Harmonic Oscillator Spectrum and Eigenstates
The one-dimensional harmonic oscillator consists of a particle moving under the influence of a harmonic oscillator potential, which has the form, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V(x)=\frac{1}{2}k x^2,} where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle k\!} is the "spring constant".
We see that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle V(x)\rightarrow \infty} as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\rightarrow \pm\infty.} Therefore, all stationary states of this system are bound, and thus the energy spectrum is discrete and non-degenerate. Furthermore, because the potential is an even function, the parity operator commutes with Hamiltonian, and thus the wave functions will be either even or odd.
The energy spectrum and the energy eigenstates can be found by either an algebraic method using raising and lowering operators, which is described below, or by solving the Schrödinger equation for the system, as described in the next section.
Solution of the Harmonic Oscillator by Operator Methods
The Hamiltonian of the one-dimensional harmonic oscillator is:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\frac{\hat{p}^2}{2m}+\tfrac{1}{2}k\hat{x}^2,}
or, in terms of the natural frequency, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \omega=\sqrt{\frac{k}{m}},}
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\frac{\hat{p}^2}{2m}+\tfrac{1}{2}m\omega^2\hat{x}^2.}
With the aid of the operator identity,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{A}^2+\hat{B}^2=(\hat{A}-i\hat{B})(\hat{A}+i\hat{B})-i[\hat{A},\hat{B}],\!}
we may factorize the Hamiltonian as follows.
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\hbar\omega\left (\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}\hat{x}^2+\frac{\hat{p}^2}{2m\hbar\omega}\right )=\hbar\omega\left (\sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}\hat{x}-i\frac{\hat{p}}{\sqrt{2m\hbar\omega}}\right )\left (\sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}\hat{x}+i\frac{\hat{p}}{\sqrt{2m\hbar\omega}}\right )+\tfrac{1}{2}\hbar\omega }
If we now define the operators,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}=\sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}\hat{x}+i\frac{\hat{p}}{\sqrt{2m\hbar\omega}}}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}=\sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}\hat{x}-i\frac{\hat{p}}{\sqrt{2m\hbar\omega}},}
we may write the Hamiltonian as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H=\hbar\omega\left(\hat{a}^{\dagger}\hat{a}+\frac{1}{2}\right ).}
One may easily show that the operators Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}\!} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}} satisfy the commutation relation, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle [\hat{a},\hat{a}^{\dagger}]=1.}
Let us now define the Hermitian operator, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}=\hat{a}^{\dagger}\hat{a}.} We denote the (normalized) eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}} associated with the eigenvalue Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n\!} as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle;} i.e., Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}|n\rangle=n|n\rangle.} Note that any eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}} is also an eigenstate of the Hamiltonian, with eigenvalue
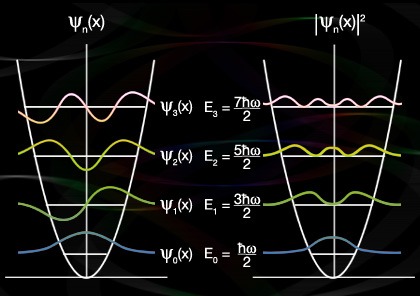
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle E_n=\left (n+\tfrac{1}{2}\right )\hbar\omega.}
One may verify that the eigenvalue Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n\geq 0\!} by acting on the left of this definition with Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle n|.} There is therefore a lower bound of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \tfrac{1}{2}\hbar\omega} on the energy of any state of the harmonic oscillator. This "zero-point energy" is a remarkable and significant feature peculiar to quantum mechanics. One may view this as a consequence of the Heisenberg uncertainty principle; because it is impossible to perfectly localize a particle in both position and momentum spaces, a particle in a harmonic oscillator potential will always possess a non-zero energy relative to the minimum of the potential.
We may now determine what the operators Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}} do to the eigenstates of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}.} Acting to the left on the definition, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}|n\rangle=n|n\rangle,} with each of these operators and employing the above commutation relation, we may show that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}|n\rangle=\sqrt{n}|n-1\rangle}
and
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}|n\rangle=\sqrt{n+1}|n+1\rangle.}
We have thus shown that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}} is a "lowering operator", in the sense that, when applied to the eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}} with eigenvalue Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n,\!} we obtain a result that is proportional to the eigenstate with eigenvalue Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n-1.\!} For a similar reason, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}} is a "raising operator".
We may use the above results to further restrict the possible values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n.\!} We may show that it is quantized, and can only take non-negative integer values; i.e., Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n=0,\,1,\,2,\,\ldots} Let us suppose that an eigenstate of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{n}} with a positive non-integer eigenvalue Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n\!} exists. Without loss of generality, let us suppose that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle 0<n<1,\!} since one can generate such a state from any other such eigenstate by repeated application of the lowering operator. If we act on this state with the lowering operator Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}} , then we will generate an eigenstate with a negative eigenvalue (note that the factor, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \sqrt{n},} does not vanish in this case!), which cannot exist, as pointed out earlier.
