Homeworks 3
Homework 3 due on 09/21/2009
Problem 1
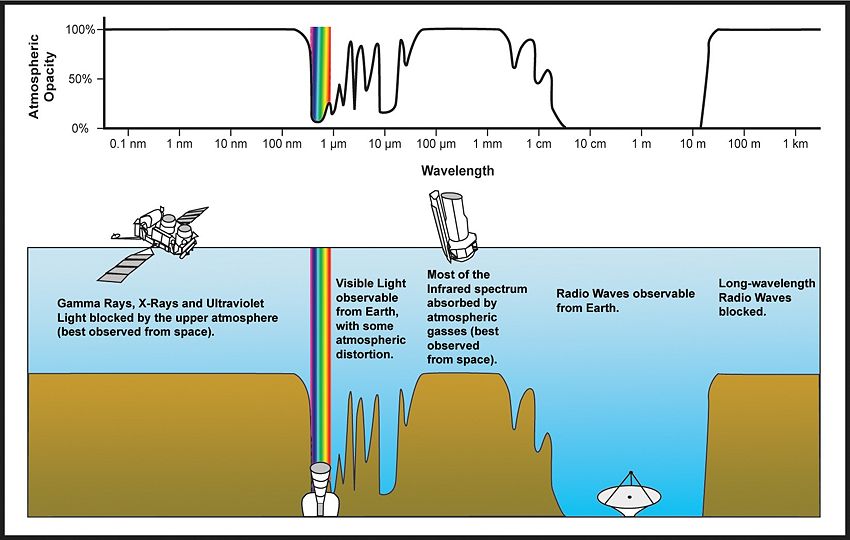
For each of the following types of electromagnetic radiation give a typical wavelength and state whether it can penetrate the Earth’s atmosphere: radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray, -ray.
| Wavelength | Wavelength Range | Does it penetrate Earth's Atmosphere? |
|---|---|---|
| Radio | 10 m - m | From ~10 m to ~20 m, yes |
| Microwave | m - 10 m | Some is absorbed at smaller wavelengths |
| Infrared | 700 nm - m | Most are absorbed by atmospheric gasses |
| Visable | 400 nm - 700 nm | Yes, with some distortion |
| Ultraviolet | m - 400 nm | No, all incoming rays are blocked |
| X-Ray | m - m | No, all incoming rays are blocked |
| -ray | m - m | No, all incoming rays are blocked |
Problem 2
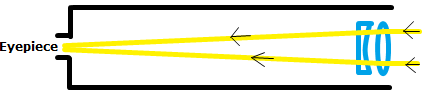
Sketch the typical light path of reflector and refractor telescopes, and name two of the advantages and disadvantages for each of the designs. Catadioptric designs such as the Maksukov and Schmidt telescopes have both a primary lense and a mirror. Name the main advantage and drawback of these designs, and their main application.
Refraction Telescope
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| High resolution | Large objective lenses deform under gravity. |
| No incoming light is blocked. | Chromatic aberration |
Reflection Telescope
Catadioptric Telescope
Catadioptric telescopes like the Schmidt telescope provide a wide-angle field of view and thus are often used as cameras. However, they suffer from both spherical and chromatic aberration.
Problem 3
Name and explain in your own words three of the optical artifacts of spherical mirrors. Explain why telescopes with multiple-mirrors such as Keck or the upcoming space based NGST are inferior for direct imaging of planets compared to mono-mirror systems. Why, then, are all large telescope systems are based on multiple mirror designs?
Problem 4
Use the Rayleigh Criterion to estimate the diffraction limit (in arc sec) for the angular resolution of a typical 1m class telescope in the near IR (2 μm), and discuss the result.
The Rayleigh Criteron:
We plug in these values and we get that:
Problem 5
Estimate the size of the spherical abberation of a spherical mirror of 1m-diameter and a focal length of 2 meter. (Hint: Calculate the size of the smeared image of a star at the focal point and compare it to the size (in arc-sec) of an extended object, and remember your PHY2048/9).