the logical framework introduced therein, i.e. broken symmetry and adiabatic continuity. The course will cover a range of topics, such as the connection between the phenomenological Ginzburg-Landau and the microscpic BCS theory, Migdal-Eliashberg treatment of phonon mediated superconductivity, unconventional superconductivity, superfluidity in He-4 and He-3, and Kosterlitz-Thouless theory of two dimensional superfluids.
The key component of the course is the collaborative student contribution to the course Wiki-textbook. Each team of students is responsible for BOTH writing the assigned chapter AND editing chapters of others.
Team assignments: Spring 2011 student teams
Outline of the course:
Pairing Hamiltonian and BCS instability
To see the origins of superconductivity, it is helpful to look at a toy system, which we already know will give us superconducting behavior. This is useful because the toy system is only a simple change to a non-interacting electron gas. By adding in some small attractive interaction, we will arrive at a superconducting system! This interaction need only occur between two electrons occupying the same position in space (and necessarily having opposite spin!). Additionally, we still find the interesting behaviour regardless of the size of the interaction; the only requirement is that it be non-zero!
We can write the Hamiltonian of the system as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\sum_\vec{r}[\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r})(\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r}) +g\psi_\uparrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\vec{r})]}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ g<0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ |g|<<\epsilon_{F}} .
For this system, the partition function is:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D[\psi_\sigma ^{*} (\tau, \vec{r}), \psi_\sigma (\tau, \vec{r})]e^{-S_{BCS}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}=\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_\vec{r}[\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\tau, \vec{r})(\partial _\tau+\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\vec{r}) +g\psi_\uparrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow^\dagger (\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\vec{r})]}
It doesn't matter to multiply partition function by a constant:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z\rightarrow Z=\int D[\psi_\sigma ^{*} (\tau, \vec{r}), \psi_\sigma (\tau, \vec{r})] D[\Delta^{*}(\tau, \vec{r}),\Delta (\tau, \vec{r})] e^{-S_{BCS}-S_{\Delta}}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_\Delta=-\int_0^\beta d\tau\sum_{\vec{r}}\frac{1}{g}\Delta^*(\tau,\vec{r})\Delta(\tau,\vec{r})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^\dagger} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \psi} are grassmann numbers. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta^*} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta} are constant. Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_\uparrow\psi_\downarrow} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_\downarrow\psi_\uparrow} behave like constant.
Let's make a shift of the constant:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \rightarrow \Delta+g\psi_\uparrow\psi_\downarrow}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta^*\rightarrow \Delta^*+g\psi^\dagger_\downarrow\psi^\dagger_\uparrow}
Then, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_\Delta=-\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_{\vec{r}}{\{\frac{1}{g}\Delta^*\Delta + \Delta^*\psi_\uparrow \psi_\downarrow + \Delta\psi^\dagger_\downarrow \psi^\dagger_\uparrow+g\psi^\dagger_\downarrow \psi^\dagger_\uparrow \psi_\uparrow \psi_\downarrow}\}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align}S=&S_{BCS}+S_{\Delta}\\ =&\int_0^\beta d\tau \sum_{\vec{r}}\{ \psi_\sigma^\dagger(\tau, \vec{r})(\partial _\tau+\epsilon_\vec{p}-\mu)\psi_\sigma^\dagger (\tau, \vec{r}) \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \rightarrow S_0 \\ &+\Delta^*(\tau, \vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\tau, \vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\tau, \vec{r}) \Delta (\tau, \vec{r})\psi^\dagger_\downarrow (\tau, \vec{r})\psi^\dagger_\uparrow (\tau, \vec{r}) \rightarrow S_{int}\\ &-\frac{1}{g}\Delta^* (\tau, \vec{r})\Delta (\tau, \vec{r}) \} \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \rightarrow S_{\Delta} \end{align}}
then, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D[\psi_{\sigma}^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}),\psi_{\sigma}(\tau,\mathbf{r})]D[\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}),\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})]e^{-(S_{0}+S_{int.}+S_{\Delta})}} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\langle e^{-S_{int.}}\right\rangle _{0}\cong exp[\frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}+\frac{1}{4!}(\left\langle S_{int.}^{4}\right\rangle _{0}-3\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}^{2})]} by cumulant expansion, which guarantees that until the 2nd order, it is accurate.
Use Matsubara's Method
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_{\sigma}(\tau,\mathbf{r})=\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}e^{-i\omega_{n}\tau}\psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}), \omega_{n}=(2n+1)\frac{\pi}{\beta};}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})=\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}}e^{-i\Omega_{n}\tau}\Delta_{\mathbf{k}}(i\Omega_{n}), \omega_{n}=2n\frac{\pi}{\beta}.}
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{0}=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}[-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu]\psi_{\sigma}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}).}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int.}=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{2}}\underset{\omega_{n},\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}[\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\psi_{\uparrow}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{\mathbf{q}-k})\psi_{\downarrow}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})+\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})\psi_{\downarrow}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\uparrow}^{\dagger}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{\mathbf{q}-k})].}
The Fourier transform of 1 body Green's function is (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i=1,2} mean Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle {\mathbf{r}_{i},\tau_{i}}} ) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G(1-2)=\left\langle \psi(1)\psi^{*}(2)\right\rangle =\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n}}{\sum}\frac{1}{L^{D}}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}e^{-i\omega_{n}(\tau_{1}-\tau_{2})}e^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot(\mathbf{r}_{1}-\mathbf{r}_{2})}\frac{1}{-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} ,
so Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G_{\sigma}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})=\left\langle \psi_{\sigma}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\psi_{\sigma}^{\dagger}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})\right\rangle _{0}=\frac{\beta}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{-i\omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} .
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=\frac{2L^{2D}}{\beta^{4}}\underset{\omega_{n},\Omega_{n}}{\sum}\underset{\mathbf{k},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}[G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})]\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})=L^{D}\frac{2}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})} ,
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{3}}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})} is called pairing susceptibility.
Let's calculate it:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(\mathbf{q},i\Omega_{n})=\frac{L^{D}}{\beta^{3}}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}G_{\uparrow}^{0}(i\omega_{n},\mathbf{k})G_{\downarrow}^{0}(i\Omega_{n}-i\omega_{n},\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k})=\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\omega_{n},\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\frac{-1}{i\omega_{n}-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{i\omega_{n}-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow=\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\oint_{c}\frac{dz}{2\pi i}\frac{-1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}\frac{1}{e^{\beta z}+1}} .
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}+\mu}\times\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}=\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[\frac{1}{z-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}+\mu}-\frac{1}{z-i\Omega_{n}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-\mu}]} ,
and change the integral path to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow=-\frac{1}{L^{D}}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\mathbf{k}}{\sum}\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[\frac{1}{e^{\beta(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}-\mu)}+1}-\frac{1}{e^{\beta(-\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}+\mu)}+1}]=\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{1}{\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}}+\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}}-2\mu-i\Omega_{n}}[1-f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}})-f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{q}-\mathbf{k}})].}
In the static (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Omega_{n}=0} ) and uniform (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbf{q}=0} ) limit,Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1-2f(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}})=Tanh[\frac{\beta}{2}(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)]} .
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_{p}(0,0)=\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{Tanh[\frac{\beta}{2}(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)]}{2(\varepsilon_{\mathbf{k}}-\mu)}} .
In low energy, integrate the energy in the shell near Fermi energy:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\chi_{p}(0,0)\cong N(0)\int_{\hbar\omega_{D}}^{-\hbar\omega_{D}}d\xi\frac{Tanh[\xi\beta/2]}{2\xi}\cong N(0)\int_{0}^{-\hbar\omega_{D}}d\xi\frac{Tanh[\xi\beta/2]}{\xi}=N(0)ln[\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T}].}
Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\chi_{p}(0,0)\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})} .
If we ignore the higher order in the cumulant expansion,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}=-\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau\frac{1}{g}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})-\frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}=\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau[\frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})]\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r})\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})} .
Because the partition function Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D\Delta^{*}D\Delta e^{-S_{eff}(\Delta)}} , if we only consider the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors.
The superconductivity phase transition temperature is the temperature makes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})=0} , which is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}=\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}}\frac{2}{\pi}e^{\gamma}e^{-\frac{1}{N(0)\left|g\right|}}=1.134\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}}e^{-\frac{1}{N(0)\left|g\right|}}} .
Beyond the critical temperature, the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors in the partition function is just Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1} , the same as no cooper pair, which is normal state; below the critical temperature, the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} related factors in the partition function will diverge, which means superconductivity phase transition.
Finite Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{q}} (small) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ (\Omega_n=0)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi_p (q,0)-\chi_p (0,0)=\frac{1}{L^D} \sum_k \frac{1}{\beta} \sum_{i\omega_n}\frac{-1}{i\omega_n-\epsilon_k+\mu}(\frac{1}{i\omega_n+\epsilon_{q-k}-\mu}-\frac{1}{i\omega_n+\epsilon_{-k}-\mu}) }
for small ,
and
Thus,
Consider the states near the shell near fermi surface, we have
where,
and
So,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{N=-\infty}^{+\infty}\frac{1}{|2n+1|^3}=\sum_{n=0}^\infty\frac{2}{(2n+1)^3}=\frac{2}{\pi}\frac{7\zeta(3)}{8} }
where, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \zeta(3)} is Riemann zeta function.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <(\hat{q}\cdot \hat{v}_F)^2>_{F.S.}=\frac{1}{D} }
For spherical F.S. in 3D,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(\hat{q}\cdot\hat{v}_F)^2=\frac{2\pi}{4\pi}\int_{-1}^{1}dcos\theta cos^2\theta = \frac{1}{3} }
For circular F.S. in 2D,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int\frac{d\Omega}{\Omega_D}(\hat{q}\cdot\hat{v}_F)^2=\frac{1}{2\pi}\int_{0}^{2\pi}d\theta cos^2\theta = \frac{1}{2} }
Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \chi_p(q,0)-\chi_p(0,0) &=-\frac{1}{4}N(0)v_{F}^{2}q^{2}\frac{1}{D}\frac{\beta^{2}}{\pi^{2}}\frac{2}{\pi}\frac{7\zeta(3)}{8} \\ &=-N(0)\frac{7\zeta(3)}{16D\pi^{2}}q^{2}\frac{1}{\pi \hbar^{2}}\left(\frac{\hbar v_{F}}{k_{B}T}\right)^{2} \\ &\equiv-N(0)q^{2}\xi^{2} \end{align} }
So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{1}{2}\left\langle S_{int.}^{2}\right\rangle _{0}&=L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\chi_{p}(q,0)\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n}) \\ &=N(0)ln[\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T}]L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n})-L^{D}\frac{1}{\beta}\underset{\Omega_{n},\mathbf{q}}{\sum}N(0)q^{2}\xi^{2}\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}^{*}(i\Omega_{n})\Delta_{\mathbf{q}}(i\Omega_{n}) \end{align} } .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}=\underset{\mathbf{r}}{\sum}\int_{0}^{\beta}d\tau\left[\left(\frac{1}{\left|g\right|}-N(0)ln(\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma}}{\pi k_{B}T})\right)\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r})\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r})-N(0)\xi^{2}(\nabla\cdot\Delta^{*}(\tau,\mathbf{r}))(\nabla\cdot\Delta(\tau,\mathbf{r}))\right]} .
Note that the last term in the expression tells us that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff} } would increase if gradient of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta } is not zero.
Note that the above expression has a one-one correspondant to the Giznburg-Landau functional:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\int d^{D}r\left[ \alpha (T-T_{c}) |\Psi(\vec{r})|^{2}+\frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}}|\nabla \Psi(\vec{r})|^{2} \right] } ,
here Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Psi(\vec{r}) } corresponds to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \frac{\Delta(\tau,\vec{r})}{|g|N(0)a_{0}} } in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}} .
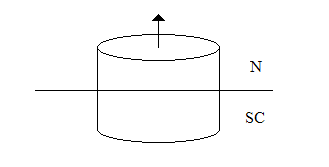
Little Parks experiment
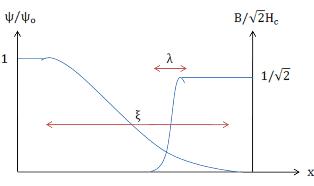
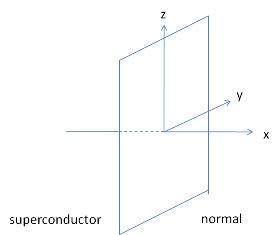
Refer to the fig, a thin shell of superconductor with radius R is shown and a small uniform magnetic field is passing through the hollow center of the cylinder. The experiment intends to show the variation of the critical temperature with change of the magnetic field passing through the hollow superconductor cylinder.
Before showing it, we first have to rewrite the Giznburg-Landau functional to make it taken the presence of magnetic field into account. Hamiltonian for a free electron moving in a magnetic field can be written as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2m}(p+\frac{eA}{c})^{2}\psi + V\psi = E\psi }
The physical observable magnetic field B would remain the same if we choose a different vector potential Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A\rightarrow A+ \nabla \chi } (ie perform gauge transformation). To maintain the same eigen-energy E which is observable, the wave function have to undergo a phase change: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi \rightarrow e^{i\phi}\psi } where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi=\frac{e}{c\hbar}\chi }
Now in our Hamiltonian, the wave function is arranged as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta^{*}(\tau,\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow (\tau,\vec{r})\psi_\downarrow (\tau,\vec{r}) + \Delta(\tau,\vec{r}) \psi_\downarrow^\dagger (\tau,\vec{r})\psi_\uparrow^\dagger (\tau,\vec{r}) }
since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi \rightarrow e^{i\phi}\psi } , so if we want the Hamiltonian to remind the same, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta } has to transform as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \rightarrow e^{-2i\phi}\Delta }
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Delta } corresponds to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ \Psi } in the Giznburg-Landau functional, so the Giznburg-Landau functional is modified as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\int d^{D}r\left[ \alpha (T-T_{c}) |\Psi(\vec{r})|^{2}+\frac{1}{2m^{*}}| ( \frac{\hbar \nabla}{i} - \frac{2e}{c}A(\vec{r}) ) \Psi(\vec{r})|^{2} \right] }
choose symmetric gauge: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}=\frac{1}{2}\vec{H}\times\vec{r}=\frac{1}{2}Hr\hat{\phi} }
In cylindrical coordinate: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{\nabla}=\hat{r}\frac{\partial}{\partial r} + \frac{\hat{\phi}}{r}\frac{\partial}{\partial \phi} + \hat{z}\frac{\partial}{\partial z} }
define unit flux as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi_{0}=\frac{hc}{2e} }
define fluxoid as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(R) = \pi HR^{2}\ } , so we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} F&=\int d^{D}r\left[ \alpha (T-T_{c})|\Psi(\vec{r})|^{2} +\frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}}| (\frac{1}{R}\frac{\partial}{\partial \phi} - \frac{ie}{\hbar c} HR )\Psi(\vec{r}) |^{2}+ \frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}}|\frac{\partial}{\partial z} \Psi(\vec{r}) |^{2} \right] \\ &=\int d^{D}r\left[ \alpha (T-T_{c})|\Psi(\vec{r})|^{2} +\frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}R^{2}}| (\frac{\partial}{\partial \phi} - \frac{i\Phi}{\Phi_{0}} )\Psi(\vec{r}) |^{2} \right] \\ \end{align} }
When Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi = N\Phi_{0}\ } , the critical temperature will remain the same and the phase of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi\ } is changed as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi \rightarrow e^{iN\phi} \Psi } . When Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi \neq N\Phi_{0}\ } , the critical temperature is found to vary as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}^{new}=T_{c}- \frac{\hbar^{2}}{2m^{*}R^{2}\alpha}\left (N-\frac{\Phi}{\Phi_{0}}\right )^{2}} . See the fig.
Microscopic derivation of the Giznburg-Landau functional
Let us consider the model of a metal close to the transition to the superconducting state. A complete description of its thermodynamic properties can be done through the calculation of the partition function.
The classical part of the Hamiltonian in the partition function, dependent of bosonic fields, may be chosen in the spirit of the Landauer theory of phase transition. However, in view of the space dependence of wave functions, Ginzberg and Landauer included in it additionally the first non vanishing term of the expansion over the gradient of the fluctuation field. Symmetry analysis shows that it should be quadratic. The weakness of the field coordinate dependence permits to omit the high-order terms of such an expansion. Therefore, the classical part of the Hamiltonian of a metal close to a superconducting transition related to the presence of the fluctuation Cooper pairs in it (the so called Ginzberg-Landauer functional)can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F[\psi(r)]=F_{n}+\int dV\{a\mid\psi(r)\mid^{2}+\frac{b}{2}\mid\psi(r)\mid^{4}+\frac{1}{4m}\mid\nabla\psi(r)\mid^{2}\}}
The basic postulate of G-L is that if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} is small and varies slowly in space, so we can expand the free energy in a series of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mid\psi(r)\mid^{2}} .These two terms should be adequate so long as one stays near the second-order phase transition at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}} , where the order parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mid\psi(r)\mid^{2}\rightarrow0} . Inspection of G-L functional shows that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta} must be positive if the theory is to be useful; otherwise the lowest free energy would occur for arbitrarily large values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mid\psi(r)\mid^{2}} , where the expansion is surely inadequate.