The only way to guarantee that no states with negative values of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n\!} are generated is to restrict Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle n\!} to be a non-negative integer. This is guaranteed because, by repeated application of the lowering operator, we will eventually obtain the state, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |0\rangle,} and Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}|0\rangle=0.} Therefore, we have shown that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |0\rangle} is the ground state of the harmonic oscillator.
So, starting from any energy eigenstate, we can construct all other energy eigenstates by applying Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}\!} or Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger}\!} repeatedly. In particular, by repeated application of the raising operator, we may generate all of the eigenstates of the harmonic oscillator from its ground state:
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle |n\rangle=\frac{(\hat{a}^{\dagger})^n}{\sqrt{n!}}|0\rangle}
The Ground State Wave Function
We may use the above results to easily determine the ground state of the harmonic oscillator in position space. Starting from the fact that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}|0\rangle=0,\!} we may write, remembering that Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{p}\rightarrow-i\hbar\frac{d}{dx}} in the position basis,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \left( \sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}x+\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\frac{d}{dx}\right )\psi_0(x)=0\!}
This is a first-order ordinary differential equation, which can easily be solved; the solution is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_0(x)=A e^{-m\omega x^2/2\hbar},}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle A\!} is a normalization constant. Upon normalization, we find that the ground state wave function is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_0(x)=\left(\frac{m\omega}{\pi\hbar}\right)^{1/4}e^{-m\omega x^2/2\hbar}.}
We may obtain the ground state wave function in momentum space as well. Remembering that, in this case, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{x}\rightarrow i\hbar\frac{d}{dp},} the differential equation satisfied by the momentum-space wave function is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\left (\sqrt{\frac{m\hbar\omega}{2}}\frac{d}{dp}+\frac{p}{\sqrt{2m\hbar\omega}}\right )\phi_0(p)=0,}
and its normalized solution is
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi_0(p)=\frac{1}{(\pi m\hbar\omega)^{1/4}}e^{-p^2/2m\hbar\omega}.}
The Excited State Wave Functions
Given the ground state wave function, we may obtain the excited state wave functions by repeated application of Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{a}^{\dagger},} as described earlier. In position space,
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_n(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{n!}}\left (\frac{m\omega}{\pi\hbar}\right )^{1/4}\left( \sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{2\hbar}}x-\sqrt{\frac{\hbar}{2m\omega}}\frac{d}{dx}\right )^ne^{-m\omega x^2/2\hbar}.}
We may show that
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \psi_n(x)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2^nn!}}\left (\frac{m\omega}{\pi\hbar}\right)^{\frac{1}{4}}e^{-m\omega x^2/2\hbar}H_n\left(\sqrt{\frac{m\omega}{\hbar}}x\right ),}
where Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle H_n(\xi)=(-1)^n e^{\xi^2}\frac{d^n}{d\xi^n}e^{-\xi^2}} is a Hermite polynomial.
In the momentum representation, the excited states may be written as
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi_n(p)=\frac{i^n}{\sqrt{n!}}\frac{1}{(\pi m\hbar\omega)^{1/4}}\left (\sqrt{\frac{m\omega \hbar}{2}}\frac{d}{dp}-\frac{p}{\sqrt{2m \omega\hbar}}\right )^ne^{-p^2/2m\hbar\omega},}
or
Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \phi_n(p)=\frac{(-i)^n}{\sqrt{2^n n!}}\frac{1}{(\pi m\hbar\omega)^{1/4}}H_n\left (\frac{p}{\sqrt{m\omega\hbar }}\right )e^{-p^2/2m\hbar\omega}.}
Note the appearance of the imaginary unit Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle i\!} that is not present in the position representation of these states. This solution can also be obtained via a Fourier transformation of the position representation wave functions.
Notice that there are two factors in the wave functions for the excited states, a Gaussian function and a Hermite polynomial. The former causes the wave function to decrease exponentially as Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle x\rightarrow\pm\infty,} as required of any bound state, while the later accounts for the behavior of the wave function at short distances and the number of nodes of the wave function.
The quantum harmonic oscillator is of particular interest as a problem due to the fact that it can be used to (at least approximately) describe many different systems. A few examples include molecular vibrations, quantum LC circuits, and phonons in solids.
Problems
(1) Calculate the expectation value of the position Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{x}\!} in an eigenstate of the harmonic oscillator.
(2) Calculate the expectation value of the momentum Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \hat{p}\!}
in an eigenstate of the harmonic oscillator.
(3) Show that the average kinetic energy, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\hat{T}\rangle,}
is equal to the average potential energy, Failed to parse (SVG (MathML can be enabled via browser plugin): Invalid response ("Math extension cannot connect to Restbase.") from server "https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/":): {\displaystyle \langle\hat{V}\rangle.}
This is a special case of the virial theorem, which we will discuss in a later section.
(See Liboff, Richard Introductory Quantum Mechanics, 4th Edition, Problem 7.10 for reference.)