We already got the quadratic terms in the Ginzberg-Landauer by expanding Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <e^{-S_{int}}>} to the second order, and we are going to go the higher order. As we discussed, we expect that this term will be a negative value to keep Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}} as a negative value under Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}} . To catch this goal we start with the partition function:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=Z_{0}< e^{-S_{int}} >}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z_{0}=\int D\psi ^{*} D\psi D\Delta ^{*} D\Delta e^{-(S_{\Delta} +S_{0})}}
we can expand this average for smallFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} nearFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}} , for this perpose we can assume asecond order phase transition so that it increases continiously from zero to finite number after Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{c}}
we need to calculate the average of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-s_{int}}} which can be calculated by Tylor expansion:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-S_{int}}=<-S_{int}+\frac{1}{2}S_{int}^{2}-\frac{1}{3}S_{int}^{3}+\frac{1}{4!}S_{int}^{4}+...>}
=Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1-<S_{int}>+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}> -\frac{1}{3!}< S_{int}^{2}> +\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}> +...}
the odd power terms are zero because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <\psi _{\uparrow}(r,\tau )\psi _{\downarrow}(r,\tau ) > =0 }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =e^{\frac{1}{2}< S_{int}^{2}>}e^{\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>-\lambda }}
if we expand these two terms in to the second order the following expression can be got:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (1+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}>+\frac{1}{2}(<\frac{1}{2} S_{int}^{2}>)^{2} +...)(1+\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>+...)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =1+\frac{1}{2} < S_{int}^{2}>+\frac{1}{8}(< S_{int}^{2}>)^{2} +...)+\frac{1}{4!}< S_{int}^{4}>-\lambda +...}
can be choosed in such a way .......
so,
according to the expression we got before:
let's write in terems od for simplification. where
is a couple grassman number, so we do not need to be worry about the sign when these terms comute with other terms.
Recall the Fourier transform of one body Green function is:
To seek solution of which are independent using Feynman diagram
after getting integration over we will get and similarly by getting integration over we have
So, the final result can be written:
Now, we wish to perform gradiant expansion:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta ^{\ast }(2)=\Delta ^{\ast }(\frac{r_{2}+r_{3}}{2}+\frac{r_{2}-r_{3}}{2})=\Delta ^{\ast }(\frac{r_{2}+r_{3}}{2})+(\frac{r_{2}-r_{3}}{2})\nabla\Delta^{\ast }(\frac{r_{2}+r_{3}}{2})+... } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -12\int d^{D}R_{1,4}d^{D}R_{2,3}d^{D}\mu _{1,4}d^{D}\mu_{2,3}\Delta ^{\ast }(R_{1,4})\Delta ^{\ast }(R_{2,3})\Delta (R_{2,3}) \Delta (R_{1,4})\sum_{\omega_{n}}G(i\omega_{n},R_{1,4}-R_{2,3}+\frac{1}{2}(\mu _{1,4}+\mu _{2,3}))}
where:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R=\frac{1}{2}(R_{1,4}+R_{2,3})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r_{1}-r_{3}=\frac{1}{2}(\mu _{1,4}+\mu_{2,3})+\mu}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r_{2}-r_{4}=\frac{1}{2}(\mu _{1,4}+\mu_{2,3})-\mu}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq -12\int d^{D}R d^{D}\mu d^{D}\mu_{1.4}d^{D}\mu_{2,3}\Delta ^{\ast }(R)\Delta^{\ast } (R)\Delta (R)\Delta (R)\sum_{\omega _n}G(i\omega _{n},\mu +\frac{1}{2}(\mu_{1,4}+\mu _{2,3}))G(-i\omega _{n},\mu _{1,4})\times}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G(-i\omega _{n},\mu _{2,3})G(i\omega _{n},\mu +\frac{1}{2}(\mu_{1,4}+\mu _{2,3}))}
integrate overFailed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu} gives us Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l^{D}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta_{k_{1},k_{4}}}
and similarly Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu_{1,4}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l^{D}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta_{k_{1},-k_{2}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mu_{2,3}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l^{D}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta_{k_{1},-k_{3}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -12\int d^{D}R\left | \Delta (R)^{4} \right |\sum_{\omega _{n}}\frac{1}{L^{D}}\sum_{k}\frac{1}{(-i\omega _{n}+\varepsilon_{k}-\mu)^{2}}\frac{1}{(i\omega _{n}+\varepsilon_{-k}+\mu)^{2}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon _{k}=\epsilon _{-k}} because of timereversal symetry.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon _{k}-\mu =\xi }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -12\int d^{D}R\left | \Delta (R)\right |^{4}\sum_{\omega_{n}}\int_{-\infty }^{+\infty }d\xi N(\xi +\mu )\frac{1}{(-i\omega _{n}+\xi )^{2}}\frac{1}{(i\omega _{n}+\xi )^{2}} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I(p,q)=\int_{-\infty }^{+\infty }d\xi \frac{1}{(\xi -p)^{2}}\frac{1}{(\xi +p)^{2}}={\frac{\partial }{\partial p}}\int d\xi \frac{1}{\xi -p}\frac{1}{(\xi +p)^{2}} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial }{\partial p}2\pi i \frac{1}{(p+q)^{2}}=2\pi i\frac{-2}{(p+q)^{2}}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq -12\int d^{D}R\left | \Delta (R) \right |^{4}\sum_{\omega _{n}}N(0)\frac{-4\pi i}{(2i\omega _{n})^{3}} }
Starting from the microscopic model, we found that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z\backsimeq Z_{0}\int D\Delta*D\Delta e^{-S_{eff}} }
,
where the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 4^{th}}
order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta}
, and keeping only quadratic qradient terms, we have:
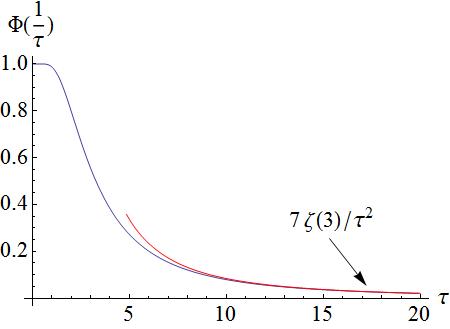
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}=\frac{1}{k_{B}T}\sum_{r}\left[\underset{A}{\underbrace{\left(\frac{1}{|g|}-N(0)In\left[\frac{2\hbar\omega_{D}e^{\gamma_{E}}}{\pi k_{B}T}\right]\right)}}|\Delta(r)|^{2}+N(0)\xi^{2}(\nabla\Delta*(r)).(\nabla\Delta(r))+\frac{1}{2}\underset{B}{\underbrace{\frac{7\zeta(3)N(0)}{8\pi^{2}k_{B}^{2}T^{2}}}}|\Delta(r)|^{4}\right]}
We can use this expression to make quantitative experimental predictions. The path integral over Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} is still imposible to carry out exactly, despite our approximations for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}} , because Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}} contains quartic terms in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} and so we are not dealing with a Gaussian integral. The approximation strategy whic we will pursue is called saddle point approxiation, which in our contetxt means that we will expand teh integrand about a solution which minimizes S_{eff} with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} . What we end up doing is replacing Z with , where is determined from At this point, let's seek uniform solutions to their equations, in whcih case we can drop the gradient terms in : where: and
Note that for : and
So ,
and
.
,
Since, we now have the approximate expression for the partition function we can calculate thermodynamic physical properties. the one we will focus on is the specific heat. Recall that,
if we only study the constribution to from the superconducting order parameter terms in , we have So, we see that if the double derivateive of with respect to is finite at , then the specific heat jumps at , since for . We are interested in the size of this jump. Therefore, we need to simply expand near . Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} vanishes at , we can simply evaluate Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B} at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_{C}} and expand Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A(T)=\frac{1}{|g|}-N(0)ln\left(\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}\left(T_{C}+T-T_{C}\right)}\frac{2e^{\gamma}}{\pi}\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{1}{|g|}-N(0)ln\left(\frac{2e^{\gamma}}{\pi}\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}T_{C}}\left(1+\frac{T-T_{C}}{T_{C}}\right)^{-1}\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\underset{vanishes\; by\; def.\; of\; T_{C}}{\underbrace{\frac{1}{|g|}-N(0)ln\left(\frac{2e^{\gamma}}{\pi}\frac{\hbar\omega_{D}}{k_{B}T_{C}}\right)}}by+N(0)ln\left(1+\frac{T-T_{C}}{T_{C}}\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow A(T)=N(0)ln\left(1+\frac{T-T_{C}}{T_{C}}\right)\simeq N(0)\frac{T-T_{C}}{T_{C}}+...}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow\frac{-A^{2}(T)}{2B(T)}\simeq-\frac{1}{2}\frac{N^{2}(0)\left(\frac{T-T_{C}}{T_{C}}\right)^{2}}{\frac{7\zeta(3)}{8\pi}\frac{N(0)}{k_{B}^{2}T^{2}}}+...}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta c_{V}\simeq-\frac{T_{C}}{2}\frac{8\pi^{2}}{7\zeta(3)}k_{B}^{2}N(0)+...}
What is the specific heat of a non-interacting electron gas?
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c_{V}^{(n)}=\frac{\partial}{\partial T}\left(2(from\; spin)\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{\left(\epsilon_{k}-\mu\right)}{e^{\frac{\epsilon_{k}-\mu}{k_{B}T}+1}}\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =2\int\frac{d^{D}k}{(2\pi)^{D}}\frac{-\left(\epsilon_{k}-\mu\right)}{\left(e^{\frac{\epsilon_{k}-\mu}{k_{B}T}+1}\right)^{2}}\left(\frac{-\left(\epsilon_{k}-\mu\right)}{k_{B}T^{2}}\right)e^{\left(\frac{\epsilon_{k}-\mu}{k_{B}T}\right)}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq2k_{B}N(0)\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}d\xi\left(\frac{\xi}{2k_{B}T}\right)^{2}\frac{1}{cosh^{2}\left(\frac{\xi}{2k_{B}T}\right)}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq4k_{B}^{2}TN(0)\underset{\frac{\pi^{2}}{6}}{\underbrace{\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}dx\frac{x^{2}}{cosh^{2}x}}}=\frac{2\pi^{2}}{3}k_{B}^{2}T}
So, if we measure the jump in the specific heat at T_c in the units of the normal state electronic contribution we find: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\Delta c_{V}}{c_{V}^{(n)}}=\frac{\frac{8\pi^{2}}{7\zeta(3)}k_{B}^{2}T_{C}N(0)}{\frac{2\pi^{2}}{3}k_{B}^{2}T_{C}N(0)}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{12}{7\zeta(3)}\simeq1.426} This is dimensionless number is a “famous” prediction of the BCS theory, although we derived it using different formalism. Let's check it with experiment:
First the caveats:
when specific is measured, all excitations contribute. Most importantly lattice vibrations (phonons) contribute as well. At low T, however, the phonon contribution drops of as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T^3} and we can neglect it if the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_C} is sufficiently low. In practice we have do an example:
| materials | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_C} | phonon contribution at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_C} |
| Al | 1.2K | 1% |
| Zn | 0.8K | 3% |
| Cd | 0.5K | 3% |
| Sn | 3.7K | 45% |
| In | 3.4K | 77% |
| Th | 2.4K | 83% |
| Pb | 7.2K | 94% |
Experimental data for Aluminum gives
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\Delta c_{V}}{c_{V}^{(n)}}\simeq 1.39}
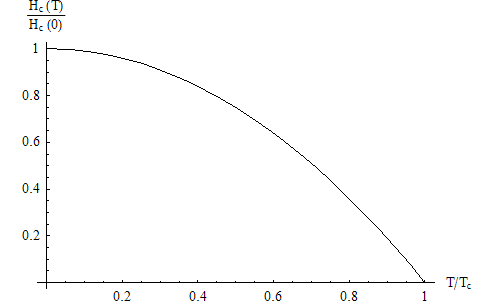
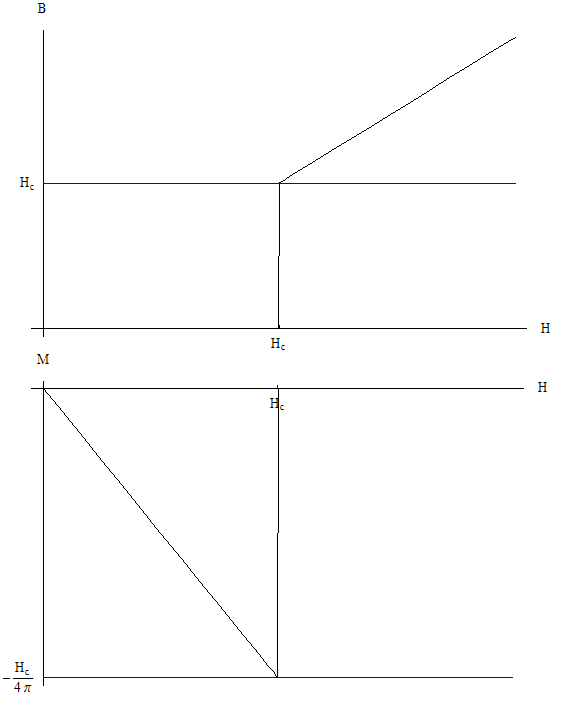
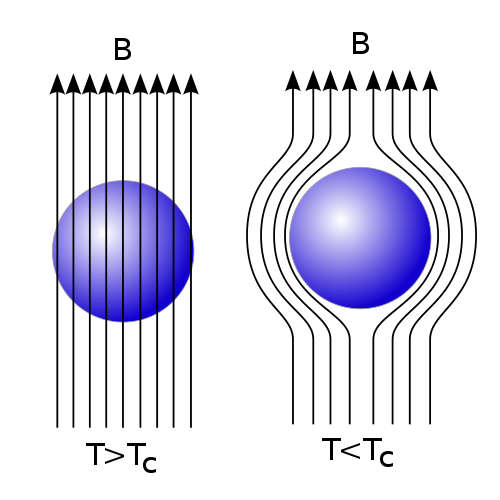
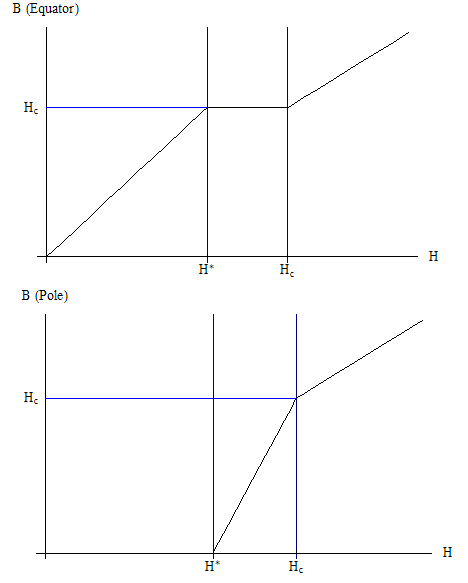
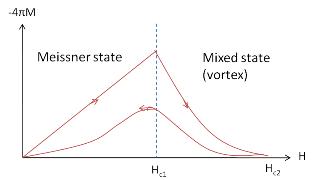
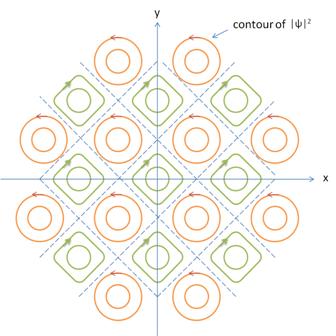
Effects of an applied magnetic field; Type I and Type II superconductivity
Derivation of the Ginzburg-Landau equations
Our starting point will be the Ginzburg-Landau (GL) free energy in the presence of an external magnetic field,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\int d^d \vec{r} \left [\alpha(T-T_c)|\Psi(\vec{r})|^2+\tfrac{1}{2}b|\Psi(\vec{r})|^4+\frac{\hbar^2}{2m}\left |\left (\nabla-i\frac{2e}{\hbar c}\vec{A}(\vec{r})\right )\Psi(\vec{r})\right |^2+\frac{1}{8\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}))^2-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}(\vec{r})\cdot\vec{A}(\vec{r})\right ],}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}} is the total vector potential and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{J}_{\text{ext}}} is an external current density, assumed to be controlled experimentally. This current satisfies
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times\vec{H}=\frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}},}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} is the external magnetic field. The expression is the sum of the energy due to the superconducting order parameter, with the magnetic field introduced via the gauge invariance argument given above, the energy of the magnetic field alone, and the work done by the superconductor to maintain the external current at a constant value.
Let us first derive the "saddle point" equations satisfied by the magnetic field in the normal state. In this case, we set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi} to zero everywhere and set
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left. \frac{\delta F}{\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r})}\right |_{\vec{A}=\vec{A}_\text{min}}=0.}
We will find this derivative by first finding the variation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F} in the free energy for this case, which is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^d \vec{r}' \left [\frac{1}{4\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))\cdot(\nabla\times\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}(\vec{r}')\cdot\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right ],}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\vec{A}} is a small variation in the vector potential; we assume that it vanishes on the "surface" of our system. We now transform the first term using the identity,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\nabla\times\vec{A})\cdot(\nabla\times\vec{B})=\nabla\cdot[\vec{A}\times(\nabla\times\vec{B})]+\vec{A}\cdot[\nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{B})],}
obtaining
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^d \vec{r}' \left [\frac{1}{4\pi}\nabla\cdot[\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\times(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))]+\frac{1}{4\pi}\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\cdot[\nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))]-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}(\vec{r}')\cdot\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right ].}
The first term is a "surface" term; since we assumed that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\vec{A}} vanishes everywhere on the "surface", we are left with just
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^d \vec{r} \left [\frac{1}{4\pi}[\nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))]-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}(\vec{r}')\right ]\cdot\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}').}
We conclude that the variational derivative that we are interested in is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta F}{\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r})}=\frac{1}{4\pi}[\nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{A}(\vec{r}'))]-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}(\vec{r}').}
At the "saddle point", this derivative is zero, so we obtain the equation,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{A})=\frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}.}
We may introduce the total magnetic field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\nabla\times\vec{A}} , thus obtaining
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times\vec{B}=\frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}.}
Comparing this to the definition of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{J}_{\text{ext}}} given above, we conclude that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\vec{H}} in the normal state. In reality, this will only be approximately true due to para- or diamagnetic effects in the metal, but these effects will be small in comparison to those due to superconductivity, which we will now derive.
First, we will apply the "saddle point" condition for the superconducting order parameter, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi} , which is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left. \frac{\delta F}{\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r})}\right |_{\Psi=\Psi_{\text{min}}}=0.}
Again, we start by finding the variation in the free energy in terms of a small variation Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Psi^{*}} in the order parameter:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^d \vec{r}' \left [\alpha(T-T_c)\Psi(\vec{r}')\,\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')+b|\Psi(\vec{r}')|^2\Psi(\vec{r}')\,\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')-\frac{e}{mc}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')\,\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')-\frac{1}{2m}\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')\right ]}
The last term is equal to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{2m}\left\{\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\cdot\left [\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')\,\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')\right ]-\left [\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r} ')\right ]\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')\right\}.}
The second term in this expression is a "surface" term. If we assume that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Psi^{*}} is zero on the "surface", then this term vanishes, leaving us with
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F=\int d^d \vec{r}' \left\{\alpha(T-T_c)\Psi(\vec{r}')+b|\Psi(\vec{r}')|^2\Psi(\vec{r}')-\frac{e}{mc}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')+\frac{1}{2m}\left [\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')\right ]\right\}\delta\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}').}
We can now immediately write down the variational derivative, which, upon being set to zero, gives us the first GL equation,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2m}\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )^2\Psi+\alpha(T-T_c)\Psi+b|\Psi|^2\Psi=0.}
We also need to minimize the free energy with respect to the magnetic field. We have already done this for the normal case, and there is only one more term that we need to consider in the superconducting case; we will therefore only treat this term. We can quickly write down the variation in the superconducting part of the free energy Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_{SC}} , which is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta F_{SC}=i\frac{e\hbar}{mc}\int d^d \vec{r}' \left [\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')\left (\nabla-i\frac{2e}{\hbar c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi(\vec{r}')-\Psi(\vec{r}')\left (\nabla+i\frac{2e}{\hbar c}\vec{A}(\vec{r}')\right )\Psi^{*}(\vec{r}')\right ]\cdot\delta\vec{A}(\vec{r}').}
Combining this result with the previous result for the normal metal, we obtain the second GL equation,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{4\pi}\nabla\times(\nabla\times\vec{A})-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_{\text{ext}}-\frac{e}{mc}\left (\Psi^{*}\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi-\Psi\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi^{*}\right )+\frac{4e^2}{mc^2}|\Psi|^2\vec{A}=0,}
or, introducing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{e}{m}\left (\Psi^{*}\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi-\Psi\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi^{*}\right )-\frac{4e^2}{mc}|\Psi|^2\vec{A}=\frac{c}{4\pi}\nabla\times(\vec{B}-\vec{H}).}
Given the definition of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} and the Maxwell equation (assuming static fields),
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times\vec{B}=\frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J},}
where is the total current density, we conclude that the left-hand side of this equation is the current density induced inside the superconductor.
Let us now suppose that we do not assume that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Psi^{*}} vanishes on the surface. It may then be shown that the following boundary condition holds on the surface (see P. G. de Gennes, Superconductivity in Metals and Alloys):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}\cdot\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )\Psi=\frac{i\hbar}{b_{dG}}\Psi.}
This relation holds for a superconductor-metal interface; for a superconductor-insulator interface, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b_{dG}\rightarrow\infty} . We may show that this condition implies that the normal component of the current density on the surface vanishes. If we multiply the above condition by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi^{*}} on both sides, we obtain
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}\cdot\Psi^{*}\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )\Psi=\frac{i\hbar}{b_{dG}}\Psi^{*}\Psi.}
Taking the complex conjugate of both sides gives us
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}\cdot\Psi\left (-\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )\Psi^{*}=-\frac{i\hbar}{b_{dG}}\Psi^{*}\Psi.}
Adding these two equations together gives us
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}\cdot\left [\left (\Psi^{*}\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi-\Psi\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\Psi^{*}\right )-\frac{4e}{c}|\Psi|^2\vec{A}\right ]=0.}
The left-hand side is proportional to the normal component of the current density inside the superconductor.
The GL Equations in Dimensionless Form
We will find it convenient to introduce dimensionless variables when working with the GL equations. We start by introducing a dimensionless order parameter, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=\frac{\Psi}{\Psi_0}} , where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi_0^2=\frac{\alpha(T_c-T)}{b}.}
We may rewrite the first GL equation in terms of this parameter as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2mb\Psi_0^2}\left (\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla-\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )^2\psi-(\left |\psi\right |^2-1)\psi=0,}
and the second as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{e\Psi_0^2}{mc}\left (\psi^{\ast}\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\psi-\psi\frac{\hbar}{i}\nabla\psi^{\ast}\right )-\frac{4e^2\Psi_0^2}{mc^2}\left |\psi\right |^2\vec{A}=\frac{1}{4\pi}\nabla\times[\nabla\times(\vec{A}-\vec{A}_0)],}
where we re-introduced Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}} into the right-hand side and also introduced Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}_0} , defined as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}=\nabla\times\vec{A}_0.}
Next, we introduce a dimensionless position vector,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{r}=\frac{1}{\lambda}\vec{r},}
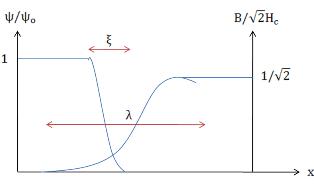
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda=\sqrt{\frac{mc^2}{16\pi e^2\Psi_0^2}}} is known as the penetration depth of the superconductor; we will see where this name comes from shortly. In terms of this vector, the first GL equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left (\frac{1}{\Psi_0\lambda\sqrt{2mb}}\frac{\hbar}{i}\tilde{\nabla}-\frac{1}{\Psi_0\sqrt{2mb}}\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}\right )^2\psi+(\left |\psi\right |^2-1)\psi=0}
and the second becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{4\pi e\lambda\Psi_0^2}{mc}\left (\psi^{\ast}\frac{\hbar}{i}\tilde{\nabla}\psi-\psi\frac{\hbar}{i}\tilde{\nabla}\psi^{\ast}\right )-\left |\psi\right |^2\vec{A}=\tilde{\nabla}\times[\tilde{\nabla}\times(\vec{A}-\vec{A}_0)].}
Finally, we introduce a dimensionless vector potential,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}=\frac{1}{\Psi_0\sqrt{2mb}}\frac{2e}{c}\vec{A}}
and the dimensionless parameter,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=\frac{\Psi_0\lambda\sqrt{2mb}}{\hbar}.}
In terms of these, the first GL equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left (-\frac{i}{\kappa}\tilde{\nabla}-\tilde{A}\right )^2\psi+(\left |\psi\right |^2-1)\psi=0}
and the second becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2\kappa}\left (\psi^{\ast}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}\psi-\psi\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}\psi^{\ast}\right )-\left |\psi\right |^2\vec{A}=\tilde{\nabla}\times[\tilde{\nabla}\times(\tilde{A}-\tilde{A}_0)].}
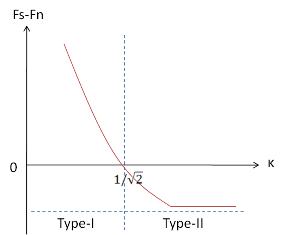
We see that our theory has a dimensionless parameter in it, namely Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa} , which is known as the Ginzburg-Landau parameter. We may write this parameter as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=\frac{\lambda\sqrt{2m\alpha(T_c-T)}}{\hbar}=\frac{\lambda}{\xi_\text{GL}},}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \xi_\text{GL}=\frac{\hbar}{2m\alpha(T_c-T)}}
is the GL coherence length. This tells us that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa} is the ratio of two length scales associated with the superconductor, namely the scale over which the order parameter "heals" (the coherence length Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \xi_\text{GL}} ) and that over which the magnetic field dies out (the penetration depth Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} , as we will demonstrate shortly). It also turns out that this parameter decides what type of superconductor we are dealing with. If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa < \tfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}} , then we have a Type I superconductor, while, if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa > \tfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}} , then we have a Type II superconductor.
We may now find the value of this parameter in the microscopic model we considered earlier. In that case, we found that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\hbar^2}{2m}=N(\mu)\xi^2=N(\mu)\frac{7\zeta(3)}{16\pi^2 d}\ell_T^2,}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N(\mu)} is the density of states at the Fermi level, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \xi} is the coherence length, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d} is the number of dimensions that we are working in, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l_T} is the thermal wavelength. We will state the result for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d=3} . Given that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ell_T=\frac{\hbar v_F}{k_B T}}
and that, in this case,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle N(\mu)=\frac{1}{2\pi^2}\frac{mk_F}{\hbar^2},}
we find that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=\sqrt{\frac{18\pi^3}{7\zeta(3)}}\frac{k_B T_c}{\sqrt{mc^2}\sqrt{e^2 k_F}}\left (\frac{c}{v_F}\right )^2.}
Note that we set in the expression for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l_T} ; this is because the GL theory is only valid just below the transition temperature. We may also express this in terms of the Fermi energy,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_F=\frac{p_F^2}{2m}=\tfrac{1}{2}p_F v_F.}
Doing so, we obtain
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=\sqrt{\frac{18\pi^3}{7\zeta(3)}}\frac{k_B T_c}{\sqrt{mc^2}\sqrt{\alpha}\sqrt{2E_F}}\left (\frac{c}{v_F}\right )^{3/2}=8\times 10^{-6}\cdot\frac{T_c\,[\text{K}]}{\sqrt{E_F\,[\text{eV}]}}\left (\frac{c}{v_F}\right )^{3/2}.}
In a typical metal, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle v_F\approx 10^5 - 10^6\,\tfrac{\text{m}}{\text{s}},} so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=(0.04 - 1.3)\cdot\frac{T_c\,[\text{K}]}{\sqrt{E_F\,[\text{eV}]}}.}
A Simple Example - The Strongly Type-I Superconductor With a Planar Surface
As a simple demonstration of the solution of the GL equations, let us consider a strongly Type I (Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa\ll 1} ) superconductor with a planar boundary between it and an insulator. Let us set up our coordinate system so that the boundary is at .
We apply a magnetic field along the Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z} axis,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}=H\hat{z}.}
We expect by symmetry that the total magnetic field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=B(x)\hat{z}} . We will choose our gauge such that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}=A_y(x)\hat{y}.}
We also take the order parameter to depend only on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x} . The first GL equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2\psi}{d\tilde{x}^2}+A_y^2\psi-\psi+\psi^3=0.}
Since we are taking Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa} to be small, the derivative term dominates, and we may therefore approximate this equation as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^2\psi}{d\tilde{x}^2}=0,}
so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(\tilde{x})=c_1+c_2\tilde{x}} . Our boundary condition states that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left. \frac{1}{i\kappa}\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}\right |_{\tilde{x}=0}=0,}
so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle c_2=0} . Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi=\Psi_0} in the bulk, we conclude that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(\tilde{x})=1} for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}<0} . Similarly, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi=0} deep into the insulating region, so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(\tilde{x})=0} for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}>0} .
Now we consider the second equation. In this case, it becomes, for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}<0} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\tilde{A}=\tilde{\nabla}\times(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})=\tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{B},}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\tilde{B}=\tilde{\nabla}\times(\tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{B}).}
The right-hand side is just
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{\nabla}\times(\tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{B})=-\frac{d^2\tilde{B}}{d\tilde{x}^2},}
so that the equation is now
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^2\tilde{B}}{d\tilde{x}^2}=\tilde{B}.}
The solution to the equation in simply Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}(\tilde{x})=\tilde{B}_{+}e^{\tilde{x}}+\tilde{B}_{-}e^{-\tilde{x}}} , or, in terms of dimensional quantities,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B(x)=B_{+}e^{x/\lambda}+B_{-}e^{-x/\lambda}.}
Since our superconductor is in the region Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x<0} , we must take Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{-}=0} . Furthermore, the field must equal the applied field at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=0} , so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B(x)=He^{x/\lambda}.}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x>0} , the second GL equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^2\tilde{B}}{d\tilde{x}^2}=0.}
The solution, in terms of dimensional quantities, is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B(x)=B_0+B_1 x} . We must set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_1=0} so that the field does not increase indefinitely as we move away from the superconductor. Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\vec{H}} in the normal state, we conclude that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B(x)=H} for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x>0} .
We have now shown why we called Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda} the penetration depth; it sets the length scale over which the magnetic field tends to zero inside the superconductor. We have also illustrated the expulsion of applied magnetic fields from the interior of a Type I superconductor; this is known as the Meissner effect.
Thermodynamics of Type-I Superconductors in Magnetic Fields
In a bulk superconductor, surface effects are unimportant; for now, we will assume that the order parameter Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi} is constant everywhere in the superconductor and that magnetic fields are completely expelled. In this case, the free energy per unit volume of the superconductor is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_s=\alpha(T-T_c)\Psi_0^2+\tfrac{1}{2}b\Psi_0^4=-\frac{\alpha^2}{2b}(T-T_c)^2.}
This is known as the condensation energy (per unit volume). We see that we can "save" energy by going into the superconducting state.
In the normal state, only the magnetic field terms are present, so that the free energy is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_n=\int d^d\vec{r}\,\left [\frac{1}{8\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A})^2-\frac{1}{c}\vec{J}_\text{ext}\cdot\vec{A}\right ].}
We may substitute in
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J}_\text{ext}=\nabla\times\vec{H}}
to get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_n=\int d^d\vec{r}\,\left [\frac{1}{8\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A})^2-\frac{1}{4\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{H})\cdot\vec{A}\right ]=\int d^d\vec{r}\,\left [\frac{1}{8\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A})^2-\frac{1}{4\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A})\cdot\vec{H}\right ] =\int d^d\vec{r}\,\left [\frac{1}{8\pi}B^2-\frac{1}{4\pi}\vec{B}\cdot\vec{H}\right ].}
In the normal state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\vec{H}} , so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_n=-\int d^d\vec{r}\,\frac{1}{8\pi}H^2.}
The free energy per unit volume of the normal state is therefore
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle f_n=-\frac{1}{8\pi}H^2.}
We see that, overall, we also "save" energy in the normal state. Which state we go into depends on which "saves" more energy. We may now define a field at which the "savings" are the same for both states; this is the (thermodynamic) critical field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} (sometimes also denoted Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_{cm}} ). Equating the free energies per unit volume of each state, we obtain
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\alpha^2}{2b}(T-T_c)^2=\frac{1}{8\pi}H_c^2,}
or, solving for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c=\sqrt{\frac{4\pi}{b}}\alpha\left |T-T_c\right |.}
We see, therefore, that GL theory predicts a linear dependence of the critical field on the temperature. This is not what is observed experimentally, however. The dependence of the critical field on temperature in many real superconductors can, in fact, be modeled with the following empirical law:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c(T)=H_c(0)\left [1-\left (\frac{T}{T_c}\right )^2\right ].}
We plot this relation below.
We see that, near Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} , the dependence of the critical field on temperature does indeed follow the linear relation that we just derived. However, it deviates from said relation when we go far below Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} . This is not surprising; the GL theory from which we obtained the linear relation is only valid near Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} . In order to obtain a more accurate relation, we require a theory for the superconductor that is valid far below Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} .
We may rewrite our dimensionless vector potential and magnetic field in terms of the critical field. We may write our expression for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c^2=4\pi b\left |\Psi_0\right |^4.}
Our dimensionless vector potential is then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}=\frac{2e}{c}\frac{\Psi_0}{\sqrt{2mb\Psi_0^4}}\vec{A}=\frac{2e}{c}\Psi_0\sqrt{\frac{4\pi}{2mH_c^2}}\vec{A}=\sqrt{\frac{8\pi e^2\Psi_0^2}{mc^2}}\vec{A}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}H_c \lambda}\vec{A}.}
We may rewrite the definition of the magnetic field as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\tilde{\nabla}\times\sqrt{2}H_c\tilde{A},}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{A}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}H_c}\vec{B}=\tilde{B}.}
Magnetic Properties of a Type-I Superconductor
In the approximation stated above, we find that, in the superconducting state (the applied magnetic field is below ), the total magnetic field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}} is completely expelled, while Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\vec{H}} when the applied field is above Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} . From the defining relation for the magnetization Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{M}} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\vec{H}+4\pi\vec{M},}
we find that the magnitude of the magnetization increases linearly with, and points in the opposite direction to, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} , in the superconducting state, but is zero in the normal state. We plot these two relations below.
We will now demonstrate two consequences of the total expulsion of a magnetic field from a superconductor.
1) The total field is always tangential to the surface of a superconductor.
First, recall the Maxwell equation,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\cdot\vec{B}=0.}
Let us now consider the boundary between a superconductor and a normal region:
We will find the flux of a magnetic field through the "pill box" shown above. Let the area of the circular surfaces be Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta A} , and let us assume that the contribution from the "tube" part of the surface is negligible (we will assume that its height is small compared to the radius of the circular surfaces). Then the total flux may be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{n,\bot}\cdot\Delta A-B_{sc,\bot}\cdot\Delta A,}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{n,\bot}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{sc,\bot}} are the components of the magnetic field normal to the circular surfaces of the "pill box" in the normal and superconducting regions, respectively. The Maxwell equation stated above is equivalent to the statement that the total flux through a closed surface, such as the "pill box" we consider here, must be zero. Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{n,\bot}=B_{sc,\bot}.}
However, we know that the superconductor completely expels magnetic fields, so that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}_{sc}=0} . Therefore, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{n,\bot}=0} , thus proving that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}_n} can only have tangential components.
2) As a direct consequence of (1), a type-I superconductor in an external magnetic field always carries an electrical current near its surface.
To show this, first recall the Maxwell equation (Ampere's Law in the case of static fields),
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times\vec{B}=\frac{4\pi}{c}\vec{J},}
or, in integral form,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \oint_{\partial S}\vec{B}\cdot d\vec{\ell}=\frac{4\pi}{c}I,}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S} is a surface with bounding curve Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \partial S} , the line integral on the left is taken in the direction that would cause a right-handed screw to advance in the direction of the normal to the surface, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle I} is the total current passing through the surface.
Let us now, once again, consider the boundary between a superconductor and a normal region and a rectangular contour drawn around the boundary:
In this case, because the magnetic field is zero in the superconducting region and because the magnetic field in the normal region is tangential to the surface of the superconductor, then, assuming that the lengths of segments 14 and 23 are small compared to that of segments 12 and 34. In this case, the left-hand side of the Maxwell equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \oint_{\partial S}\vec{B}\cdot d\vec{\ell}=B\ell_{12},}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \ell_{12}} is the length of segment 12. The right-hand side, on the other hand, is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{4\pi}{c}I=\frac{4\pi}{c}K\ell_{12},}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle K} is the surface current density (per unit length). This implies that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=\frac{4\pi}{c}K,}
or, in vector form,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{K}=\frac{c}{4\pi}\hat{n}\times\vec{B},}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}} is the normal to the surface pointing into the normal region. In this case, we see that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{K}} points into the page or screen.
An Example: The Magnetic Field Around a Spherical Superconductor
These observations lead to interesting conclusions for superconductors with geometries more complex than a cylinder inside a magnetic field parallel to its axis. Consider, for example, a spherical superconductor, depicted below:
As we can see, the magnetic field near the equator is stronger than the applied field, while the field at the poles vanishes. This implies that the magnetic field near the equator may exceed Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} even if the applied field is less than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} , simply due to the geometry of the sample. In fact, for a certain range of fields,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (1-\eta)H_c<H<H_c,}
the sample will enter an intermediate state, in which superconducting and normal regions coexist. The above inequality holds for any geometry, in fact, and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} is known as the demagnetizing factor of the sample. Its value will depend on the exact geometry of the sample; we will now show that, for a sphere, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta=\tfrac{1}{3}} . We will do so by solving Maxwell's equations for a spherical superconductor of radius Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R} in a uniform applied magnetic field Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}=H\hat{z}} . The boundary conditions for this problem are
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}(\vec{r})=H\hat{z}}
for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{r}|\rightarrow\infty} and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}\cdot\vec{B}(\vec{r})=0}
on the surface of the sphere. Outside the superconductor, the equations satisfied by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}} are
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\cdot\vec{B}=0}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times\vec{B}=0.}
The second equation implies that there are no current sources outside the superconductor. It also implies that we may write the magnetic field in terms of a scalar potential. We therefore write
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\nabla\Phi+H\vec{z}.}
Substituting this into the first equation, we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla^2\Phi=0,}
which is just Laplace's equation. Our boundary conditions for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi} are, in spherical coordinates,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(\vec{r}\rightarrow\infty)=0}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}+H\cos{\theta}=0}
on the surface. Laplace's equation in spherical coordinates is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{r^2}\frac{\partial}{\partial r}\left (r^2\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}\right )+\frac{1}{r^2\sin{\theta}}\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta}\left (\sin{\theta}\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial\theta}\right )+\frac{1}{r^2\sin^2{\theta}}\frac{\partial^2\Phi}{\partial\phi^2}=0.}
Because our system has azimuthal symmetry, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi} should be independent of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi} . Therefore, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(\vec{r})=\Phi(r,\theta)} and Laplace's equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{r^2}\frac{\partial}{\partial r}\left (r^2\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}\right )+\frac{1}{r^2\sin{\theta}}\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta}\left (\sin{\theta}\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial\theta}\right )=0.}
Multiplying by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r^2} , we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial}{\partial r}\left (r^2\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}\right )+\frac{1}{\sin{\theta}}\frac{\partial}{\partial\theta}\left (\sin{\theta}\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial\theta}\right )=0.}
We will now attempt to solve this equation by separation of variables. Let us try a solution of the form
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(r,\theta)=R(r)\chi(\theta).}
Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{R}\frac{d}{dr}\left (r^2\frac{dR}{dr}\right )=-\frac{1}{\chi}\frac{1}{\sin{\theta}}\frac{d}{d\theta}\left (\sin{\theta}\frac{d\chi}{d\theta}\right ).}
We see that we have an expression depending only on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} on one side and one depending only on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta} on the other. The only way for this equation to be satisfied is if both equal a constant, which we will call Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\lambda} . Let us first consider the equation for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi} . This equation is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sin{\theta}}\frac{d}{d\theta}\left (\sin{\theta}\frac{d\chi}{d\theta}\right )=\lambda\chi.}
If we make the substitution, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x=\cos{\theta}} , into this equation, we get
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d}{dx}\left [(1-x^2)\frac{d\chi}{dx}\right ]=\lambda\chi.}
We recognize this as the Legendre differential equation. The only physically interesting solutions to this equation occur when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda=-l(l+1)} , in which case we find that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi} is a Legendre polynomial,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi(\theta)=P_l(\cos{\theta}).}
The first few Legendre polynomials are Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_0(x)=1} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_1(x)=x} , and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle P_2(x)=\tfrac{1}{2}(3x^2-1)} .
Now we will consider the equation for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R} . If we take Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi(\theta)=P_l(\cos{\theta})} , then our differential equation for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R} becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d}{dr}\left (r^2\frac{dR}{dr}\right )=l(l+1)R,}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d^2 R}{dr^2}+2r\frac{dR}{dr}-l(l+1)R=0.}
This is an Euler-Cauchy differential equation. Let us assume a power law dependence for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R(r)=r^\alpha.}
The equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha(\alpha-1)r^\alpha+2\alpha r^\alpha-l(l+1)r^\alpha=0.}
The exponent Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha} must therefore satisfy
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha(\alpha+1)=l(l+1).}
This equation has two possible solutions, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha=l} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \alpha=-(l+1)} , so the general solution for the differential equation is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R(r)=A_l r^l+\frac{B_l}{r^{l+1}}.}
The general solution to the original partial differential equation is then a linear combination of all possible products Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle R(r)\chi(\theta)} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(r,\theta)=\sum_{l=0}^{\infty}\left (A_l r^l+\frac{B_l}{r^{l+1}}\right )P_l(\cos{\theta}).}
Since Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r^l\rightarrow\infty} for all Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l>0} , we must set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_l=0} for all such values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l} . We will also set Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_0=0} , so that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(r,\theta)=\sum_{l=0}^{\infty}\frac{B_l}{r^{l+1}}P_l(\cos{\theta}).}
We now apply the boundary condition,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}+H\cos{\theta}=0,}
to obtain
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{l=0}^{\infty}\frac{(l+1)B_l}{R^{l+2}}P_l(\cos{\theta})=H\cos{\theta}.}
By inspection, we find that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_l=0} for all Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l\neq 1} . For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle l=1} , we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_l=\tfrac{1}{2}HR^3.}
Therefore, the solution for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi} is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(r,\theta)=\frac{HR^3}{2r^2}\cos{\theta},}
and thus Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}} is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\tfrac{1}{2}HR^3\nabla\left (\frac{\cos{\theta}}{r^2}\right )+H\hat{z}.}
In spherical coordinates, the gradient operator is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\Phi=\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial r}\hat{r}+\frac{1}{r}\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial\theta}\hat{\theta}+\frac{1}{r\sin{\theta}}\frac{\partial\Phi}{\partial\phi}\hat{\phi},}
so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=-H\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3(\cos{\theta}\hat{r}+\tfrac{1}{2}\sin{\theta}\hat{\theta})+H\hat{z}.}
We recognize that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{z}=\cos{\theta}\hat{r}-\sin{\theta}\hat{\theta}} , so that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{B}=\left [1-\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3\right ]H\cos{\theta}\hat{r}-\left [1+\tfrac{1}{2}\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3\right ]H\sin{\theta}\hat{\theta}.}
We now want to find the point at which the magnetic field has the largest magnitude. The magnitude of this vector is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{B}|^2=H^2\left [1+\tfrac{1}{2}\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3\right ]^2+3\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3\left [\tfrac{1}{4}\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3-1\right ]\cos^2{\theta}}
We see that the second term, which is proportional to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \cos^2{\theta}} , is clearly negative when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r>R} . Therefore, we must make the size of this term as small as possible. This may be done by letting Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta=\tfrac{\pi}{2}} . For this value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta} , we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{B}|^2=H^2\left [1+\tfrac{1}{2}\left (\frac{R}{r}\right )^3\right ]^2.}
This function is monotonically decreasing as we increase Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} ; therefore, we choose the smallest possible value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r} , which is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r=R} . This gives us
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{B}|^2=\tfrac{9}{4}H^2,}
or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\vec{B}|=\tfrac{3}{2}H} . Therefore, the total magnetic field achieves its maximum magnitude at the equator of the sphere, where it is three halves the applied field. Therefore, if the applied field is larger than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\tfrac{2}{3}H_c} , the field at the equator would become larger than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_c} , which would destroy the sphere's superconductivity at that point. Therefore, the sphere enters an intermediate state when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tfrac{2}{3}H_c<H<H_c} , so that the demagnetizing factor Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta=\tfrac{1}{3}} .
Superconductors of General Geometries
In general, the maximum magnetic field on the surface of a superconductor will be related to the applied field by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{\text{max}}=\frac{H}{1-\eta}.}
We will now list the values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} for a few different geometries.
| Geometry | Demagnetizing factor Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \eta} |
| Cylinder with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} parallel to its axis | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0} |
| Cylinder with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} perpendicular to its axis | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tfrac{1}{2}} |
| Sphere | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tfrac{1}{3}} |
| Infinite thin plate with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{H}} perpendicular to the plate | Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1} |
The sample will enter the intermediate state at the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=H^{\ast}} at which Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_{\text{max}}=H_c} , which is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H^{\ast}=(1-\eta)H_c.}
Therefore, the superconductor will be in the intermediate state when
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (1-\eta)H_c<H<H_c.}
We will now show plots of the magnetic field of a sphere at the equator and at the pole as a function of the applied field (for details on how to derive the dependence in the intermediate state, see P. G. DeGennes, Superconductivity of Metals and Alloys).
In the intermediate state, the energy per volume of both the normal and superconducting states is the same. Therefore, the energy per unit area of a "domain wall" will be the dominant contribution.
Surface Term of the Free Energy
The free energy in the reduced units can be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\int d^3 r \,\left[\alpha (T-T_c)|\Psi|^2 + \frac{b}{2} |\Psi|^4 + \frac{\hbar^2}{2m} |(\nabla - \frac{2ei}{\hbar c}\vec{A})\Psi|^2 + \frac{1}{8\pi}(\nabla\times\vec{A})^2 - \frac{1}{4\pi}\vec{H}\cdot\vec{B}\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\lambda^D\int d^D\tilde{r}\,\left[\alpha (T-T_c)|\Psi_o|^2 |\psi|^2 + \frac{b}{2} |\Psi_o|^4 |\psi|^4 + \frac{\hbar^2}{2m_{GL}}|\Psi_o|^2|(\frac{1}{\lambda}\tilde{\nabla}-\frac{2ei}{\hbar c}\sqrt{2}\lambda H_c \tilde{A})\psi|^2 + \frac{1}{8\pi \lambda^2} (\sqrt{2}\lambda H_c)^2 (\tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{A})^2 - \frac{2\lambda^2 H_c^2}{4\pi \lambda^2} \tilde{H}\cdot\tilde{B}\,\right]}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{r}=\frac{r}{\lambda}, \tilde{H}=\frac{H}{\sqrt{2}H_c}}
Using the following relations:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle b|\Psi_o|^4 = \frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\alpha (T-T_c)}{b|\Psi_o|^2} = -1}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\Psi_o|^2 \frac{4e^2}{mc^2} = \frac{1}{4\pi\lambda^2}}
one has
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D\tilde{r}\,\left[-|\psi|^2+\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+|(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi|^2+\tilde{B}^2-2\tilde{H}\cdot\tilde{B}\,\right]}
Now let's consider the gradinet term:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi|^2 = \,\left[ (\frac{-1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi^*\,\right]\,\left[ (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi\,\right] = (-\tilde{A}\psi^*)(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi - (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}\psi^*)(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi }
Integration by part leads the 2nd term to the form:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\tilde{\nabla}\cdot(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\psi^*(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi) + \psi^*(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi)}
where the 1st term needs to be evaluated on the surface where it vanishes by the boundary condition for an insulating interface. Hence the gradient term becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})\psi|^2 = \psi^*(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi}
Assuming that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}} satisfy the GL equation, namely,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2 \psi = \psi - \psi |\psi|^2}
we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^*(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi = |\psi|^2-|\psi|^4}
and the free energy becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F=\frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D \tilde{r} \,\left[-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+\tilde{B}^2-2\tilde{H}\cdot\tilde{B}\,\right]}
This is true at the saddle point. Now the free energy for the normal state and the superconducting state are given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_n=\frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D \tilde{r} \,\left[-\tilde{H}^2\,\right]}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s=\frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D \tilde{r} \,\left[-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+\tilde{B}^2-2\tilde{B}\cdot\tilde{H}\,\right]}
Therefore, the surface free energy of the interface is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D \tilde{r} \,\left[-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+\tilde{B}^2-2\tilde{B}\cdot\tilde{H}+\tilde{H}^2\,\right] = \frac{\lambda^D H_c^2}{4\pi}\int d^D \tilde{r} \,\left[-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})^2\,\right]}
As shown in the figures below, type-I superconductor (left) has positive wall energy while type-II superconductor (right) negative wall energy.
Free Energy of a Normal-Superconducting Interface
Now let's consider the free energy of a normal-superconducting interface. Recall the GL equations:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi - \psi + \psi|\psi|^2 = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(\psi^*\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}\psi + c.c.)-\tilde{A}|\psi|^4 =\tilde{\nabla}\times(\tilde{\nabla}\times\tilde{A})}
Assume that the interface is along y-z plane and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}//\hat{z}} . We can choose Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}(\tilde{r})=\hat{y}\tilde{A}(\tilde{x})} which implies the order parameter depends only on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}} . Then the GL equation become
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2\psi}{d\tilde{x}^2}+\tilde{A}_y^2(\tilde{x})\psi -\psi + \psi^3 = 0} (*)
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}_y(\tilde{x})\psi^2 = \frac{d^2\tilde{A}_y(\tilde{x})}{d\tilde{x}^2}}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}(\psi^*\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}\psi + c.c.) = 0}
Note that we can choose Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} to be real since the coefficients are real. Now let's manipulate Eq.(*):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}\frac{d^2\psi}{d\tilde{x}^2}+\tilde{A}_y^2\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}\psi - \frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}\psi + \frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^3 = 0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2+\frac{1}{2}\tilde{A}_y^2\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2 - \frac{1}{2}\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2 + \frac{1}{4}\frac{d}{\tilde{x}}\psi^4 = 0}
Integrating we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2 + \frac{1}{2}\int d\tilde{x}\tilde{A}_y^2\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2 - \frac{1}{2}\psi^2 + \frac{1}{4}\psi^4 = const.}
This integral can be further manipulated:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int d\tilde{x}\tilde{A}_y^2\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2 = \int d\tilde{x}\,\left[\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}(\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2)-\frac{d\tilde{A}_y^2}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2\,\right] = \tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2 - 2\int d\tilde{x}\tilde{A}_y\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}}\psi^2 = \tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2 - 2\int d\tilde{x}\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}}\frac{d^2\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}^2} = \tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2 - \int d\tilde{x}\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}(\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}})^2 = \tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2 - (\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}})^2 = const.}
Thus, Eq.(*) becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2+\frac{1}{2}\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2-\frac{1}{2}(\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}})^2 - \frac{1}{2}\psi^2 + \frac{1}{4}\psi^4 = const.}
or,
To determine the const., note that as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\rightarrow -\infty} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi \rightarrow 1} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}_y \rightarrow 0} , so
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0 + 0 + 1 - \frac{1}{2} = const.}
Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\kappa^2}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2+(\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}})^2+\psi^2(1-\tilde{A}_y^2)-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4 = \frac{1}{2}}
Consider the case where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa << 1} , that is, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda << \xi} . The main contribution to the surface energy comes from the region where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}=0} but Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi < 1} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\kappa^2}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2+\psi^2-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4=\frac{1}{2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\kappa^2}(\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}})^2 = \frac{1}{2}-\psi^2+\frac{1}{2}\psi^4 = \frac{1}{2}(1-\psi^2)^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(1-\psi^2)}
Note that the minus sign is from the experimental setup. Further,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\psi}{1-\psi^2}=-\frac{\kappa}{\sqrt{2}}d\tilde{x};\frac{1}{1-\psi^2}=\frac{1}{2}(\frac{1}{1-\psi}+\frac{1}{1+\psi})}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle ln\frac{1+\psi}{1-\psi}=-\sqrt{2}\kappa \tilde{x}+const.}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1+\psi(\tilde{x})}{1-\psi(\tilde{x})}=const.\times e^{-\sqrt{2}\kappa \tilde{x}}}
Requiring Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=0} at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}=0} gives Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle const.=1} Now we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi = \frac{e^{-\sqrt{2}\kappa \tilde{x}}-1}{e^{-\sqrt{2}\kappa \tilde{x}}+1}=-tanh\frac{\kappa \tilde{x}}{\sqrt{2}}}
whose curve is shown in the figure. Moreover,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{8\pi}L^2\lambda\int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}(1-\psi^4)}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}(1-\psi^4)=\int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}(1+\psi^2)(1-\psi^2) =\int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}(1+\psi^2)(-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa})\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}} =-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa}\psi |_{-\infty}^{0}-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa}\int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}\psi^2\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa}\psi |_{-\infty}^{0}-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3\kappa}\int_{-\infty}^{0}d\tilde{x}\frac{d\psi^3}{d\tilde{x}} = -\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa}\psi |_{-\infty}^{0}-\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3\kappa}\psi^3 |_{-\infty}^{0} = \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\kappa}+\frac{\sqrt{2}}{3\kappa} = \frac{4\sqrt{2}}{3\kappa}}
Hence one has
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{8\pi}L^2\lambda\cdot\frac{4\sqrt{2}}{3\kappa}}
Below we show that given Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}_y} satisfying the GL equation, the surface energy of the surface vanishes at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=1/2} :
(**)
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}L^2\lambda\int d\tilde{x}\,\left[(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})^2-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4\,\right]}
Assume Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=1/\sqrt{2}} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}L^2\lambda\int d\tilde{x}\,\left[(\frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}})^2-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4\,\right]}
Choosing
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\psi^2}
then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=0} and the 2nd GL equation becomes
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}_y\psi^2=\frac{d^2\tilde{A}_y}{d\tilde{x}^2}=\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\psi^2)=-\sqrt{2}\psi\frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{d\psi}{d\tilde{x}}=-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\tilde{A}_y\psi}
Insert this into Eq.(**):
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{1}{2}\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2+(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}-\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\psi^2)^2+\psi^2(1-\tilde{A}_y^2)-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4-\frac{1}{2}=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2\kappa^2}\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2+\frac{1}{2}-\psi^2+\frac{1}{2}\psi^4+\psi^2-\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2-\frac{1}{2}\psi^4-\frac{1}{2}=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}-1)\tilde{A}_y^2\psi^2=0}
Therefore, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa=1/\sqrt{2}} as expected.
In summary, for type-I superconductor (positive surface energy) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa < 1/\sqrt{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} is uniform in the bulk and jumps at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} . On the other hand, for type-II superconductor (negative surface energy) Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa > 1/\sqrt{2}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} is not uniform in the bulk but grows continuously when crossing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} from above.
The "Landau-Level"-Like States above Hc and the Upper Critical Field Hc2
Now we have the surface free energy:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}\lambda^3\int d^3\tilde{r} \,\left[-|\psi|^2+|(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi|^2+\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4+(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})^2\,\right]}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}=\frac{B}{\sqrt{2}H_c}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{A}=\frac{A}{\sqrt{2}\lambda H_c}}
Assuming 2nd order phase transition and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T=T_c} , then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi\rightarrow 0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}\rightarrow\tilde{H}} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}\lambda^3\int d^3\tilde{r} \,\left[-|\psi|^2+|(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi|^2\,\right]}
Using the Landau gauge:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{A}=\hat{y}Hx=\hat{y}\frac{H}{\sqrt{2}H_c}\frac{x}{\lambda}=\hat{y}\tilde{H}\tilde{x}}
Recall
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\tilde{\nabla}}{i}-\tilde{A})^2\psi-\psi=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}})^2\psi+(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{d}{d\tilde{y}}-\tilde{H}\tilde{x})^2\psi+(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{d}{d\tilde{z}})^2\psi-\psi=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{d\tilde{x}^2}\psi+(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{d}{d\tilde{y}}-\tilde{H}\tilde{x})^2\psi-\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{d\tilde{z}^2}\psi-\psi=0}
Let
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(\tilde{x},\tilde{y},\tilde{z})=e^{ik_z\tilde{z}}e^{ik\tilde{y}}\Phi_k(\tilde{x})}
then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{ik_z\tilde{z}}e^{ik\tilde{y}}\,\left[-\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{d\tilde{x}^2}\Phi+(\frac{k}{\kappa}-\tilde{H}\tilde{x})^2\Phi+\frac{k_z^2}{\kappa^2}\Phi-\Phi\,\right]=0}
Let
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\tilde{H}X=\frac{k}{\kappa}-\tilde{H}\tilde{x};\frac{d}{d\tilde{x}}=\frac{dX}{d\tilde{x}}\frac{d}{dX}=\frac{d}{dX}}
then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{ik_z\tilde{z}}e^{ik\tilde{y}}(-\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{dX^2}+\tilde{H}^2 X^2+\frac{k_z^2}{\kappa^2}-1)\Phi=0}
Recall for a harmonic oscillator we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{-\hbar^2}{2m}\frac{d^2}{dx^2}+\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2 x^2)\Psi=E\Psi}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E=\hbar\omega(n+\frac{1}{2})}
Comparison leads to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-\hbar^2}{2m}\rightarrow\frac{-1}{\kappa^2};\frac{1}{2}m\omega^2\rightarrow\tilde{H}^2;\hbar\omega\rightarrow\frac{2\tilde{H}}{\kappa}}
and the eigenvalues
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2\frac{\tilde{H}}{\kappa}(n+\frac{1}{2})+\frac{k_z}{\kappa}-1}
The exponent is zero when
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 2\frac{\tilde{H}}{\kappa}(n+\frac{1}{2})+\frac{k_z}{\kappa}-1=0}
If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=0} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k_x=0} we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{H}_{c2}=\kappa=\frac{H_{c2}}{\sqrt{2}H_c}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_{c2}=\sqrt{2}\kappa H_c}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa < 1/\sqrt{2}} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_{c2}<H_c} , the bulk is preempted by the Meissner phase. On the other hand, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa > 1/\sqrt{2}} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_{c2}>H_c} , the bulk undergoes a 2nd order phase transition into a mixed state in which normal state and superconducting state coexist.
Now let's look at the wavefunction at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_{c2}} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{dX^2}+\tilde{H}_{c2}^2 X^2)\Phi=\lambda\Phi;\tilde{H}_{c2}=\kappa}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (-\frac{1}{\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{dX^2}+\kappa^2 X^2)\Phi=\lambda\Phi}
Let
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{d}{dX}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\kappa X = a}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{\sqrt{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{d}{dX}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\kappa X = a^+}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [a,a^+]=1} Note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle a^+ a=\frac{-1}{2\kappa^2}\frac{d^2}{dX^2}+\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2 X^2-\frac{1}{2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (2a^+ a+1)\Phi=\lambda\Phi}
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \lambda=1} we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{d}{dX}+\kappa K)\Phi=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi=const.\times e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2 X^2}}
and the order parameter is of the form
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle const.\times e^{ik\tilde{y}}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(\tilde{x}-\frac{k}{\kappa^2})^2}}
Abrikosov Solution of the GL Equation for Type-II Superconductor near Hc2
Note. In this section we will drop the "tilde(~)" on relevant quantities and recover it when necessary.
Since the conditions along the entire superconductor are uniform, we seek a linear combination of solutions centered through equal intervals, namely,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^{(0)}=\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_n e^{ikn\hat{y}} e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}}
or,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_n e^{ikny}\phi_n(x)}
with
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi_n(x)=e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}}
Consider the solution to GL equation at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H} slightly less than Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa} .The 2nd GL equation gives
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times(\nabla\times A^{(1)})=\frac{-i}{2\kappa}(\psi^{(0)*} \nabla\psi^{(0)}-\psi^{(0)}\nabla\psi^{(0)*})-|\psi^{(0)}|^2 A^{(0)}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \nabla\times B=\hat{x}\frac{\partial B_z}{\partial y}-\hat{y}\frac{\partial B_z}{\partial x}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A=\hat{y}A_y(x,y);\nabla\times A=\hat{z}\frac{\partial A}{\partial x}}
For the x-component, we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial B_z}{\partial y}=\frac{\partial^2 A_y}{\partial x\partial y}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{-i}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}\Sigma_{m=-\infty}^{\infty}C_n^* e^{-ikny}\phi_n(x)(\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\phi_m(x))C_me^{ikmy} + \frac{i}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}\Sigma_{m=-\infty}^{\infty}C_n^* e^{-ikny}(\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\phi_n(x))\phi_m(x)C_m e^{ikmy}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{-i}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n,m}C_n^* C_m e^{-ik(n-m)y}\,\left[\phi_n(x)\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\phi_m(x)-\phi_m(x)\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\phi_n(x)\,\right]}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [...]=-\kappa^2(x-\frac{km}{\kappa^2})\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x)+\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x) =k(m-n)\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial B_z}{\partial y}=\frac{-i}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n,m}C_n^* C_m e^{-ik(n-my)}k(m-n)\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x) =frac{\partial}{\partial y}\,\left[\frac{1}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n,m}C_n^* C_m e^{-ik(n-m)y}\phi_n(x)\phi_m(y)\,\right] =\frac{\partial}{\partial y}\,\left[\frac{-1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2\,\right]}
Similarly, for the y-component we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{\partial B_z}{\partial x}=\frac{-i}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n,m}\,\left[C_n^* e^{-ikny}\phi_n(x)ikm e^{ikmy}\phi_m(x)C_m+C_n^* ikne^{-ikny}\phi_n(x)e^{ikmy}\phi_m C_m\,\right]-\kappa x|\psi^{(0)}|^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{1}{2\kappa}\Sigma_{n,m}\,\left[k(n+m)-2\kappa^2x\,\right]C_n^* C_me^{-ik(n-m)y}\phi_m(x)\phi_n(x)}
Note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial}{\partial x}\,\left[\phi_m(x)\phi_m(x)\,\right]=\,\left[-\kappa^2(x-\frac{km}{\kappa^2})-\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})\,\right]\phi_m(x)\phi_n(x)=-\,\left[2\kappa^2x-k(m+n)\,\right]\phi_m(x)\phi_n(x)}
Therefore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{\partial B_z}{\partial x}=\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\,\left[\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2\,\right]}
Now we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial B_z}{\partial y}=-\frac{\partial}{\partial y}\,\left[\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2\,\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial B_z}{\partial x}=-\frac{\partial}{\partial x}\,\left[\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2\,\right]}
or,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_z(x,y)=f(x)-\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_z(x,y)=g(y)-\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2}
which implies
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_z(x,y)=const.-\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2}
At points where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^{(0)}=0} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_z(x,y)=H_z} . So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B_z(x,y)=H_z-\frac{1}{2\kappa}|\psi^{(0)}|^2}
Note that the correction (the 2nd term) comes from induced current. Furthermore,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_y=xH_z-\frac{1}{2\kappa}\int dx |\psi^{(0)}|^2}
Now let's consider the 1st GL equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A)^2\psi-\psi+\psi|\psi|^2=0}
which is solced by dropping the non-linear term and A and leads to Hc2.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A^{(0)}-A^{(1)})^2(\psi^{(0)}+\psi^{(1)})-(\psi^{(0)}+\psi^{(1)})+(\psi^{(0)}+\psi^{(1)})|\psi^{(0)}+\psi^{(1)}|^2=0}
To 0th oeder:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A^{(0)})^2\psi^{(0)}-\psi^{(0)}=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_y^{(0)}=\kappa x}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^{(0)}=\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_ne^{ikny}\phi_n(x)}
To 1st order:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A^{(0)})^2\psi^{(1)}-(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A^{(0)})\cdot A^{(1)}\psi^{(0)}-A^{(1)}\cdot(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{\nabla}{i}-A^{(0)})\psi^{(0)}-\psi^{(1)}+\psi^{(0)}|\psi^{(0)}|^2=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A_y^{(1)}=(H-\kappa)x-\frac{1}{2\kappa}\int^{x}|\psi|^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi^{(1)}=\Sigma_{-\infty}^{\infty}e^{ikny}\psi_n^{(1)}(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \,\left[\frac{-1}{\kappa^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{\partial}{\partial y}-\kappa x)^2 \,\right] \Sigma_n e^{ikny} \psi_n^{(1)}(x)= \Sigma_n e^{ikny} \,\left[\frac{-1}{\kappa^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+(\frac{kn}{\kappa}-\kappa x)^2\,\right]\psi_n^{(1)}(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{\partial}{\partial y}-\kappa x)\,\left[(H-\kappa)x-\frac{1}{2\kappa}\int^x |\psi^{(0)}|^2\,\right]\Sigma_n e^{ikny} \phi_n(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_ne^{ikny}(-\frac{kn}{\kappa}+\kappa x)(H-\kappa)x\phi_n(x) +(\frac{1}{\kappa}\frac{1}{i}\frac{\partial}{\partial y}-\kappa x)\frac{1}{2\kappa}\int^x dx'\Sigma_{m,p}C_m^*C_pe^{-ikmy}e^{ikpy}\phi_m(x')\phi_p(x')\Sigma_nC_ne^{ikny}\phi_n(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_ne^{ikmy}(-\frac{kn}{\kappa}+\kappa x)(H-\kappa)\phi_n(x)+\Sigma_{n,m,p}C_nC_m^*C_pe^{ik(n-m+p)y}(\frac{n-m+p}{\kappa}-\kappa x)\frac{1}{2\kappa}\phi_n(x)\int^x dx'\phi_m(x')\phi_p(x')}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Sigma_nC_ne^{ikny}(-\frac{kn}{\kappa}+\kappa x)(H-\kappa)x\phi_n(x)+\Sigma_{n,m,p}C_nC_m^*C_pe^{ik(n-m+p)y}(\frac{kn}{\kappa}-\kappa x)\frac{1}{2\kappa}\phi_n(x)\int^x dx'\phi_m(x')\phi_p(x')}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\Sigma_ne^{ikny}\psi_n^{(1)}(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Sigma_{n,m,p}C_nC_m^*C_pe^{ik(n-m+p)y}\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x)\phi_p(x)}
Add them up, we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Sigma_ne^{ikny}\,\left[\frac{-1}{\kappa^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+(\frac{kn}{\kappa}-\kappa x)^2 + 1\,\right]\psi^{(1)}=\Sigma_ne^{ikny}C_n2x(H-\kappa)(\frac{kn}{\kappa}-\kappa x)\phi_n(x)-\Sigma_{n,m,p}e^{ik(n-m+p)y}C_nC_m^*C_p\,\left[(\frac{(2n-m+p)k}{\kappa}-2\kappa)\frac{1}{2\kappa}\phi_n(x)\int^xdx'\phi(x')\phi(x')+\phi_n(x)\phi_m(x)\phi_p(x)\,\right]}
Multiplying the whole equation by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle e^{-ikNy}} and integrating over the variable y leads to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \,\left[\frac{-1}{\kappa^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+(\frac{kN}{\kappa}-\kappa)^2-1\,\right]\psi_N^{(1)}(x)=C_N2x(H-\kappa)(\frac{kx}{\kappa}-\kappa x)\phi_N(x)-\Sigma_{m,p}C_{N+m-p}C_m^*C_p\,\left[(\frac{k}{\kappa}(2N+2m-2p-m+p)-2\kappa x)\frac{1}{2\kappa}\phi_{N+m-p}(x)\int^xdx'\phi_m(x')\phi_p(x')+\phi_{N+m-p}(x)\phi_m(x)\phi_p(x)\,\right]}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi_n(x)=e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}}
The above equation has this (inhomogeneous) form:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{O}|\psi_N^{(1)}>=|\Phi>}
Consider the homogeneous version of this equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{O}|\chi>=0}
The only way for the inhomogeneous equation to have a solution is if
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <\chi|\Phi>=0}
Thus we need
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \,\left[\frac{-1}{\kappa^2}\frac{\partial^2}{\partial x^2}+(\frac{kN}{\kappa}-\kappa x)^2-1\,\right]\chi(x)=0}
Let
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \chi(x)=e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kN}{\kappa^2})^2}=\phi_N(x)}
then the identity is satisfied.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0=C_N2(H-\kappa)\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}dxx(\frac{kN}{\kappa}-\kappa x)\phi_N^2(x)-\Sigma_{m,p}C_{N-p+m}C_m^*C_p \,\left[\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}dx\phi_N(x)(\frac{k}{2\kappa^2}(2N+m-p)-x)\phi_{N+m-p}(x)\int^xdx'\phi_m(x')\phi_p(x') +\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}dx\phi_N(x)\phi_{N+m-p}(x)\phi_m(x)\phi_p(x)\,\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\kappa}(1-\frac{H}{\kappa})C_N-\Sigma_{m,p}C_{N-p+m}C_m^*C_p(1-\frac{1}{2\kappa^2})\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}dx\phi_N(x)\phi_{N+m-p}(x)\phi_m(x)\phi_p(x)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\kappa}(1-\frac{H}{\kappa})C_N+\Sigma_{m,p}C_{N-p+m}C_m^*C_p(1-\frac{1}{2\kappa^2})\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}e^{-\frac{k^2}{2\kappa^2}((m-p)^2+(N-p)^2)}}
Now, multiply both sides by Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_N^*} and sum over N we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0=(1-\frac{H}{\kappa})\Sigma_NC_N^*C_N+\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}(\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}-1)\Sigma_{N,m,p}C_N^*C_{N-p+m}C_m^*C_pe^{-\frac{k^2}{2\kappa^2}((m-p)^2+(N-p)^2)}}
Taking the spatial average results in
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0=(1-\frac{H}{\kappa})<|\psi|^2>+(\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}-1)<|\psi|^4>}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 1=\frac{\frac{H}{\kappa}-1}{\frac{1}{2\kappa^2}-1}\frac{<|\psi|^2>}{<|\psi|^4>}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <B>=H-\frac{1}{2\kappa}<|\psi|^2>=H-\frac{1}{2\kappa}\frac{H-\kappa}{\frac{1}{2\kappa}-\kappa}\frac{<|\psi|^2>^2}{<|\psi|^4>}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <B>=H-\frac{\kappa -H}{2\kappa^2-1}\frac{1}{\beta_A}}
or, recovering the "tilde(~)",
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <\tilde{B}>=\tilde{H}-\frac{\kappa -\tilde{H}}{2\kappa^2-1}\frac{1}{\beta_A}}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A=\frac{<|\psi|^4>}{<|\psi|^2>^2}}
is the famous Abrikosov parameter which does not depend on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{H}} or the normalization of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} . It is easy to see that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A} is always greater than or equal to 1:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^2=<|\psi|^2>+\delta |\psi|^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <|\psi|^4>=<|\psi|^2>^2+2<|\psi|^2><\delta |\psi|^2>+<(\delta |\psi|^2)^2>}
Note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <\delta |\psi|^2>=0}
Hence
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <|\psi|^4>=<|\psi|^2>^2+<(\delta |\psi|^2)^2>\ge <|\psi|^2>^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A=\frac{<|\psi|^4>}{<|\psi|^2>^2}\ge 1}
The equality holds when Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=1} .
Recall that the surface free energy is given by
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle F_s-F_n=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}\lambda^3\int d^3\tilde{r}\,\left[(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})^2-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4\,\right]}
In order to obtain the thermodynamic potential which when differentiated with respect to H gives B we need to subtract Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{H}^2} (which came from the normal term) from the above expression:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega=\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}\lambda^3\int d^3\tilde{r}\,\left[(\tilde{B}-\tilde{H})^2-\tilde{H}^2-\frac{1}{2}|\psi|^4\,\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{H_c^2}{4\pi}L^3\,\left[\frac{1}{4\kappa^2}<|\psi|^4>-\tilde{H}^2-\frac{1}{2}<|\psi|^4>\,\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{H_c^2}{8\pi}L^3\,\left[\frac{1-2\kappa^2}{2\kappa^2}<|\psi|^4>-2\tilde{H}^2\,\right]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{H_c^2}{8\pi}L^3\,\left[\frac{2}{1-2\kappa^2}\frac{1}{\beta_A}(\tilde{H}-\kappa)^2-2\tilde{H}^2\,\right]}
Note that for type-II superconductor, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \kappa >1/\sqrt{2}} , the whole expression is negative. So, to lower the the free energy we need to minimize Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A} .
Knowing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega} we can obtain Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{B}} by differentiating Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega} with respect to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{H}} and hence obtain the magnetization which is measurable.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle -\frac{4\pi}{L^3}\frac{\partial\Omega}{\partial H}=B}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{H}=\frac{H}{\sqrt{2}H_c};\frac{\partial}{\partial H}=\frac{\partial\tilde{H}}{\partial H}\frac{\partial}{\partial H}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}H_c}\frac{\partial}{\partial\tilde{H}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=-\frac{H_c}{2\sqrt{2}}4(\frac{1}{\beta_A}\frac{\tilde{H}-\kappa}{1-2\kappa^2}-\tilde{H}) =-\frac{2H_c}{\sqrt{2}}\,\left[\frac{1}{\beta_A}\frac{1}{1-2\kappa^2}(\frac{H}{\sqrt{2}H_c}-\frac{H_{c2}}{\sqrt{2}H_c})-\frac{H}{\sqrt{2}H_c}\,\right]=\frac{1}{\beta_A}\frac{1}{1-2\kappa^2}(H-H_{c2})+H\le H}
for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H<H_{c2}} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle B=H+4\pi M}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 4\pi M=B-H=\frac{1}{\beta_A}\frac{1}{2\kappa^2-1}(H-H_{c2})<0}
which means the type-II superconductor behaves like a diamagnet.
Abrikosov Vortex States
Now let's follow the step of Abrikosov to derive the vortex structure in type-II superconductor.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}C_ne^{ikny}e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2} =C\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}e^{ikny}e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_n=C} .
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^2=|C|^2\Sigma_{m,n}e^{-ikny}e^{ikmy}e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(\tilde{x}-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2(\tilde{x}-\frac{km}{\kappa^2})^2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int d\tilde{x}d\tilde{y}d\tilde{z}|\psi|^2=L_yL_z\Sigma_n\int d\tilde{x}|C|^2e^{-\kappa^2(\tilde{x}-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}=L_yL_z\frac{\kappa^2}{k}\tilde{L}_x\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{\kappa}|C|^2}
Thus
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle <|\psi|^2>=|C|^2\frac{\sqrt{\pi}\kappa}{k}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^4=|C|^4\Sigma_{m,n}\Sigma_{s,t}e^{-ikmy}e^{ikny}e^{-iksy}e^{ikty}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{km}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{ks}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{kt}{\kappa^2})^2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \int dxdydz|\psi|^4=L_yL_z|C|^4\Sigma_{m,n,s}\int dx e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{km}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{kn}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{ks}{\kappa^2})^2}e^{-\frac{\kappa^2}{2}(x-\frac{k(m-n+s)}{\kappa^2})^2}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =L_yL_z|C|^4\Sigma_{m,n,s}\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}e^{-\frac{k^2}{2\kappa^2}((m-n)^2+(n-s)^2)}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =L_yL_z|C|^4\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{k}\frac{\kappa^2}{k}\tilde{L}_x\Sigma_{m,n}e^{-\frac{k^2}{2\kappa^2}(m^2+n^2)}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\frac{k}{\kappa}(\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}e^{-\frac{k^2n^2}{2\kappa^2}})^2}
Minimize Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A} with respect to k we find that at minimum
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k=\sqrt{2\pi}\kappa}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=C\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}e^{i\sqrt{2}\pi n\kappa\tilde{y}}e^{-\frac{1}{2}(\kappa\tilde{x}-\sqrt{2}\pi n)^2}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A=1.18034} and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi=Ce^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2\tilde{x}^2}\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}e^{i\sqrt{2\pi}n\kappa\tilde{y}}e^{\sqrt{2\pi}n\kappa\tilde{x}}e^{-\pi n^2}=Ce^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2\tilde{x}^2}\Sigma_{n=-\infty}^{\infty}e^{\sqrt{2\pi}\kappa (\tilde{x}+i\tilde{y})n}e^{-\pi n^2}=Ce^{-\frac{1}{2}\kappa^2\tilde{x}^2}\theta_3 (\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\kappa (\tilde{y}-i\tilde{x}),e^{-\pi})}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \theta_3} is the Jacobi elliptic theta function. The Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi} vanishes at points:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{y}=\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}(2m-1)}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tilde{x}=\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}(1-2n)\rightarrow\sqrt{\frac{\pi}{2}}\frac{1}{\kappa}(2n-1)}
Obviously, the zeros form a square lattice of spacing Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2\pi}}{\kappa}} in reduced units.
Now consider the current lines:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{j}=\frac{-i}{2\kappa}(\psi^*\nabla\psi-\psi\nabla\psi^*)-|\psi|^2\tilde{A}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j_x=\frac{1}{2\kappa i}\Sigma_{m,n}k(n-m)C_m^*C_ne^{-ik(m-n)\tilde{y}}\phi_n(\tilde{x})\phi_m(\tilde{x})=\frac{-1}{2\kappa}\frac{\partial}{\partial\tilde{y}}|\psi|^2}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j_y=\frac{1}{2\kappa}\frac{\partial}{\partial\tilde{x}}|\psi|^2}
The lines of constant current magnitude are determined by the following condition:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{j_y}{j_x}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle j_xdy-j_ydx=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{2\kappa}(\frac{\partial}{\partial y}|\psi|^2)dy-\frac{1}{2\kappa}(\frac{\partial}{\partial x}|\psi|^2)dx=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle d|\psi|^2=0}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^2=const.}
which means the current flows along the contours of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |\psi|^2} .
However, the actual solution which minimizes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A} is a triangular lattice for which the coefficients satisfy
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle C_{n+4}=C_n;C_0=C_1=C;C_2=C_3=-C}
and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta_A=1.16} .
Going below Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} with the Saddle Point Approximation
So, previously all of this work has shown us the behaviour of a superconducting system near Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} only. If we want to go into lower temperatures, we will have to make a careful saddle-point approximation, following Bardeen, Cooper, and Schrieffer (BCS). Once again, we can start from our microscopic 'toy' Hamiltonian, and gain useful information.
Recall that the partition function can be written,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \mathbb{Z} = \int{d\Delta^* d\Delta} \left[ \int{D\psi^* D\psi \ e^{-S_{BCS} - S_{\Delta}}} \right] }
Where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{\Delta} = \frac{-1}{g} \int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau} \int{d^3r}\Delta^*(\vec{r},\tau) \Delta(\vec{r},\tau) }
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS} = S_0 + S_{int} \;\; \text{where} \;\; S_0 = \int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau}\int{d^3r}\left[ \psi_{\sigma}^*(\vec{r},\tau) \left( \frac{\partial}{\partial \tau} + \epsilon_p - \mu \right) \psi_{\sigma}(\vec{r},\tau) \right] } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \text{and} \;\; S_{int} = \int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau}\int{d^3r} \left[\Delta^*(\vec{r},\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau) + \Delta(\vec{r},\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r}.\tau) \right]}
Previously, we used a cumulant expansion around Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = T_c} to find the Ginzburg-Landau equations, along with the assumption that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} was small. Now, if we throw away this assumption, pray that fluctuations are small, and that there is only one saddle point, we will be able to successfully describe the superconducting state deep below Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} by demanding:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial S_{eff}[\Delta]}{\partial \Delta*} = 0 }
Self-Consistency Equation
The solution of this functional derivative equation will give the value of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta = \Delta_{sp}} at the saddle point (and also the self-consistency equation for this mean-field theory.)
To that end:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}[\Delta] = S_{\Delta} - \ln \left( \int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}\right) }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial S_{\Delta}}{\partial \Delta^*(\vec{r},\tau)} = \frac{-\Delta(\vec{r},\tau)}{g}}
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial \left[ -\ln\left(\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}\right) \right] }{\partial \Delta^*(\vec{r},\tau)} = \frac{-1}{\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}} \int{D\psi D\psi*} \frac{\partial e^{-S_{BCS}}}{\partial \Delta^*} = \frac{\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}} \frac{\partial S_{BCS}}{\partial \Delta^*}}{\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}} }
and, since
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial S_{BCS}}{\partial \Delta^*} = \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)}
We arrive at
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\partial \left[ -\ln\left(\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}\right) \right] }{\partial \Delta^*(\vec{r},\tau)} = \frac{\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}} \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)}{\int{D\psi D\psi^*} \;\; e^{-S_{BCS}}} = \langle \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\rangle_{BCS} }
So that, from the saddle-point condition, we find the Self-Consistency Equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\Delta_{sp}(\vec{r},\tau)}{g} = \langle\psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\rangle_{BCS} }
This contains the same information as the Ginzburg-Landau equations, but also more, as we can now go far below Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T_c} . Evaluation of this cam be done formally, but is difficult and not terribly enlightening. Instead, we will search for a solution in which <math\psi</math> is independent of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{r}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau} , similar to our solution near will be independent of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{r}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau} .
First, it is useful to write down the action in momentum and frequency space, before evaluating the correlator.
Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi(\vec{r},\tau) = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{1}{\sqrt{V}} e^{i\vec{k}\cdot\vec{r}}\psi_{k}(i\omega_n)}
For the three terms in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}} , we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_0 = \int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau}\int{d^3r}\left[ \psi_{\sigma}^*(\vec{r},\tau) \left( \frac{\partial}{\partial \tau} + \epsilon - \mu \right) \psi_{\sigma}(\vec{r},\tau) \right] }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k},\vec{k'}} \frac{1}{\beta^2}\sum_{\omega_n,\nu_m}\int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau}\int{d^3r}e^{i\nu_{m}\tau}e^{-i\vec{k'}\cdot\vec{r}} \left(-i\omega_n + \epsilon_p - \mu \right) e^{-i\omega_n\tau}e^{i\vec{k}\cdot\vec{r}}\psi_{\sigma,\vec{k'}}^*(i\nu_m)\psi_{\sigma, \vec{k}}(i\omega_n)}
The integral over all space give Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V \delta_{\vec{k},\vec{k'}}} , and the integral over imaginary time gives a factor of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta \delta(\omega_n - \nu_m)} , so that we find
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_0 = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\sum_{\vec{k}} \psi_{\sigma, \vec{k}}^*(i\omega_n)\left( -i\omega_n + \epsilon_p - \mu \right)\psi_{\sigma,\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) }
Now, for the 2nd (pairing) term:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta^*\int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau} \int{d^3r} \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau) \psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau) = \Delta^* \frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k},\vec{k'}} \frac{1}{\beta^2}\sum_{\omega_n,\nu_m}\int_{0}^{\beta}{d\tau}\int{d^3r} e^{-i(\nu_m + \omega_n)\tau) e^{i(\vec{k} + \vec{k'})\cdot\vec{r}} \psi_\downarrow,\vec{k'}}(i\nu_m) \psi_{\uparrow,\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) }
This time, the integral over real space gives Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V \delta(\vec{k}+\vec{k'})} , and the integral over imaginary time gives a factor of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \beta \delta(\omega_n + \nu_m)} , so the 2nd term becomes:
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\Delta^*}{\beta}\sum_{\vec{k}}\sum_{\omega_n}\psi_{\downarrow,\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)\psi_{\uparrow,-\vec{k}}(-i\omega_n)}
The hermitian conjugate of the above (the 3rd term in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}} ) gives
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \;\; \frac{\Delta}{\beta}\sum_{\vec{k}}\sum_{\omega_n}\psi_{\uparrow,-\vec{k}}^*(-i\omega_n)\psi_{\downarrow,\vec{k}}^*(i\omega_n)}
So that, for the entire Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}} , we have found:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\sum_{\vec{k}}\left[ \left( i\omega_n + \epsilon_{-\vec{k}} - \mu \right)\psi_{\uparrow, -\vec{k}}^*(-i\omega_n)\psi_{\uparrow,-\vec{k}}(-i\omega_n) + \left( -i\omega_n + \epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu \right)\psi_{\downarrow, \vec{k}}^*(i\omega_n)\psi_{\downarrow,\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) \right] }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle + \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\sum_{\vec{k}}\left[ \Delta^*\psi_{\downarrow,\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)\psi_{\uparrow,-\vec{k}}(-i\omega_n) + \Delta\psi_{\uparrow,-\vec{k}}^*(-i\omega_n)\psi_{\downarrow,\vec{k}}^*(i\omega_n) \right] }
Now, to evaluate the Gaussian integrals in the correlator, it is extremely beneficial to write Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS}} like a matrix. To this end, we construct the so-called Nambu Spinors:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) = \begin{pmatrix} \psi_{-\vec{k},\uparrow}(-i\omega_n) \\ \psi^*_{\vec{k},\downarrow}(i\omega_n) \end{pmatrix} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) = \begin{pmatrix} \psi^*_{-\vec{k},\uparrow}(-i\omega_n) & \psi^*_{\vec{k},\downarrow}(i\omega_n) \end{pmatrix} }
So now, we can write the BCS action as:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{BCS} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_N}\sum_{\vec{k}}\Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) \begin{pmatrix} i\omega_n + \epsilon_{-\vec{k}} - \mu & \Delta \\ \Delta^* & i\omega_n - \epsilon_{\vec{k}} + \mu \end{pmatrix} \Psi_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n) }
Now, we can examine the correlator we found on the right-hand-side of the self-consistency equation:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\rangle = \frac{1}{\beta^2 V}\sum_{\omega_n,\nu_m}e^{-i(\omega_n + \nu_M)\tau} \sum_{\vec{k},\vec{k'}} e^{i(\vec{k} + \vec{k'})\cdot\vec{r}}\langle \psi_{\vec{k},\downarrow}(i\omega_n) \psi_{\vec{k'},\uparrow}(i\nu_m) \rangle }
- Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{\beta^2 V}\sum_{\omega_n,\nu_m}e^{-i(\omega_n + \nu_M)\tau} \sum_{\vec{k},\vec{k'}} e^{i(\vec{k} + \vec{k'})\cdot\vec{r}} \langle \Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)_2 \Psi_{-\vec{k'}}(-i\nu_m)_1 \rangle }
So, we need to write down a generic matrix for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)_{\mu} \Psi_{-\vec{k'}}(-i\nu_m)_{\lambda} \rangle} , and take element Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (2,1) } for our result. The gaussian integrals require that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{k} = -\vec{k'}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\omega_n = -i\nu_m } for convergence. Using our technology from last semester, we can show that:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)_{\mu} \Psi_{-\vec{k'}}(-i\nu_m)_{\lambda} \rangle = \delta(\vec{k} + \vec{k'})\beta \delta(\omega_n + \nu_m) \left[ \begin{pmatrix} i\omega_n + \epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu & \Delta \\ \Delta^* & i\omega_n - \epsilon_{\vec{k}} + \mu \end{pmatrix}^{-1} \right]_{\mu\lambda} }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi^*_{\vec{k}}(i\omega_n)_2 \Psi_{-\vec{k'}}(-i\nu_m)_1 \rangle = \delta(\vec{k} + \vec{k'})\beta \delta(\omega_n + \nu_m)\frac{\Delta}{-\omega_n^2 - (\epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu)^2 - \Delta^* \Delta } }
Now, we can easily write down the correlator:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle \psi_{\downarrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(\vec{r},\tau)\rangle = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{\Delta}{-\omega_n^2 - (\epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu)^2 - \Delta^* \Delta } }
This reshapes our consistency equation to:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\Delta}{g} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{\Delta}{-\omega_n^2 - (\epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu)^2 - \Delta^* \Delta } }
Which has a trivial, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta = 0 } solution, and far more interesting solution where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{g} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{1}{-\omega_n^2 - (\epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu)^2 - |\Delta|^2 } }
Note that this is only possible if Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g < 0 } !
-We will not get S-wave superconductivity for Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta} independent of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k}
-In cuprates, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta(k)} changes sign with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 90^{0}} . It changes sign like D-wave.
-If Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle g} is repulsive system does not like to make uniform gap!
-In Fe-Pnictides, pairing gaps on different Fermi surfaces have different signs, with repulsion.
Let us define
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_{k}^{2} = (\epsilon_{k} - \mu)^{2} + |\Delta|^{2} }
So Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{g} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{1}{-\omega_n^2 - (\epsilon_{\vec{k}} - \mu)^2 - |\Delta|^2 } }
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{g} = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{1}{-\omega_n^2 - E_{\vec{k}}^{2} } } Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_{n}}\frac{1}{(i\omega_{n} - E_{\vec{k}})(i\omega_{n} + E_{\vec{k}})}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_{n} = \frac{(2n + 1)\pi}{\beta}}
We can solve this by going to the complex lane
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{-1}{g} = \oint_{c} \frac{dz}{2\pi i}\frac{1}{e^{\beta z} + 1}f(z)\frac{1}{e{????????????}} = \frac{1}{-e^{\beta \delta z +1}} = \frac{-1}{\beta\delta z}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \oint_{c}\frac{dz}{(2\pi i)}\frac{1}{e{\beta z + 1}}\frac{1}{(z-E_{\vec{k}})(z+E_{\vec{k}})}}
There is no divergence as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle z \to i\infty} There are two poles, at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z = \pm E_{\vec{k}}}
The contour can be deformed so that they exclude these two poles, and the integrand is tiny as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Re(z) \to \infty} The only contribution comes from the the loop around the two poles. For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Re(z)\to -\infty} , the integrand falls off as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{z^{2}}} , which, by Jordan's lemma,is fast enough for convergence.
So the integrand becomes Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{-1}{2\pi i}2\pi i \left [\frac{1}{(e^{\beta E_{\vec{k}}} +1)}\frac{1}{2E_{\vec{k}}} + \frac{1}{(e^{\beta E_{\vec{k}}}+1)}\frac{1}{-2E_{\vec{k}}} \right ]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{2E_{\vec{k}}}\left [ \frac{1}{(e^{-\beta E_{\vec{k}}} +1)} - \frac{1}{(e^{\beta E_{\vec{k}}} +1)}\right ]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle =\frac{1}{2E_{\vec{k}}}\left [ \frac{1}{e^{-\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2}2\cosh(\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2)} - \frac{1}{e^{\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2}2\cos(\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2)}\right ]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{4E_{\vec{k}}\cosh(\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2)}\left [ e^{\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2}2 - e^{-\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2}2 \right ]}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{1}{2E_{\vec{k}}}\tanh(\beta E_{\vec{k}}/2)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Rightarrow \frac{1}{g} = \frac{-1}{V}\sum_{\vec{k}}\frac{1}{2E_{\vec{k}}}\tanh(E_{\vec{k}}/2k_{b}T)}
Solution of the Self-Consistency Equation
By using our usual trick of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sum_{\vec{k}} \to V\int \frac{d^{3}k}{(2\pi)^3}} ,
we can convert the sum into an integral: Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{|g|} = \frac{-1}{g} = \int \frac{d^{3}k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{\tanh(E_{\vec{k}}/2k_{b}T)}{2E_{\vec{k}}}}
At this point, we can, if we wish, solve this equation on a computer, at any temperature
For Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta \to 0} , the RHS is Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\tanh((\epsilon_{\vec{k}}-\mu)}{/2k_{b}T)}{(2\epsilon_{\vec{k}}}-\mu)}} always intersects the LHS Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left (\frac{1}{|g|} \right )} , and we are guaranteed a solution.
Condensation energy and T dependence of the thermodynamic field
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z = \int D\psi^{*}D\psi\int D\Delta^{*}\Delta exp^{-S_{BCS}-S_{\Delta}}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \int D\Delta^{*}D\Delta exp^{S_{eff}[\Delta]}}
Beyond saddle-point approximation, collective modes and response in the broken symmetry state
Recall we can write our partition function as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D\Delta^*D\Delta e^{-S_{eff}[\Delta]}}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle Z=\int D(\Re e\Delta)D(\Im m\Delta)e^{-S_{eff}[\Re e\Delta,\Im m\Delta]}}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}[\Delta]=\frac{1}{|g|}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^Dr\left[(\Re e\Delta(r,\tau))^2+(\Im m\Delta(r,\tau))^2\right]-\ln\left[\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\right]}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} S_0&=\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^Dr \psi^*(r,\tau)(\frac{\partial}{\partial\tau}+\epsilon_p-\mu)\psi(r,\tau)\\ S_{int}&=\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^Dr(\Delta^*(r,\tau)\psi_\downarrow(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\Delta(r,\tau)\psi^*_\uparrow(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)) \end{align}}
We can rewrite the interaction term in the action as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int}=\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^Dr\left[\Re e(\Delta(r,\tau))(\psi_{\downarrow}\psi_{\uparrow}+\psi_{\uparrow}^*\psi_{\downarrow}^*)(r,\tau)+i*\Im m(\Delta(r,\tau))(\psi_{\uparrow}^*\psi_{\downarrow}^*-\psi_{\downarrow}\psi_{\uparrow})(r,\tau)\right]}
Consider now functional derivatives of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}[\Delta]} :
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta S_{eff}[\Delta]}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}=\frac{2}{|g|}\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)-\frac{1}{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}} \int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\left(-\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}\right) }
The functional derivative of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{int}} with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)} is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}=\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi_{\uparrow}^*(r,\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}^*(r,\tau)}
Therefore, we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta S_{eff}[\Delta]}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}=\frac{2}{|g|}\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)+\langle\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi_{\uparrow}^*(r,\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}^*(r,\tau)\rangle\ \ (1)}
Similarly
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta S_{eff}[\Delta]}{\delta \Im m\Delta(r,\tau)}=\frac{2}{|g|}\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)+i\langle\psi_{\uparrow}^*(r,\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}^*(r,\tau)-\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\rangle\ \ (2)}
If we were to set the LHS of the above two equations to zero, we would obtain our self-consistency conditions.
The strategy is to take
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}[\Delta(r,\tau)]=S_{eff}\left[\Delta_{sp}+(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\right]}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}} solves (1) and (2) with LHS set to zero and expand in powers of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp}} . So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &S_{eff}[\Delta_{sp}+(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})]\\ &=S_{eff}[\Delta_{sp}]+\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^3r\Re e(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\frac{\delta S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}|_{\Delta_{sp}}+\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^3r\Im m(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\frac{\delta S_{eff}}{\delta\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)}|_{\Delta_{sp}}\\ &+\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int_0^\beta d\tau'\int d^3r\int d^3r'\Re e(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\Re e(\Delta(r',\tau')-\Delta_{sp})\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}|_{\Delta_{sp}}\\ &+\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int_0^\beta d\tau'\int d^3r\int d^3r'\Im m(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\Im m(\Delta(r',\tau')-\Delta_{sp})\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Im m\Delta(r',\tau')}|_{\Delta_{sp}}\\ &+\int_0^\beta d\tau\int_0^\beta d\tau'\int d^3r\int d^3r'\Re e(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\Im m(\Delta(r',\tau')-\Delta_{sp})\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Im m\Delta(r',\tau')}|_{\Delta_{sp}}+... \end{align}}
Since by definition of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}} we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}|_{\Delta_{sp}}=\frac{\delta S_{eff}}{\delta\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)}|_{\Delta_{sp}}=0}
So only the 0th and 2nd order terms contribute. The 0th order term gave us the condensation energy, and the 2nd order term will give us information about collective modes (in the broken symmetry phase).
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}\\ &=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')+\frac{\delta}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}\left[\frac{1}{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}}\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\left(\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}\right)\right]\\ &=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')-\frac{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\left(\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}\right)\left(\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}\right)}{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}}\\ &+\left(\frac{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\left(\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r,\tau)}\right)}{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}}\right)\left(\frac{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}\left(\frac{\delta S_{int}}{\delta \Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}\right)}{\int D\psi^*D\psi e^{-S_0-S_{int}}}\right) \end{align}}
So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')\\ &-\langle\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\right)\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\psi_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\right)\rangle_{S_0+S_{int}}\\ &+\langle\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\rangle\langle\psi_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\psi_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\rangle_{S_0+S_{int}} \end{align}}
i.e.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')\\ &-\langle\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\right)\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\psi_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\right)\rangle_{S_0+S_{int}}^{\mbox{con}} \end{align}}
Similarly,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Im m\Delta(r',\tau')}=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')\\ &+\langle\left(\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)-\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\right)\left(\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')-\psi_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\psi_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\right)\rangle_{S_0+S_{int}}^{\mbox{con}} \end{align}}
And
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\delta^2 S_{eff}}{\delta\Im m\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}=-i\langle\left(\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)-\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)\right)\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\psi_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')+\psi^*_{\uparrow}(r',\tau')\psi^*_{\downarrow}(r',\tau')\right)\rangle_{S_0+S_{int}}^{\mbox{con}} }
If we evaluate these functional derivatives at the saddle point Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}} we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} S_0+S_{int}&\rightarrow\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^3r\sum_{\sigma=\uparrow,\downarrow}\psi^*_\sigma(r,\tau)\left(\frac{\partial}{\partial\tau}+\epsilon_p-\mu\right)\psi_{\sigma}(r,\tau)\\ &+\Delta_{sp}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int d^3r\left(\psi_{\downarrow}(r,\tau)\psi_{\uparrow}(r,\tau)+\psi_{\uparrow}^*(r,\tau)\psi_{\downarrow}^*(r,\tau)\right) \end{align}}
where we take the saddle point solution Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}} to be purely real. Arranging the Grassman fields into the Nambu spinor we have:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle (\psi^*_{\uparrow}\ \psi_\downarrow)\left(\begin{align}&\frac{\partial}{\partial\tau}+\epsilon_p-\mu&\Delta_{sp}\\ &\Delta_{sp}&\frac{\partial}{\partial\tau}-\epsilon_p+\mu\end{align}\right) \left(\begin{align}&\psi_\uparrow\\&\psi^*_\downarrow\end{align}\right)}
where the Nambu spinor is defined as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Psi=\left(\begin{align}&\psi_\uparrow\\&\psi^*_\downarrow\end{align}\right)}
So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\psi^*_\uparrow\psi^*_\downarrow+\psi_\downarrow\psi_\uparrow=\Psi^*\left(\begin{align}&0&1\\&1&0\end{align}\right)\Psi =\Psi^*\sigma_x\Psi\\ &\psi^*_\uparrow\psi^*_\downarrow-\psi_\downarrow\psi_\uparrow=\Psi^*\left(\begin{align}&0&1\\-&1&0\end{align}\right)\Psi =\Psi^*i\sigma_y\Psi \end{align}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \frac{\delta^2S_{eff}}{\delta\Re e\Delta(r,\tau)\delta\Re e\Delta(r',\tau')}|_{\Delta_{sp}}&=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')-\langle\Psi^*(r,\tau)\sigma_x\Psi(r,\tau)\Psi^*(r',\tau')\sigma_x\Psi(r',\tau')\rangle^{\mbox{con}}\\ &=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')+\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_xG(r-r',\tau-\tau')\sigma_xG(r'-r,\tau'-\tau)\right] \end{align}}
where the Green's functions are 2*2 matrices,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle G^{-1}_k(i\omega_n)=\left(\begin{align}&-i\omega_n+\epsilon_k-\mu&\Delta_{sp}\\&\Delta_{sp}&-i\omega_n-\epsilon_k+\mu\end{align}\right)}
Notice that this is a function of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tau-\tau'} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle r-r'} . Let's call it Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}(r-r',\tau-\tau')} . This will give rise to
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int_0^\beta d\tau'\int d^3r\int d^3r'\Re e(\Delta(r,\tau)-\Delta_{sp})\Pi_{++}(r-r',\tau-\tau')\Re e(\Delta(r',\tau')-\Delta_{sp})\\ &=\frac{1}{2}\int_0^\beta d\tau\int_0^\beta d\tau'\int d^3r\int d^3r'\delta\Delta_+(r,\tau)\Pi_{++}(r-r',\tau-\tau')\delta\Delta_+(r',\tau') \end{align}}
Fourier transforming we find the contribution to Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle S_{eff}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\Omega_n}\sum_{q}\delta\Delta_+(-q,-i\Omega_n)\Pi_{++}(q,i\Omega_n)\delta\Delta_+(q,i\Omega_n)}
Similarly
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Pi_{--}(r-r',\tau-\tau')&=\frac{2}{|g|}\delta(\tau-\tau')\delta(r-r')+\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_yG(r-r',\tau-\tau')\sigma_yG(r'-r,\tau'-\tau)\right]\\ \Pi_{-+}(r-r',\tau-\tau')&=\langle\Psi^*\sigma_y\Psi(r,\tau)\Psi^*\sigma_x\Psi(r',\tau')\rangle^{\mbox{con}}=-\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_yG(r-r',\tau-\tau')\sigma_xG(r'-r,\tau'-\tau)\right] \end{align}}
Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &S_{eff}[\Delta]\approx S_{eff}[\Delta_{sp}]+\\ &\frac{1}{2}\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\Omega_n}\sum_q\left[\delta\Delta_+(-q,-i\Omega_n)\Pi_{++}(q,i\Omega_n)\delta\Delta_+(q,i\Omega_n)+\delta\Delta_-(-q,-i\Omega_n)\Pi_{--}(q,i\Omega_n)\delta\Delta_-(q,i\Omega_n)\right.\\ &\left.+2\delta\Delta_-(-q,-i\Omega_n)\Pi_{-+}(q,i\Omega_n)\delta\Delta_+(q,i\Omega_n)\right]+... \end{align}}
To proceed with the evaluation of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi} 's, note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &G^{-1}_k(i\omega_n)=-i\omega_n\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_k-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1\\ \Rightarrow&G_k(i\omega_n)=\frac{i\omega_n\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_k-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1}{\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2} \end{align}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_n=\frac{(2n+1)\pi}{\beta}} . After Fourier transform,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Pi_{++}(q,i\Omega_n)&=\frac{2}{|g|}+\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_1G_{k+q}(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)\sigma_1G_k(i\omega_n)\right]\\ \Pi_{--}(q,i\Omega_n)&=\frac{2}{|g|}+\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_2G_{k+q}(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)\sigma_2G_k(i\omega_n)\right]\\ \Pi_{-+}(q,i\Omega_n)&=-\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_2G_{k+q}(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)\sigma_1G_k(i\omega_n)\right]\\ \end{align}}
Consider now
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_{1,2}\frac{(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1}{(\omega_n+\Omega_n)^2+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2}\sigma_{1,2}\frac{i\omega_n\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_k-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1}{\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2}\right]\\ =&2\frac{(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)i\omega_n-(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)(\epsilon_k-\mu)\pm\Delta^2_{sp}}{\left[(\omega_n+\Omega_n)^2+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]\left[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]} \end{align}}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} &\mbox{Tr}\left[\sigma_{2}\frac{(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1}{(\omega_n+\Omega_n)^2+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2}\sigma_{1}\frac{i\omega_n\mathbb{I}+(\epsilon_k-\mu)\sigma_3+\Delta_{sp}\sigma_1}{\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2}\right]\\ =&\frac{(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)(\epsilon_k-\mu)\mbox{Tr}[\sigma_2\sigma_1\sigma_3]+i\omega_n(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)\mbox{Tr}[\sigma_2\sigma_3\sigma_1]}{\left[(\omega_n+\Omega_n)^2+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]\left[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]}\\ =&\frac{(i\omega_n+i\Omega_n)(\epsilon_k-\mu)(-2i)+i\omega_n(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)2i}{\left[(\omega_n+\Omega_n)^2+(\epsilon_{k+q}-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]\left[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2\right]} \end{align}}
Now, note that at Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q=0,\Omega_n=0} ,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{-+}(0,0)=0}
because the numerator vanishes for all Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_n} . Also note that by self-consistency condition
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Pi_{--}(0,0)&=\frac{2}{|g|}-\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}2\frac{1}{[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2]}\\ &=\frac{2}{|g|}+2\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{1}{(i\omega_n-E_k)(i\omega_n+E_k)}\\ &=\frac{2}{|g|}+2\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\left(\frac{n_F(E_k)}{2E_k}-\frac{n_F(-E_k)}{2E_k}\right)\\ &=2\left(\frac{1}{|g|}-\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{1-2n_F(E_k)}{2E_k}\right)\\ &=0 \end{align}}
However,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Pi_{++}(0,0)&=\frac{2}{|g|}+\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}2\frac{-\omega_n^2-(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2}{[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2]^2}\\ &=4\Delta_{sp}^2\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{1}{[\omega_n^2+(\epsilon_k-\mu)^2+\Delta_{sp}^2]^2}\\ &=4\Delta_{sp}^2N_0\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\int_{-\infty}^\infty\frac{d\xi}{[\xi^2+\omega_n^2+\Delta_{sp}^2]^2}\\ &=4\Delta_{sp}^2N_0\frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}\frac{\pi}{2}\frac{1}{(\omega_n^2+\Delta_{sp}^2)^{\frac{3}{2}}}\\ &=2\pi N_0\Delta_{sp}^2\frac{1}{\pi^3T^2}\sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty\frac{1}{[(2n+1)^2+(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\pi T})^2]^{\frac{3}{2}}} \end{align}}
This sum is slowly convergent. To evaluate it efficiently, we note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{a^{\frac{3}{2}}}=\frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}}\int_0^\infty d\lambda\sqrt{\lambda}e^{-\lambda a}\ \ \mbox{for }a>0}
So
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty\frac{1}{[(2n+1)^2+(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\pi T})^2]^\frac{3}{2}}&=\frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}} \int_0^\infty d\lambda\sqrt{\lambda}e^{-\lambda(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\pi T})^2}\left(\sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty e^{-\lambda(2n+1)^2}\right)\\ &=\frac{2}{\sqrt{\pi}} \int_0^\infty d\lambda\sqrt{\lambda}e^{-\lambda(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\pi T})^2}\Theta_2(0,e^{-4\lambda})\\ &=\frac{1}{4\sqrt{\pi}} \int_0^\infty d\xi\sqrt{\xi}e^{-\xi(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{2\pi T})^2}\Theta_2(0,e^{-\xi}) \end{align}}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Theta_2} is Jacobi elliptic theta function. Then
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \begin{align} \Pi_{++}(0,0)&=2\pi N_0\Delta^2_{sp}\frac{1}{\pi^3T^2}\sum_{n=-\infty}^\infty\frac{1}{[(2n+1)^2+(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\pi T})^2]^\frac{3}{2}}\\ &=2N_0\Phi(\frac{\Delta_{sp}}{2\pi T}) \end{align}}
where
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Phi(x)=x^2\frac{1}{\sqrt{\pi}}\int_0^\infty d\xi\sqrt{\xi}e^{-\xi x^2}\Theta_2(0,e^{-\xi})}
Note that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}(0,0)\rightarrow 2N_0\frac{7\zeta(3)}{4\pi^2T^2}\Delta^2_{sp}}
as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}\rightarrow 0} , i.e. as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T\rightarrow T_C} .
That is precisely the curvature of the new minimum in the Ginzburg-Landau free energy we found before. So, at 2nd order our effective action corresponds to the action for two real free bosons, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_+} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_-} . At Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q=0, i\Omega_n=0} , Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_+} mode is gapped (massive), but Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_-} mode is not gapped (massless). Physically, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_+} corresponds to the fluctuations of the order parameter amplitude (because we chose Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Delta_{sp}} to be real).
Recall our discussion from many-body course:
Amplitude fluctuations are not hydrodynamic modes since they do not correspond to either conserved or to broken symmetry variable. We have to extend our approach to higher order in Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_\pm} to describe its (rapid) decay.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \delta\Delta_-} corresponds to fluctuations along the direction of the minimum of the double well potential, where there is no barrier. It corresponds to (part of) a "phase" mode.
To determine the kinematics (of our collective modes) we need to expand Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{\mu\nu}(q, i\Omega_n)} in powers of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{q}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega_n} . Our small expansion parameters are
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega_n \ll \Delta_{sp}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q \ll \frac{\Delta_{sp}}{\hbar v_F}}
(Obviously Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q \ll k_F} )
Start with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}} : What we need is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}\left(q, i\Omega_n\right) - \Pi_{++}\left(0, 0\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\left[\frac{1}{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2} - \frac{\omega_n\left(\omega_n + \Omega_n\right) + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \mu\right) - \Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)\left(\left(\omega_n + \Omega_n\right)^2 + E_{k + q}^2\right)} - \frac{2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2}\right]}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\left[\frac{\omega_n^2 + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)^2 - \Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2} - \frac{\omega_n\left(\omega_n + \Omega_n\right) + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \mu\right) - \Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)\left(\left(\omega_n + \Omega_n\right)^2 + E_{k + q}^2\right)}\right]}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\left[\frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2} - \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 + \omega_n\Omega_n + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \epsilon_k\right) - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 + 2\omega_n\Omega_n + \Omega_n^2 + \left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \mu\right)^2 - \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\right)}\right]}}}
The second term in the brackets:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2 + \overbrace{\omega_n\Omega_n + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \epsilon_k\right)}^{\text{small}}}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 + \underbrace{2\omega_n\Omega_n + \Omega_n^2 + \left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \mu\right)^2 - \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)}_{\text{small}}\right)}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle = \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2 + \omega_n\Omega_n + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \epsilon_k\right)}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2}\left[1 + \frac{2\omega_n\Omega_n + \Omega_n^2 + \left(\epsilon_{k + q} - \epsilon_k\right)\left(\epsilon_{k + q} + \epsilon_k - 2\mu\right)}{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2}\right]^{-1}}
Now, by Taylor expansion,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \epsilon_{k + q} \simeq \epsilon_k + q\cdot \nabla\epsilon_k + \ldots}
and near the Fermi level we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q\cdot \nabla\epsilon_k \simeq q\cdot v_F}
Also note that after integrating over Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \vec{k}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_n} , terms with odd power of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega_n} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q\cdot v_F} vanish. Keeping only terms of order Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle q^2} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Omega_n^2} we have
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2}\left(1 - \frac{\Omega_n^2 + \left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2}{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2}\right) - \frac{2\omega_n^2\Omega_n^2 + 2\left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)^2\left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^3} + \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2}\cdot\frac{4\omega_n^2\Omega_n^2 + 4\left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)^2\left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^2}}
The terms which we dropped are down by powers of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle qk_F} and/or vanish assuming particle-hole symmetry.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}\left(q, i\Omega_n\right) - \Pi_{++}\left(0, 0\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^3}\left(\Omega_n^2 + \left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2\right)}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle + \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3}\frac{2\omega_n^2\Omega_n^2 + 2\left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)^2\left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^3}}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle - \frac{2}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n}{\int{\frac{d^3k}{(2\pi)^3} 4 \cdot \frac{\omega_n^2 + E_k^2 - 2\Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega_n^2 + E_k^2\right)^4}\left(\omega_n^2\Omega_n^2 + \left(\epsilon_k - \mu\right)^2\left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2\right)}}}
Let's focus on Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle T = 0} . Then Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \frac{1}{\beta}\sum_{\omega_n} \longrightarrow \int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\frac{d\omega}{2\pi}}} Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Longrightarrow}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \Pi_{++}\left(q, i\Omega_n\right) - \Pi_{++}\left(0, 0\right)}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \simeq -2N_0\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\frac{d\omega}{2\pi}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{d\xi\frac{\omega^2 + \xi^2 - \Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega^2 + \xi^2 + \Delta_{sp}^2\right)^3}\left(\Omega_n^2 + q^2\langle \left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2 \rangle_{FS}\right)}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle + 4N_0\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\frac{d\omega}{2\pi}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{d\xi\frac{\omega^2\Omega_n^2 + \xi^2q^2\langle\left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2\rangle_{FS}}{\left(\omega^2 + \xi^2 + \Delta_{sp}^2\right)^3}}}}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle - 8N_0\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{\frac{d\omega}{2\pi}\int_{-\infty}^{\infty}{d\xi\frac{\omega^2 + \xi^2 - \Delta_{sp}^2}{\left(\omega^2 + \xi^2 + \Delta_{sp}^2\right)^4}\left(\omega^2\Omega_n^2 + \xi^2q^2\langle \left(q\cdot v_F\right)^2 \rangle_{FS}\right)}}}
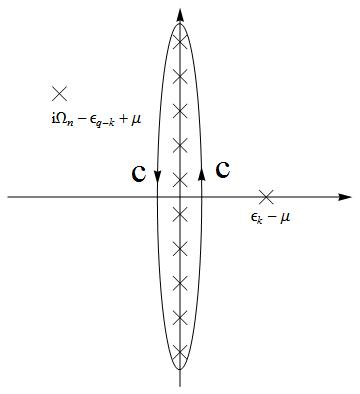
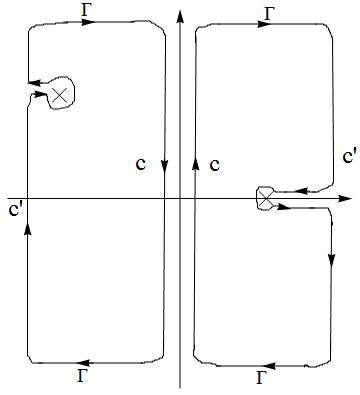
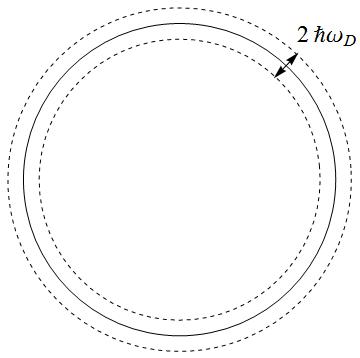









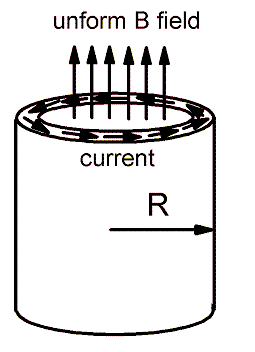
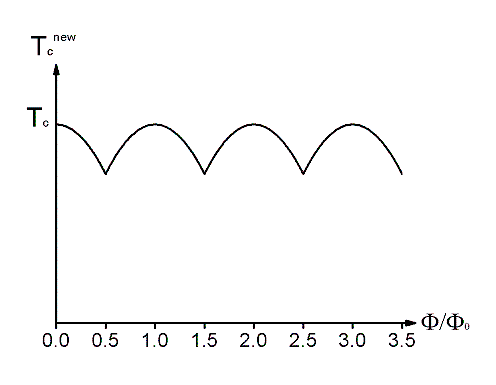



![{\displaystyle S_{int}={\frac {L^{D}}{\beta ^{2}}}\sum _{\omega _{n},\Omega _{n}}\sum _{k,q}[\Delta _{q}^{*}(i\Omega _{n})\psi _{\downarrow }(i\Omega _{n}-i\omega _{n}),{\vec {q}}-{\vec {k}})\psi _{\uparrow }(i\omega _{n},k)+\Delta _{q}(i\Omega _{n})\psi _{\uparrow }^{\dagger }(i\omega _{n},k)\psi _{\downarrow }^{\dagger }(i\Omega _{n}-i\omega _{n}),{\vec {q}}-{\vec {k}})]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a85f99cd3f68852e145e1956e61803d8bfd87a8f)





















![{\displaystyle Z\sim Z_{0}e^{-S_{eff}[\Delta _{min}]}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/aac519c60f52ae1cc5a38bc1133daadd5d100131)











![{\displaystyle S_{eff}[\Delta _{min}]={\frac {L^{D}}{k_{B}T}}\left(A\Delta _{min}^{2}+{\frac {1}{2}}B\Delta _{min}^{4}\right)}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/faa3555544269331317298ea233f841c59c2b649)
![{\displaystyle T>T_{C};\quad S_{eff}[\Delta _{min}]=0}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/da6f8326a3ef33e6e6a2a637a25be50396fecd1f)
![{\displaystyle T<T_{C};\quad S_{eff}[\Delta _{min}]=\left(A{\frac {-A}{B}}+{\frac {1}{2}}B{\frac {A^{2}}{B^{2}}}\right){\frac {L^{D}}{k_{B}T}}={\frac {-A^{2}}{2B}}{\frac {L^{D}}{k_{B}T}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/4ee8046e319e073fcbd5c25fbac222fef8eb54a3)